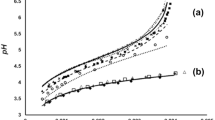
Abstract
The values of the second dissociation constant, pK 2, and related thermodynamic quantities of [N-(2-acetamido)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid] (ACES) have already been reported over the temperature range 5 to 55 °C including 37 °C. This paper reports the pa H values of four chloride ion free buffer solutions and eight buffer solutions with I=0.16 mol⋅kg−1, matching closely that of the physiological sample. Conventional pa H values for all twelve buffer solutions from 5 to 55 °C are reported. The residual liquid-junction potential correction for two widely used temperatures, 25 and 37 °C, has been made. The flowing-junction calomel cell method has been utilized to measure E j , the liquid-junction potential. The operational pH values for four buffer solutions at 25 and 37 °C are calculated using the physiological phosphate buffer standard based on the NBS/NIST convention. These solutions are recommended as pH standards in the pH range of 6.8 to 7.2 for physiological fluids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roy, R.N., Bice, J., Greer, J., Carlsten, J.A., Smithson, J., Good, W.S., Moore, C.P., Roy, L.N., Kuhler, K.M.: Buffers for the physiological pH range: Acidic dissociation constants of zwitterionic compounds (ACES and CHES) in water from 5 to 55 °C. J. Chem. Eng. Data 42, 41–44 (1997)
Roy, R.N., Roy, L.N., Simon, A.N., Moore, A.C., Seing, L.A., Richards, S.J., Craig, H.D., Childers, B.A., Tabor, B.J., Himes, C.A., Viele, K.E.: Thermodynamics of the second dissociation constant of N-bis(hydroxymethyl) piperazine-N-4-butanesulfonic acid from 5 to 55 °C. J. Solution Chem. 33, 351–362 (2004)
Good, N.E., Winget, G.D., Connolly, T.N., Izawa, S., Singh, R.M.M.: Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research. Biochemistry 5, 467–477 (1966)
Ferguson, W.J., Braunschweiger, K.I., Braunschweiger, W.R., Smith, J.R., McCormick, J.J., Wasmann, C.C., Jarvis, N.P., Bell, D.H., Good, N.E.: Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research. Anal. Biochem. 104, 300–310 (1980)
Bower, V.E., Paabo, M., Bates, R.G.: A standard for the measurement of the pH of blood and other physiological media. J. Res. Nat. Bur. Std. 65A, 267–270 (1961)
Durst, R.A., Staples, B.R.: Tris/Tris HCl: Standard buffer for use in the physiological pH range. Clin. Chem. 18, 206–208 (1972)
Feng, D., Koch, W.F., Wu, Y.C.: Second dissociation constant and pH of N-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid from 0 to 50 °C. Anal. Chem. 61, 1400–1405 (1989)
Wu, Y.C., Berezansky, P.A., Feng, D., Koch, W.F.: Second dissociation constant of 3-(N-morpholino)-2-hydroxypropanesulfonic acid and pH of its buffer solutions. Anal. Chem. 65, 1084–1087 (1993)
Bates, R.G., Roy, R.N., Robinson, R.A.: Buffer standards of tris(hydroxymethyl)methylglycine (“Tricine”) for the physiological range pH 7.2 to 8.5. Anal. Chem. 45, 1663–1666 (1973)
Roy, R.N., Robinson, R.A., Bates, R.G.: Thermodynamics of the two dissociation steps of N-tris (hydroxymethyl)methylglycine (“Tricine”) in water from 5 ° to 50 °C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 95, 8231–8235 (1973)
Roy, R.N., Mrad, D.R., Lord, P.A., Carlsten, J.A., Good, W.S., Allsup, P., Roy, L.N., Kuhler, K.M., Koch, W.F., Wu, Y.C.: Thermodynamics of the second dissociation constant and standards for pH of 3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid (MOPS) from 5 to 55 °C. J. Solution Chem. 27, 73–87 (1998)
Roy, R.N., Cramer, J., Rendon, V., Willard, D., Walter, J.L., Good, W.S., Kilker, A., Roy, L.N.: Buffers for the physiological pH range: Thermodynamics of the second dissociation of N-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine-N′-2-hydroxypropanesulfonic acid (HEPPSO) from 5 to 55 °C. J. Solution Chem. 27, 425–434 (1998)
Goldberg, R.N., Kishore, R.N., Lennen, R.M.: Thermodynamic quantities for the ionization reactions of buffers. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 31, 231–370 (2002)
Bates, R.G.: Determination of pH, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (1973) Chaps. 4, 10
Latimer, W.M.: Oxidation Potentials, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, New York (1952)
Wu, Y.C., Feng, D., Koch, W.F.: Evaluation of liquid junction potentials and determination of pH values of strong acids at moderate ionic strengths. J. Solution Chem. 18, 641–649 (1989)
Bates, R.G.: Revised standard values for pH measurements from 0 to 95 °C. J. Res. Nat. Bur. Stand. 66A, 179–184 (1962)
Bates, R.G., Vega, C.A., White, Jr.: D.R.: Standards for pH measurements in isotonic saline media of ionic strength I=0.16. Anal. Chem. 50, 1295–1300 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10953-014-0150-y.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, R.N., Roy, L.N., Fuge, M.S. et al. Buffer Standards for the Physiological pH of the Zwitterionic Compound, ACES, from 5 to 55 °C. J Solution Chem 38, 471–483 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-009-9380-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-009-9380-9