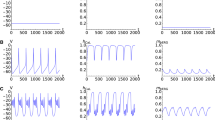
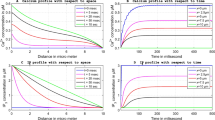
Abstract
Two models for coupled pancreatic β cells are used to investigate excited wave propagation in spatially inhomogeneous islets of Langerhans. The application concerns spatial variation of glucose concentration across the islet. A comprehensive model of coupled cells shows that wave blocking occurs as the conductance of adenosine triphosphate regulated potassium channels increases, corresponding to spatially decreasing glucose concentration. A simplified model based on a perturbed version of Fisher’s equation has been investigated using perturbation theory. We show that the perturbed Fisher’s equation likewise can exhibit wave blocking.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eddlestone, G.T., Goncalves, A., Bangham, J.: Electrical coupling between cells in islets of langerhans from mouse. J. Membr. Biol. 77, 1–14 (1984)
Meissner, H.: Electrophysiological evidence for coupling between beta cells of pancreatic islets. Nature 262(5568), 502–504 (1976)
Ravier, M.A., Güldenagel, M., Charollais, A., Gjinovci, A., Caille, D., Sohl, G., Wollheim, C.B., Willecke, K., Henquin, J.C., Meda, P.: Loss of connexin36 channels alters beta-cell coupling, islet synchronization of glucose-induced Ca2 + and insulin oscillations, and basal insulin release. Diabetes 54, 1798–1807 (2005)
Aslanidi, O.V., Mornev, O., Skyggebjerg, O., Arkhammar, P., Thastrup, O., Sørensen, M.P., Christiansen, P.L., Conradsen, K., Scott, A.C.: Excitation wave propagation as a possible mechanism for signal transmission in pancreatic islets of langerhans. Biophys. J. 80, 1195–1209 (2001)
Rocheleau, J.V., Walker, G.M., Head, W.S., McGuinness, O.P., Piston, D.W.: Microfluidic glucose stimulation reveals limited coordination of intracellular Ca2 + activity oscillations in pancreatic islets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101(12), 899–903 (2004)
Sherman, A.: Calcium and membrane potential oscillations in pancreatic β-cells. In: Othmer, H.G., Adler, F.R., Lewis, M.A., Dallon, J.C. (eds.) Case Studies in Mathematical Modelling: Ecology, Physiology, and Cell Biology, pp. 199–217. Prentice-Hall, New York (1997)
Pedersen, M.G.: Wave speeds of solutions to density dependent nonlinear nagumo diffusion equations—inspired by oscillating gap-junction conductance in the pancreatic islets of langerhans. J. Math. Biol. 80, 683–698 (2005)
Keener, J.P.: Homogenization and propagation in the bistable equation. Physica D 136, 1–17 (2000)
Scott, A.C.: Nonlinear Science. Emergence and Dynamics of Coherent Structures. Oxford University Press, New York (2003)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge financial support from the European Union through the Network of Excellence BioSim, LSHB-CT-2004-005137. MGP was partially supported by the Villum Kann Rasmussen Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedersen, M.G., Sørensen, M.P. Wave-Block Due to a Threshold Gradient Underlies Limited Coordination in Pancreatic Islets. J Biol Phys 34, 425–432 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-008-9069-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-008-9069-0