Abstract
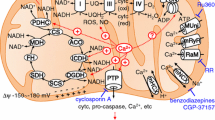
For induction of the mitochondrial permeability transition (PT) by Ca2+, the addition of a respiratory substrate such as succinate is required. However, earlier studies indicated the possible induction of the mitochondrial PT by Ca2+ in the absence of a respiratory substrate (Hunter, D.R., and Haworth, R.A. (1979) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 195, 453–459). In the present study, we obtained clear evidence showing that the mitochondrial PT could be induced by Ca2+ even in the absence of respiratory substrate. We next examined the protein release from mitochondria that accompanied the induction of PT in the absence of a respiratory substrate. Interestingly, distinct from the ordinary mitochondrial PT induced by Ca2+ in the presence of a respiratory substrate, which is associated with the release of mitochondrial cytochome c and adenylate kinase, the mitochondrial PT occurring in the absence of a respiratory substrate was associated with release of mitochondrial adenylate kinase but not with that of mitochondrial cytochrome c. This experimental system should be quite useful for understanding the mechanisms of protein release from mitochondria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnoult D, Gaume B, Karbowski M, Sharpe JC, Cecconi F, Youle RJ (2003) Mitochondrial release of AIF and EndoG requires caspase activation downstream of Bax/Bak-mediated permeabilization. EMBO J. 22:4385–4399
Bernardi P (1999) Mitochondrial transport of cations: channels, exchangers, and permeability transition. Physiol. Rev. 79:1127–1155
Brenner C, Grimm S (2006) The permeability transition pore complex in cancer cell death. Oncogene 25:4744–4756
Crouser ED, Gadd ME, Julian MW, Huff JE, Broekemeier KM, Robbins KA, Pfeiffer DR (2003) Quantitation of cytochrome c release from rat liver mitochondria. Anal. Biochem. 317:67–75
Gogvadze V, Robertson JD, Enoksson M, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S (2004) Mitochondrial cytochrome c release may occur by volume-dependent mechanisms not involving permeability transition. Biochem. J. 378:213–217
Gunter TE, Pfeiffer DR (1990) Mechanisms by which mitochondria transport calcium. Am. J. Physiol. 258:C755–C786
Hunter DR, Haworth RA (1979) The Ca2+-induced membrane transition in mitochondria. I. The protective mechanisms. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 195:453–459
Köhler C, Gahm A, Noma T, Nakazawa A, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (1999) Release of adenylate kinase 2 from the mitochondrial intermembrane space during apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 447:10–12
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C (2007) Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev. 87:99–163
Modjtahedi N, Giordanetto F, Madeo F, Kroemer G (2006) Apoptosis-inducing factor: vital and lethal. Trends Cell Biol. 16:264–272
Orrenius S, Gogvadze V, Zhivotovsky B (2007) Mitochondrial oxidative stress: implications for cell death. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 47:143–183
Ott M, Robertson JD, Gogvadze V, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S (2002) Cytochrome c release from mitochondria proceeds by a two-step process. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99:1259–1263
Pfeiffer DR, Gudz TI, Novgorodov SA, Erdahl WL (1995) The peptide mastoparan is a potent facilitator of the mitochondrial permeability transition. J. Biol. Chem. 270:4923–4932
Scarlett JL, Murphy MP (1997) Release of apoptogenic proteins from the mitochondrial intermembrane space during the mitochondrial permeability transition. FEBS Lett. 418:282–286
Shinohara Y, Almofti MR, Yamamoto T, Ishida T, Kita F, Kanzaki H, Ohnishi M, Yamashita K, Shimizu S, Terada H (2002) Permeability transition-independent release of mitochondrial cytochrome c induced by valinomycin. Eur. J. Biochem. 269:5224–5230
Sultan A, Sokolove PM (2001) Palmitic acid opens a novel cyclosporin A-insensitive pore in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 386:37–51
Yamamoto T, Tachikawa A, Terauchi S, Yamashita K, Kataoka M, Terada H, Shinohara Y (2004) Multiple effects of DiS-C3(5) on mitochondrial structure and function. Eur. J. Biochem. 271:3573–3579
Yamamoto T, Terauchi S, Tachikawa A, Yamashita K, Kataoka M, Terada H, Shinohara Y (2005) Two critical factors affecting the release of mitochondrial cytochrome C as revealed by studies using N, N’-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide as an atypical inducer of permeability transition. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 37:299–306
Zoratti M, Szabo I (1995) The mitochondrial permeability transition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1241:139–176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, T., Yoshimura, Y., Yamada, A. et al. Distinct behaviors of adenylate kinase and cytochrome c observed following induction of mitochondrial permeability transition by Ca2+ in the absence of respiratory substrate. J Bioenerg Biomembr 40, 619–623 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-008-9190-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-008-9190-6