Abstract
Background
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease affecting nearly 1% of adults worldwide. This study aimed to investigate whether sophocarpine is a potential drug for treating RA.
Methods
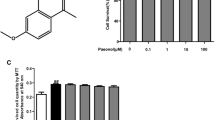
The cytotoxicity of sophocarpine to RA-fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) was evaluated using 3-[4,-dimethylthiazol-2-y]-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assays kit and released lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assays. The transcription of proinflammatory cytokines in RA-FLSs was analyzed by reverse transcription and real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The proteins levels were further verified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The alterations in the mediators of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling pathways were tested by western blotting. The clinical effects of sophocarpine were evaluated in type II collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in DBA-/1 mouse model by scoring their clinical responses, synovitis, and cartilage destructions, and ELISA was employed to analyze the concentrations of proinflammatory cytokines in the serum of CIA mice.
Results
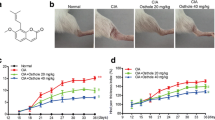
The results showed that sophocarpine contained low cytotoxicity to RA-FLS cells, and it was capable to downregulate the expressions of LPS-induced proinflammatory cytokines. The suppressions of MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways by sophocarpine were also found in LPS-induced RA-FLSs. The attenuation of the symptoms in CIA mouse model were significant, in which concentrations of proinflammatory cytokines were decreased after the sophocarpine treatment.
Conclusion
In this study, we demonstrated the potential of sophocarpine in treating RA, both in vitro and in vivo. Sophocarpine may be a potential drug in treating human RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 2003; 423: 356–61.
McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol 2007; 7: 429–42.
van der Heijden JW, Dijkmans BA, Scheper RJ, Jansen G. Drug Insight: resistance to methotrexate and other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs–from bench to bedside. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 2007; 3: 26–34.
Smolen JS, Steiner G. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2003; 2: 473–88.
O’Dell JR. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 2591–602.
Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Allaart CF, et al. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of four different treatment strategies in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (the best study): a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52: 3381–90.
Smolen JS, Aletaha D. Rheumatoid arthritis therapy reappraisal: strategies, opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2015; 11: 276–89.
Thalhamer T, McGrath MA, Harnett MM. MAPKs and their relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008; 47: 409–14.
Huber LC, Distler O, Tarner I, Gay RE, Gay S, Pap T. Synovial fibroblasts: key players in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006; 45: 669–75.
Bottini N, Firestein GS. Duality of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: passive responders and imprinted aggressors. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2013; 9: 24–33.
Bartok B, Firestein GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev 2010; 233: 233–55.
Lin Z, Huang CF, Liu XS, Jiang J. In vitro anti-tumour activities of quinolizidine alkaloids derived from Sophora flavescens Ait. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2011; 108: 304–9.
Gao Y, Li G, Li C, et al. Anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory activity of sophocarpine. J Ethnopharmacol 2009; 125: 324–9.
Zhang Y, Wang S, Li Y, Xiao Z, Hu Z, Zhang J. Sophocarpine and matrine inhibit the production of TNF-alpha and IL-6 in murine macrophages and prevent cachexia-related symptoms induced by colon26 adenocarcinoma in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 2008; 8: 1767–72.
Gao Y, Jiang W, Dong C, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of sophocarpine in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells via NF-kappaB and MAPKs signaling pathways. Toxicol In Vitro 2012; 26: 1–6.
Zhang JM, Zhu YB, Deng X, Wang CX, Luan SM, Chen YX. Mechanism of sophocarpine in treating experimental colitis in mice. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2015; 40: 3081–7.
Li J, Li L, Chu H, Sun X, Ge Z. Oral sophocarpine protects rat heart against pressure overload-induced cardiac fibrosis. Pharm Biol 2014; 52: 1045–51.
Song CY, Zeng X, Chen SW, et al. Sophocarpine alleviates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011; 26: 765–74.
Song CY, Zeng X, Wang Y, et al. Sophocarpine attenuates tolllike receptor 4 in steatotic hepatocytes to suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines synthesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015; 30: 405–12.
Wang D, Xu N, Zhang Z, et al. Sophocarpine displays antiinflammatory effect via inhibiting TLR4 and TLR4 downstream pathways on LPS-induced mastitis in the mammary gland of mice. Int Immunopharmacol 2016; 35: 111–8.
Wang XJ, Deng HZ, Jiang B, Yao H. The natural plant product sophocarpine ameliorates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice by regulating cytokine balance. Int J Colorectal Dis 2012; 27: 575–81.
Cameron M, Gagnier JJ, Little CV, Parsons TJ, Blumle A, Chrubasik S. Evidence of effectiveness of herbal medicinal products in the treatment of arthritis. Part 2: rheumatoid arthritis. Phytother Res 2009; 23: 1647–62.
Li G, Liu D, Zhang Y, et al. Celastrol inhibits lipopolysaccharidestimulated rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocyte invasion through suppression of TLR4/NF-kappaB-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. PLoS One 2013; 8: e68905.
Jin XN, Yan EZ, Wang HM, et al. Hyperoside exerts antiinflammatory and anti-arthritic effects in LPS-stimulated human fibroblast-like synoviocytes in vitro and in mice with collageninduced arthritis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2016; 37: 674–86.
Xin W, Huang C, Zhang X, et al. Methyl salicylate lactoside inhibits inflammatory response of fibroblast-like synoviocytes and joint destruction in collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Br J Pharmacol 2014; 171: 3526–38.
Niu Y, Dong Q, Li R. Matrine regulates Th1/Th2 cytokine responses in rheumatoid arthritis by attenuating the NF-KappaB signaling. Cell Biol Int 2017; 41: 611–21.
Pu J, Fang FF, Li XQ, et al. Matrine exerts a strong anti-arthritic effect on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats by inhibiting inflammatory responses. Int J Mol Sci 2016: 17.
Chen SX, Mei SW, Wang PQ. Therapeutic effect of kangke injection on viral myocarditis and its anticoxsackie virus mechanism. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 1997; 17: 207–9.
Meyer LH, Franssen L, Pap T. The role of mesenchymal cells in the pathophysiology of inflammatory arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2006; 20: 969–81.
Schett G, Tohidast-Akrad M, Smolen JS, et al. Activation, differential localization, and regulation of the stress-activated protein kinases, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-JUN N-terminal kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, in synovial tissue and cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2000; 43: 2501–12.
Koch AE. Chemokines and their receptors in rheumatoid arthritis: future targets? Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52: 710–21.
Gerlag DM, Ransone L, Tak PP, et al. The effect of a T cell-specific NF-kappa B inhibitor on in vitro cytokine production and collageninduced arthritis. J Immunol 2000; 165: 1652–8.
Simmonds RE, Foxwell BM. Signalling, inflammation and arthritis: NF-kappaB and its relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008; 47: 584–90.
Brand DD, Latham KA, Rosloniec EF. Collagen-induced arthritis. Nat Protoc 2007; 2: 1269–75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, L., Zhu, L. Sophocarpine suppress inflammatory response in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes and in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Eur Cytokine Netw 28, 120–126 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1684/ecn.2017.0400
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1684/ecn.2017.0400