Abstract
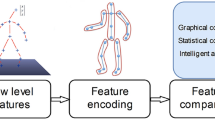
This paper presents a walking pattern detection method for a smart rollator. The method detects the rollator user’s lower extremities from the depth data of an RGB-D camera. It then segments the 3D point data of the lower extremities into the leg and foot data points, from which a skeletal system with 6 skeletal points and 4 rods is extracted and used to represent a walking gait. A gait feature, comprising the parameters of the gait shape and gait motion, is then constructed to describe a walking state. K-means clustering is employed to cluster all gait features obtained from a number of walking videos into 6 key gait features. Using these key gait features, a walking video sequence is modeled as a Markov chain. The stationary distribution of the Markov chain represents the walking pattern. Three Support Vector Machines (SVMs) are trained for walking pattern detection. Each SVM detects one of the three walking patterns. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method has a better performance in detecting walking patterns than seven existing methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
http://pointclouds.org/documentation/tutorials/region_growing_segmentation.php
Alwan, M., Ledoux, A., Wasson, G., et al.: Basic walker-assisted gait characteristics derived from forces and moments exerted on the Walker’s Handles: results on normal subjects. Med. Eng. Phys. 29, 380–389 (2007)
Chaaraoui, A.A., Padilla-López, J.R., Climent-Pére, P., et al.: Evolutionary joint selection to improve human action recognition with RGB-D devices. Expert Syst. Appl. 41, 786–794 (2014)
Dune, C., Gorce, P., Merlet, J.P.: Can smart rollators be used for gait monitoring and fall prevention? IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (2012)
Gritti, A., Tarabini, O., Guzzi, J.: Kinect-based People Detection and Tracking from Small-footprint Ground Robots. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Chicago, IL ((2014))
Joly, C., Dune, C.: Feet and Legs Tracking Using a Smart Rollator Equipped with a Kinect. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Tokyo, Japan (2013)
Laptev, I., Caputo, B., Schüldt, C., et al.: Local velocity-adapted motion events for spatio-temporal recognition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 108, 207–229 (2007)
Lowe, D.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vision 60, 91–110 (2004)
Mona, M.M., Elsayed, H., Magda, B.F., et al.: An enhanced method for human action recognition. J. Adv. Res. 6, 163–169 (2015)
Pearson, K.: On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of Points in space. Phil. Mag. 2, 559–572 (1901)
Pelleg, D., Moore, A.W.: X-means: Extending K-means with Efficient Estimation of the Number of Clusters. International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) (2000)
Qian, X., Ye, C.: NCC-RANSAC: a fast plane extraction method for 3D range data segmentation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 44, 2771–2783 (2014)
Ricardo, C., Hesam, S., Alberto, C., et al.: The opportunity challenge: a benchmark database for on-body sensor-based activity recognition. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 34, 2033–2042 (2013)
Sagha, H., Digumarti, S.T., Millán, J.D.R., Chavarriaga, R.: Benchmarking classification techniques using the Opportunity human activity dataset. In IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC) (2011)
Tung, J.: Development and Evaluation of the iWalker: An Instrumented Rolling Walker to Assess Balance and Mobility in Everyday Activities. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Toronto (2010)
Xiaodong, Y., YingLi, T.: Eigenjoints-based action recognition using naive-bayes-nearest-neighbor. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Providence (2012)
Zhang, H., Ye, C.: An RGB-D camera based walking pattern detection method for smart rollators. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 9474, 624–633 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the National Institute of Nursing Research, and the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering of the National Institutes of Health under Award R01NR016151. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Ye, C. RGB-D camera based walking pattern recognition by support vector machines for a smart rollator. Int J Intell Robot Appl 1, 32–42 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41315-016-0002-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41315-016-0002-6