Abstract
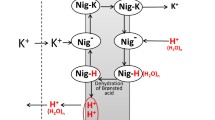
The effects of temperature and the membrane-active protein CTII on the formation of nonbilayer structures in mitochondrial membranes were studied by 31P-NMR. An increase in ATP synthase activity was found for the first time to accompany the formation of nonbilayer packed phospholipids with immobilized molecular mobility in mitochondrial membranes. Computer modeling was additionally employed in studying the interaction of important phospholipids found in mitochondrial membranes with the molecular surface of CTII, which behaves like a dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-binding protein (DCCD-BP) of the F0 group in a lipid phase. Proton permeability toroidal pores were assumed to form in mitochondrial membranes from nonbilayer-packed phospholipids immobilized via interactions with DCCD-BP. Proton transport along a concentration gradient through the transit toroidal permeability pores may induce conformational changes necessary for mediating the catalytic activity of ATP synthase in the subunits of the F0–F1 complex.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CTII:
-
cobra snake venom membrane-active protein
- DCCD-BP:
-
dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-binding protein
- MLL:
-
multilamellar liposome
References
N. Kocherginski, Progr. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 99, 20 (2009).
R. K. Nakamoto, J. A. B. Scanlon, and M. K. Al-Shawi, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 476 (1), 43 (2008). doi 10.1016/j.abb.2008.05.004
J. Weber, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1757, 1162 (2006).
S. E. Gasanov, R. K. Dagda, and E. D. Rael, J. Clinic. Toxicol. 4, 181 (2014). doi 10.4172/2161-0495.1000181
S. E. Gasanov, I. H. Shrivastava, F. S. Israilov, et al., PLOS ONE 10 (6): e0129248 (2015). doi 10.1371/journal. pone.0129248
R. H. Fillingame, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 49, 1079 (1980).
N. K. Segal’, S. E. Gasanov, L. A. Palamarchuk, et al., Biokhimiya 58 (11), 1812 (1993).
W. Sebald, T. Graf, and H. B. Lukins, Eur. J. Biochem. 93, 587 (1979).
K. Y. Hara and H. Mori, J. Biomol. Screen. 11 (3), 310 (2006).
S. E. Gasanov, L. P. Vernon, and T. F. Aripov, Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 301 (2), 367 (1993).
R. K. Dagda, S. E. Gasanov, B. Zhang, et al., J. Biol. Phys. 40 (2):193 (2014). doi 10.1007/s10867-013-9339-3
B. De Kruijff, G. A. Morris, and P. R. Culliss, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 598, 206 (1980).
H. A. Schwertner and J. B. Biale, J. Lipid Res. 14 (2), 235 (1973).
S. E. Gasanov, M. A. Alsarraj, N. E. Gasanov, et al., J. Membr. Biol. 150, 132 (1997).
S. Wi and C. Kim., J. Phys. Chem. B 112 (36), 1140 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © S.E. Gasanov, A.A. Kim, R.K. Dagda, 2016, published in Biofizika, 2016, Vol. 61, No. 4, pp. 705–710.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gasanov, S.E., Kim, A.A. & Dagda, R.K. The possible role of nonbilayer structures in regulating ATP synthase activity in mitochondrial membranes. BIOPHYSICS 61, 596–600 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350916040084
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006350916040084