Abstract
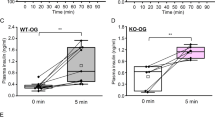
The heterodimeric protein T1R2/T1R3 is a chemoreceptor mediating taste perception of sugars, several amino acids, and non-caloric sweeteners in humans and many other vertebrate species. The T1R2 and T1R3 proteins are expressed not only in the oral cavity, but also in the intestine, pancreas, liver, adipose tissue, and in structures of the central nervous system, which suggests their involvement in functions other than gustatory perception. In this study, we analyzed the role of the T1R3 protein in regulation of glucose metabolism in experiments with the gene-knockout mouse strain C57BL/6J-Tas1r3 tm1Rfm (Tas1r3-/-), with a deletion of the Tas1r3 gene encoding T1R3, and the control strain C57BL/6ByJ with the intact gene. Glucose tolerance was measured in euglycemic or food-deprived mice after intraperitoneal or intragastric glucose administration. We have shown that in the Tas1r3-/- strain, in addition to the disappearance of taste preference for sucrose, glucose tolerance is also substantially reduced, and insulin resistance is observed. The effect of the Tas1r3 gene knockout on glucose utilization was more pronounced in the euglycemic state than after food deprivation. The baseline glucose level after food deprivation was lower in the Tas1r3-/- strain than in the control strain, which suggests that T1R3 is involved in regulation of endogenous glucose production. These data suggest that the T1R3-mediated glucoreception interacts with the KATP-dependent mechanisms of regulation of the glucose metabolism, and that the main role is likely played by T1R3 expressed in the pancreas and possibly in the central nervous system, but not in the intestinal mucosa, as it was suggested earlier.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Polakof, S., Mommsen, T.P., and Soengas, J.L., Glucosensing and glucose homeostasis: from fish to mammals, Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol Biol., 2011, vol. 160, no. 4, pp. 123–149.
Herman, M.A. and Kahn, B.B., Glucose transport and sensing in the maintenance of glucose homeostasis and metabolic harmony, J. Clin. Invest., 2006, vol. 116, no. 7, pp. 1767–1775.
Hiriart, M. and Aguilar-Bryan, L., Channel regulation of glucose sensing in the pancreatic beta-cell, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab., 2008, vol. 295, no. 6, pp. E1298–1306.
Schuit, F.C., Huypens, P., Heimberg, H., and Pipeleers, D.G., Glucose sensing in pancreatic beta-cells: a model for the study of other glucose-regulated cells in gut, pancreas, and hypothalamus, Diabetes, 2001, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 1–11.
Wang, S.Y., Chi, M.M., Li, L., Moley, K.H., and Wice, B.M., Studies with GIP/Ins cells indicate secretion by gut K cells is KATP channel independent, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab., 2003, vol. 284, no. 5, pp. E988–1000.
Reimann, F., Habib, A.M., Tolhurst, G., Parker, H.E., Rogers, G.J., and Gribble, F.M., Glucose sensing in L cells: a primary cell study, Cell Metab., 2008, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 532–539.
Miki, T., Liss, B., Minami, K., Shiuchi, T., Saraya, A., Kashima, Y., Horiuchi, M., Ashcroft, F., Minokoshi, Y., Roeper, J., and Seino, S., ATPsensitive K+ channels in the hypothalamus are essential for the maintenance of glucose homeostasis, Nat. Neurosci., 2001, vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 507–512.
Gembal, M., Gilon, P., and Henquin, J.C., Evidence that glucose can control insulin release independently from its action on ATP-sensitive K+ channels in mouse β-cells, J. Clin. Invest., 1992, vol. 89, no. 4, pp. 1288–1295.
Straub, S.G. and Sharp, G.W., Glucose-stimulated signaling pathways in biphasic insulin secretion (Review), Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev., 2002, vol. 18, pp. 451–463.
Fioramonti, X., Lorsignol, A., Taupignon, A., and Pénicaud, L., A new ATP-sensitive K+ channel-independent mechanism is involved in glucose-excited neurons of mouse arcuate nucleus, Diabetes, 2004, vol. 53, no. 11, pp. 2767–2775.
Chandrashekar, J., Hoon, M.A., Ryba, N., and Zuker, C.S., The receptors and cells for mammalian taste, Nature, 2006, vol. 444, pp. 288–294.
Bachmanov, A.A., Bosak, N.P., Floriano, W.B., Inoue, M., Li, X., Lin, C., Murovets, V.O., Reed, D.R., Zolotarev, V.A., and Beauchamp, G.K., Genetics of sweet taste preferences, Flavour Fragrance J., 2011, vol. 26, Iss. 4, pp. 286–294.
Bachmanov, A.A. and Beauchamp, G.K., Taste receptor genes, Annu. Rev. Nutr., 2007, vol. 27, pp. 389–414.
Murovets, V.O., Zolotarev, V.A., and Bachmanov, A.A., The role of the sac locus in the development of taste preference for alcohol in inbred lines of mice, Dokl. Akad. Nauk, 2010, vol. 432, no. 3, pp. 420–422.
Raliou, M., Wiencis, A., Pillias, A.M., Planchais, A., Eloit, C., Boucher, Y., Trotier, D., Montmayeur, J.P., and Faurion, A., Nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms in human tas1r1, tas1r3, and mGluR1 and individual taste sensitivity to glutamate, Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 2009, vol. 90, pp. 789S–799S.
Shi, P. and Zhang, J., Contrasting modes of evolution between vertebrate sweet/umami receptor genes and bitter receptor genes, Mol. Biol. Ev., 2006, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 292–300.
Nakagawa, Y., Nagasawa, M., Yamada, S., Hara, A., Mogami, H., Nikolaev, V.O., Lohse, M.J., Shigemura, N., Ninomiya, Y., and Kojima, I., Sweet taste receptor expressed in pancreatic beta-cells activates the calcium and cyclic AMP signaling systems and stimulates insulin secretion, PLoS One, 2009, vol. 4, no. 4, p. e5106.
Oya, M., Suzuki, H., Watanabe, Y., Sato, M., and Tsuboi, T., Amino acid taste receptor regulates in sulin secretion in pancreatic β-cell line MIN6 cells, Genes Cells, 2011, vol. 16, no. 5, pp. 608–616.
Kyriazis, G.A., Soundarapandian, M.M., and Tyrberg, B., Sweet taste receptor signaling in beta cells mediates fructose-induced potentiation of glucosestimulated insulin secretion, PNAS, 2012, vol. 109, no. 8. pp. E524-E532.
Jang, H.J., Kokrashvili, Z., Theodorakis, M.J., Carlson, O.D., Kim, B.J., Zhou, J., Kim, H.H., Xu, X., Chan, S.L., Juhaszova, M., Bernier, M., Mosinger, B., Margolskee, R.F., and Egan, J.M., Gut-expressed gustducin and taste receptors regulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2007, vol. 104, no. 38, pp. 15 069–15 074.
Rozengurt, N., Wu, S.V., Chen, M.C., Huang, C., Sternini, C., and Rozengurt, E., Colocalization of the alphasubunit of gustducin with PYY and GLP-1 in L cells of human colon, Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol., 2006, vol. 291, pp. G792–802.
Rozengurt, E. and Sternini, C., Taste receptor signaling in the mammalian gut, Curr. Opin. Pharmacol., 2007, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 557–562.
Sutherland, K., Young, R.L., Cooper, N.J., Horowitz, M., and Blackshaw, L.A., Phenotypic characterization of taste cells of the mouse small intestine, Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol., 2007, vol. 292, pp. G1420–1428.
Ren, X., Zhou, L., Terwilliger, R., Newton, S.S, and de Araujo, I.E., Sweet taste signaling functions as a hypothalamic glucose sensor, Front. Integr. Neurosci., 2009, vol. 3, Article 12, pp. 1–15.
Kokrashvili, Z., Mosinger, B., and Margolskee, R.F., T1R3 and alpha-gustducin in gut regulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 2009, vol. 1170, pp. 91–94.
Gerspach, A.C., Steinert, R.E., Schönenberger, L., Graber-Maier, A., and Beglinger, C., The role of the gut sweet taste receptor in regulating GLP-1, PYY, and CCK release in humans, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab., 2011, vol. 301, no. 2, pp. E317–325.
Geraedts, M.C.P., Takahashi, T., Vigues, S., Markwardt, M.L., Nkobena, A., Cockerham, R.E., Hajnal, A., Dotson, C.D., Rizzo, M.A., and Munger, S.D., Transformation of post-ingestive glucose responses after deletion of sweet taste receptor subunits or gastric bypass surgery, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab., 2012, vol. 303, no. 4, pp. E464–474.
Margolskee, R.F., Dyer, J., Kokrashvili, Z., Salmon, K.S., Ilegems, E., Daly, K., Maillet, E.L., Ninomiya, Y., Mosinger, B., and Shirazi-Beechey, S.P., T1R3 and gustducin in gut sense sugars to regulate expression of Na+-glucose cotransporter 1, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2007, vol. 104, no. 38, pp. 15075–15080.
Mace, O.J., Affleck, J., Patel, N., and Kellett, G.L., Sweet taste receptors in rat small intestine stimulate glucose absorption through apical GLUT2, J. Physiol., 2007, vol. 582, Pt. 1, pp. 379–392.
Kojima, I. and Nakagawa, Y., The role of the sweet taste receptor in enteroendocrine cells and pancreatic β-cells, Diabetes, Metab. J., 2011, vol. 35, no. 5, pp. 451–457.
Fujita, Y., Wideman, R.D., Speck, M., Asadi, A., King, D.S., Webber, T.D., Haneda, M., and Kieffer, T.J., Incretin release from gut is acutely enhanced by sugar but not by sweeteners in vivo, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab., 2009, vol. 296, no. 3, pp. E473–E479.
Ma, J., Bellon, M., Wishart, J.M., Young, R., Blackshaw, L.A., Jones, K.L., Horowitz, M., and Rayner, C.K., Effect of the artificial sweetener, sucralose, on gastric emptying and incretin hormone release in healthy subjects, Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol., 2009, vol. 296, no. 4, pp. G735–739.
Yee, K.K., Sukumaran, S.K., Kotha, R., Gilbertson, T.A., and Margolskee, R.F., Glucose transporters and ATP-gated K+ (KATP) metabolic sensors are present in type 1 taste receptor 3 (T1R3)-expressing taste cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2011, vol. 108, no. 13, pp. 5431–5436.
Damak, S., Rong, M., Yasumatsu, K., Kokrashvili, Z., Varadarajan, V., Zou, S., Jiang, P., Ninomiya, Y., and Margolskee, R.F., Detection of sweet and umami taste in the absence of taste receptor T1R3, Science, 2003, vol. 301, pp. 850–853.
Glendinning, J.I., Gresack, J., and Spector, A.C., A high-throughoutput screening procedure for identifying mice with aberrant taste and oromotor function, Chem. Senses, 2002, vol. 27, pp. 461–447.
Spector, A.C., Physiological evaluation of taste function in non-human mammals, Handbook of Olfaction and Gustation, 2nd Edn, NY, 2002.
Ayala, J.E., Samuel, V.T., Morton, G.J., Obici, S., Croniger, C.M., Shulman, G.I., Wasserman, D.H., and McGuinness, O.P., Standard operating procedures for describing and performing metabolic tests of glucose homeostasis in mice, Dis. Model. Mech., 2010, vol. 3, no. 9–10, pp. 525–534.
Zhao, G.Q., Zhang, Y., Hoon, M.A., Chandrashekar, J., Erlenbach, I., Ryba, N.J.P., and Zuker, C.S., The receptors for mammalian sweet and umami taste, Cell, 2003, vol. 115, pp. 255–266.
Ohkuri, T., Yasumatsu, K., Horio, N., Jyotaki, M., Margolskee, R.F., and Ninomiya, Y., Multiple sweet receptors and transduction pathways revealed in knockout mice by temperature dependence and gurmarin sensitivity, Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol., 2009, vol. 296, no. 4, pp. R960–971.
Touzani, K., Bodnar, R.J., and Sclafani, A., Neuropharmacology of learned flavor preferences, Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 2010, vol. 97, no. 1, pp. 55–62.
Mutel, E., Gautier-Stein, A., Abdul-Wahed, A., Amigó-Correig, M., Zitoun, C., Stefanutti, A., Houberdon, I., Tourette, J.A., Mithieux, G., and Rajas, F., Control of blood glucose in the absence of hepatic glucose production during prolonged fasting in mice: induction of renal and intestinal gluconeogenesis by glucagon, Diabetes, 2011, vol. 60, no. 12, pp. 3121–3131.
Andrikopoulos, S., Blair, A.R., Deluca, N., Fam, B.C., and Proietto, J., Evaluating the glucose tolerance test in mice, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab., 2008, vol. 295, no. 6, pp. E1323–1332.
Heijboer, A.C., Donga, E., Voshol, P.J., Dang, Z.C., Havekes, L.M., Romijn, J.A., and Corssmit, E.P., Sixteen hours of fasting differentially affects hepatic and muscle insulin sensitivity in mice, J. Lipid Res., 2005, vol. 46, pp. 582–588.
Renwick, A.G. and Molinary, S.V., Sweet-taste receptors, low-energy sweeteners, glucose absorption and insulin release, Br. J. Nutr., 2010, vol. 104, no. 10, pp. 1415–1420.
Egan, J.M. and Margolskee, R.F., Taste cells of the gut and gastrointestinal chemosensation, Mol. Interv., 2008, vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 78–81.
McIntyre, N., Holdsworth, C.D., and Turner, D.S., New interpretation of oral glucose tolerance, Lancet, 1964, vol. 284, no. 7349, pp. 20–21.
Erlick, H., Stimmler, L., Hlad, C.J. (Jr.), and Arai, Y., Plasma insulin response to oral and intravenous glucose administration, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 1964, vol. 24, pp. 1076–1082.
Yki-Jarvinen, H., Helve, E., and Koivisto, V.A., Hyperglycemia decreases glucose uptake in type I diabetes, Diabetes, 1987, vol. 36, pp. 892–896.
Rossetti, L., Giaccari, A., and DeFronzo, R.A., Glucose toxicity, Diabetes Care, 1990, vol. 13, pp. 610–630.
Buse, M.G., Hexosamines, insulin resistance, and the complications of diabetes: current status, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab., 2006, vol. 290, no. 1, pp. E1–E8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.O. Murovets, A.A. Bachmanov, S.V. Travnikov, A.A. Churikova, V.A. Zolotarev, 2014, published in Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi Biokhimii i Fiziologii, 2014, Vol. 50, No. 4, pp. 296s-304.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murovets, V.O., Bachmanov, A.A., Travnikov, S.V. et al. The involvement of the T1R3 receptor protein in the control of glucose metabolism in mice at different levels of glycemia. J Evol Biochem Phys 50, 334–344 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093014040061
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093014040061