Electrocatalysis ( IF 3.1 ) Pub Date : 2019-08-13 , DOI: 10.1007/s12678-019-00553-2 Satoko Takase , Yuki Aoto , Daiki Ikeda , Hideaki Wakita , Youichi Shimizu
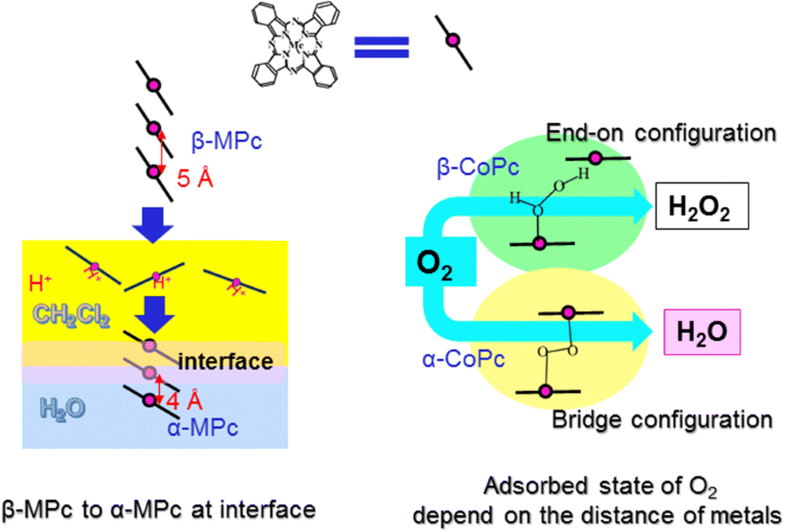
Effects of the crystallographic structures of metal-phthalocyanines (metal: Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) between α and β phases on electrochemical oxygen reduction catalytic activities were investigated in acidic condition. As the distances of centered-metal in the structures of α and β phases are 3.8 Å and 4.8 Å, respectively, they were closed to the size of an oxygen molecule (3.6 Å). The phases of metal-phthalocyanines were conducted by an interface deposition method. The obtained catalyst powders were characterized by means of X-ray diffraction and X-ray photoelectron spectra analyses. Electrochemical oxygen reduction performances were mainly measured by using a gas diffusion type carbon electrode loaded with a metal-phthalocyanine. It was confirmed that the catalytic activities of cobalt- and copper-centered phthalocyanines were enhanced by the conversion from β to α phases. The effects of the distance between the metals in the crystallographic structures of metal-phthalocyanines should be explained by the adsorbed oxygen states that depend on the distance between the metals. The α phase has the distance which allows to form the bridge configuration of oxygen molecule which requires two adsorption sites and that eventually produces H2O by the direct 4-electron pathway. Analysis with the rotating disk electrode system showed that the α-phased metal-phthalocyanines enhance the 4-electron reduction pathway.
.
中文翻译:

酞菁金属晶体结构对酸性条件下氧还原电催化性能的影响
研究了酸性条件下α和β相之间的金属酞菁(金属:Co,Ni,Cu,Zn)晶体结构对电化学氧还原催化活性的影响。由于在α相和β相结构中中心金属的距离分别为3.8Å和4.8Å,因此它们接近于氧分子的大小(3.6Å)。金属-酞菁的相通过界面沉积法进行。通过X射线衍射和X射线光电子能谱分析对获得的催化剂粉末进行表征。电化学氧还原性能主要通过使用负载有金属酞菁的气体扩散型碳电极来测量。证实了通过从β相到α相的转化提高了以钴和铜为中心的酞菁的催化活性。金属-酞菁晶体结构中金属之间距离的影响应通过取决于金属之间距离的吸附氧态来解释。α相的距离允许形成氧分子的桥结构,该结构需要两个吸附位点并最终产生H2 Ó由直接4-电子通路。用旋转盘电极系统的分析表明,α相金属酞菁增强了4-电子还原途径。

。



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号