当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
Prog. Earth Planet. Sci.
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
Evaluation of satellite precipitation products over Central Vietnam
Progress in Earth and Planetary Science ( IF 3.9 ) Pub Date : 2019-07-31 , DOI: 10.1186/s40645-019-0297-7 Long Trinh-Tuan , Jun Matsumoto , Thanh Ngo-Duc , Masato I. Nodzu , Tomoshige Inoue
Progress in Earth and Planetary Science ( IF 3.9 ) Pub Date : 2019-07-31 , DOI: 10.1186/s40645-019-0297-7 Long Trinh-Tuan , Jun Matsumoto , Thanh Ngo-Duc , Masato I. Nodzu , Tomoshige Inoue
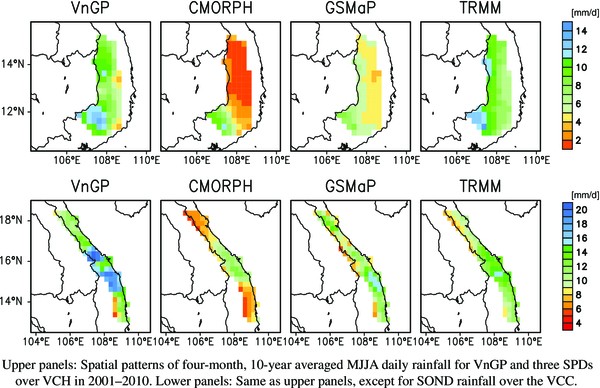
A comprehensive validation of three satellite precipitation datasets (SPDs), including (1) the Climate Prediction Center Morphing algorithm (CMORPH), (2) Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) Reanalysis, and (3) Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TRMM) 3B42, was conducted using the rain gauge-based Vietnam Gridded Precipitation dataset (VnGP) and rain gauge station data for Central Vietnam. The three SPDs were compared and evaluated for two contrasting topographic regions, i.e., the Vietnam Central Highlands (VCH) and the Vietnam Central Coast (VCC), during the rainy seasons from 2001 to 2010 at different spatial (grid and regional) and temporal (daily and monthly) scales. Widespread heavy rainfall (WHR) days caused by the Northeast Winter Monsoon (NM), the Inter-tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), and tropical cyclones (TCs) were also identified, and the accuracies of the SPDs in detecting heavy rainfall during the WHR days were evaluated. TRMM was shown to exhibit advantages over the other SPDs, regardless of the spatial and temporal scales. Although the CMORPH and GSMaP datasets appeared to correlate moderately well with the VnGP dataset and proved able to capture the spatial distribution of rainfall characteristics in the VCC, they significantly underestimated rainfall in the VCH. Regarding the capability to reproduce WHR events, the three SPDs exhibited better performance for TCs and the ITCZ than for the NM. TRMM exhibited the best performance among the three datasets, especially for rainfall thresholds ranging from 25 to 80 mm day−1. The GSMaP and CMORPH biases showed a clear dependence on elevation and zonal wind speed, indicating the need to improve correction methods.
中文翻译:

越南中部卫星降水产品评估
对三个卫星降水数据集(SPD)进行了全面验证,包括(1)气候预测中心变形算法(CMORPH),(2)全球卫星降水图(GSMaP)重新分析以及(3)热带降雨测量任务多卫星降水分析(TRMM)3B42是使用基于雨量计的越南网格化降水数据集(VnGP)和越南中部的雨量计站数据进行的。在2001年至2010年的雨季期间,在不同的空间(网格和区域)和时间(每天和每月)。东北冬季风(NM),热带辐合带(ITCZ),还确定了热带气旋和热带气旋,并评估了在WHR日期间SPD在探测强降雨中的准确性。无论空间和时间尺度如何,TRMM都显示出优于其他SPD的优势。尽管CMORPH和GSMaP数据集似乎与VnGP数据集具有适度的相关性,并被证明能够捕获VCC中降雨特征的空间分布,但它们大大低估了VCH中的降雨。关于重现WHR事件的能力,三个SPD的TC和ITCZ的性能比NM更好。TRMM在三个数据集中表现出最好的性能,尤其是对于25至80毫米/天的降雨阈值而言 并评估了SPD在WHR白天检测到强降雨的准确性。无论空间和时间尺度如何,TRMM都显示出优于其他SPD的优势。尽管CMORPH和GSMaP数据集似乎与VnGP数据集具有适度的相关性,并被证明能够捕获VCC中降雨特征的空间分布,但它们大大低估了VCH中的降雨。关于重现WHR事件的能力,三个SPD的TC和ITCZ的性能比NM更好。TRMM在这三个数据集中表现出最好的性能,尤其是对于25至80毫米/天的降雨阈值而言 并评估了SPD在WHR白天检测到强降雨的准确性。无论空间和时间尺度如何,TRMM都显示出优于其他SPD的优势。尽管CMORPH和GSMaP数据集似乎与VnGP数据集具有适度的相关性,并被证明能够捕获VCC中降雨特征的空间分布,但它们大大低估了VCH中的降雨。关于重现WHR事件的能力,三个SPD的TC和ITCZ的性能比NM更好。TRMM在三个数据集中表现出最好的性能,尤其是对于25至80毫米/天的降雨阈值而言 尽管CMORPH和GSMaP数据集似乎与VnGP数据集具有适度的相关性,并被证明能够捕获VCC中降雨特征的空间分布,但它们大大低估了VCH中的降雨。关于重现WHR事件的能力,三个SPD的TC和ITCZ的性能比NM更好。TRMM在这三个数据集中表现出最好的性能,尤其是对于25至80毫米/天的降雨阈值而言 尽管CMORPH和GSMaP数据集似乎与VnGP数据集具有适度的相关性,并被证明能够捕获VCC中降雨特征的空间分布,但它们大大低估了VCH中的降雨。关于重现WHR事件的能力,三个SPD的TC和ITCZ的性能比NM更好。TRMM在这三个数据集中表现出最好的性能,尤其是对于25至80毫米/天的降雨阈值而言 这三个SPD对TC和ITCZ的性能要优于NM。TRMM在这三个数据集中表现出最好的性能,尤其是对于25至80毫米/天的降雨阈值而言 这三个SPD对TC和ITCZ的性能要优于NM。TRMM在这三个数据集中表现出最好的性能,尤其是对于25至80毫米/天的降雨阈值而言-1。GSMaP和CMORPH偏差显示出对海拔和纬向风速的明显依赖,表明需要改进校正方法。
更新日期:2019-07-31

中文翻译:

越南中部卫星降水产品评估
对三个卫星降水数据集(SPD)进行了全面验证,包括(1)气候预测中心变形算法(CMORPH),(2)全球卫星降水图(GSMaP)重新分析以及(3)热带降雨测量任务多卫星降水分析(TRMM)3B42是使用基于雨量计的越南网格化降水数据集(VnGP)和越南中部的雨量计站数据进行的。在2001年至2010年的雨季期间,在不同的空间(网格和区域)和时间(每天和每月)。东北冬季风(NM),热带辐合带(ITCZ),还确定了热带气旋和热带气旋,并评估了在WHR日期间SPD在探测强降雨中的准确性。无论空间和时间尺度如何,TRMM都显示出优于其他SPD的优势。尽管CMORPH和GSMaP数据集似乎与VnGP数据集具有适度的相关性,并被证明能够捕获VCC中降雨特征的空间分布,但它们大大低估了VCH中的降雨。关于重现WHR事件的能力,三个SPD的TC和ITCZ的性能比NM更好。TRMM在三个数据集中表现出最好的性能,尤其是对于25至80毫米/天的降雨阈值而言 并评估了SPD在WHR白天检测到强降雨的准确性。无论空间和时间尺度如何,TRMM都显示出优于其他SPD的优势。尽管CMORPH和GSMaP数据集似乎与VnGP数据集具有适度的相关性,并被证明能够捕获VCC中降雨特征的空间分布,但它们大大低估了VCH中的降雨。关于重现WHR事件的能力,三个SPD的TC和ITCZ的性能比NM更好。TRMM在这三个数据集中表现出最好的性能,尤其是对于25至80毫米/天的降雨阈值而言 并评估了SPD在WHR白天检测到强降雨的准确性。无论空间和时间尺度如何,TRMM都显示出优于其他SPD的优势。尽管CMORPH和GSMaP数据集似乎与VnGP数据集具有适度的相关性,并被证明能够捕获VCC中降雨特征的空间分布,但它们大大低估了VCH中的降雨。关于重现WHR事件的能力,三个SPD的TC和ITCZ的性能比NM更好。TRMM在三个数据集中表现出最好的性能,尤其是对于25至80毫米/天的降雨阈值而言 尽管CMORPH和GSMaP数据集似乎与VnGP数据集具有适度的相关性,并被证明能够捕获VCC中降雨特征的空间分布,但它们大大低估了VCH中的降雨。关于重现WHR事件的能力,三个SPD的TC和ITCZ的性能比NM更好。TRMM在这三个数据集中表现出最好的性能,尤其是对于25至80毫米/天的降雨阈值而言 尽管CMORPH和GSMaP数据集似乎与VnGP数据集具有适度的相关性,并被证明能够捕获VCC中降雨特征的空间分布,但它们大大低估了VCH中的降雨。关于重现WHR事件的能力,三个SPD的TC和ITCZ的性能比NM更好。TRMM在这三个数据集中表现出最好的性能,尤其是对于25至80毫米/天的降雨阈值而言 这三个SPD对TC和ITCZ的性能要优于NM。TRMM在这三个数据集中表现出最好的性能,尤其是对于25至80毫米/天的降雨阈值而言 这三个SPD对TC和ITCZ的性能要优于NM。TRMM在这三个数据集中表现出最好的性能,尤其是对于25至80毫米/天的降雨阈值而言-1。GSMaP和CMORPH偏差显示出对海拔和纬向风速的明显依赖,表明需要改进校正方法。



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号