当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
Eur. Phys. J. E
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
Relating the physical properties of aqueous solutions of ionic liquids with their chemical structures.
The European Physical Journal E ( IF 1.8 ) Pub Date : 2020-08-21 , DOI: 10.1140/epje/i2020-11974-7 Shuverthi De Sarkar 1 , Saheli Mitra 1 , Sajal K Ghosh 1
中文翻译:

将离子液体水溶液的物理性质与其化学结构相关联。

The European Physical Journal E ( IF 1.8 ) Pub Date : 2020-08-21 , DOI: 10.1140/epje/i2020-11974-7 Shuverthi De Sarkar 1 , Saheli Mitra 1 , Sajal K Ghosh 1
Affiliation

|
Abstract.
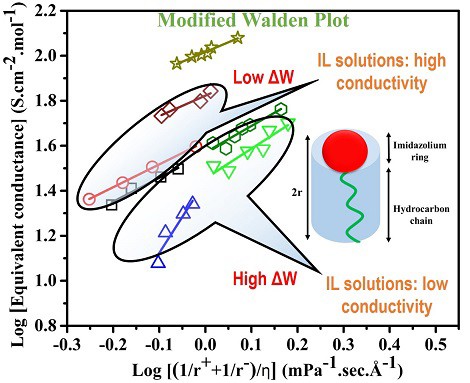
The physical properties of an aqueous solution of a macromolecule primarily depend on its chemical structure and the mesoscopic aggregates formed by many of such molecules. Ionic liquids (ILs) are the macromolecules that have caught significant research interests for their enormous industrial and biomedical applications. In the present paper, the physical properties, such as density, viscosity, ionic conductivity of aqueous solutions of various ILs, have been investigated. These properties are found to systematically depend on the shape and size of the anion and the cation along with the solution concentration. The ionic conductivity and viscosity behavior of the solutions do not strictly follow the Walden rule that relates the conductivity to the viscosity of the solution. However, the modified Walden rule could explain the behavior. A simple calculation based on the geometry of a given molecule could shed the light on the observed results.Graphical abstract

中文翻译:

将离子液体水溶液的物理性质与其化学结构相关联。
摘要。
大分子水溶液的物理性质主要取决于其化学结构和许多此类分子形成的介观聚集体。离子液体(ILs)是大分子,因其巨大的工业和生物医学应用而引起了广泛的研究兴趣。在本文中,已经研究了各种IL的水溶液的物理性质,例如密度,粘度,离子电导率。发现这些性质系统地取决于阴离子和阳离子的形状和大小以及溶液浓度。溶液的离子电导率和粘度行为未严格遵循将电导率与溶液粘度相关的Walden规则。但是,修改后的Walden规则可以解释该行为。图形概要



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号