当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
Bioresour. Bioprocess.
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
Structure-guided engineering of a Thermobifida fusca cutinase for enhanced hydrolysis on natural polyester substrate
Bioresources and Bioprocessing ( IF 4.6 ) Pub Date : 2020-07-09 , DOI: 10.1186/s40643-020-00324-8 Qilei Dong , Shuguang Yuan , Lian Wu , Lingqia Su , Qiaoling Zhao , Jing Wu , Weixue Huang , Jiahai Zhou
Bioresources and Bioprocessing ( IF 4.6 ) Pub Date : 2020-07-09 , DOI: 10.1186/s40643-020-00324-8 Qilei Dong , Shuguang Yuan , Lian Wu , Lingqia Su , Qiaoling Zhao , Jing Wu , Weixue Huang , Jiahai Zhou
Cutinases could degrade insoluble polyester, including natural cutin and synthetic plastic. However, their turnover efficiency for polyester remains too low for industrial application. Herein, we report the 1.54-Å resolution X-ray crystal structure of a cutinase from Thermobifida fusca and modeling structure in complex with a cutin mimic oligo-polyester C24H42O8. These efforts subsequently guided our design of cutinase variants with less bulky residues in the vicinity of the substrate binding site. The L90A and I213A variants exhibit increased hydrolysis activity (5- and 2.4-fold, respectively) toward cutin and also showed enhanced cotton scouring efficiency compared with the wild-type enzyme.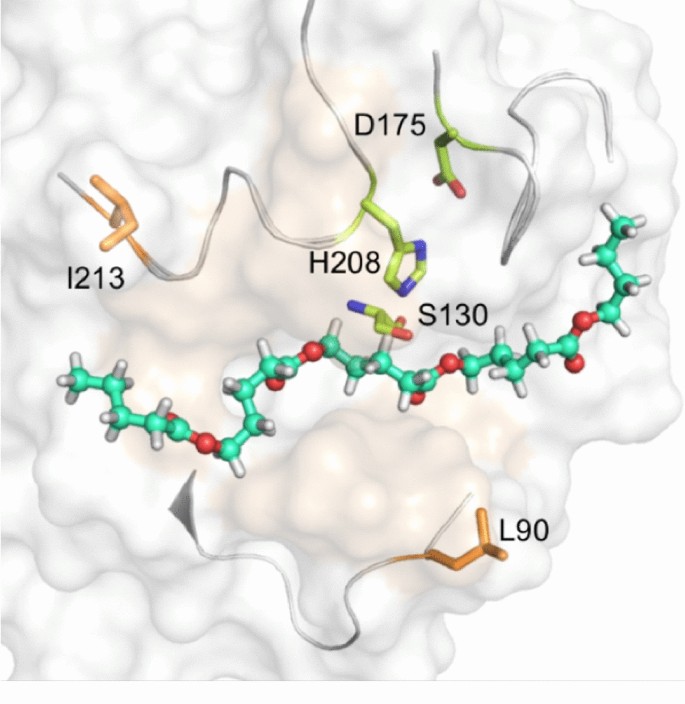
中文翻译:

Thermobifida fusca角质酶的结构指导工程,可增强天然聚酯底物上的水解
角质酶可以降解不溶性聚酯,包括天然角质和合成塑料。但是,它们对于聚酯的周转效率对于工业应用而言仍然太低。在此,我们报道了来自Thermobifida fusca的角质酶的1.54Å分辨率X射线晶体结构和与角质模拟低聚聚酯C 24 H 42 O 8配合形成的模型结构。这些努力随后指导了我们设计在底物结合位点附近残基较少的角质酶变体。与野生型酶相比,L90A和I213A变体对角质表现出增强的水解活性(分别为5倍和2.4倍),并且还显示出更高的棉花精练效率。
更新日期:2020-07-09

中文翻译:

Thermobifida fusca角质酶的结构指导工程,可增强天然聚酯底物上的水解
角质酶可以降解不溶性聚酯,包括天然角质和合成塑料。但是,它们对于聚酯的周转效率对于工业应用而言仍然太低。在此,我们报道了来自Thermobifida fusca的角质酶的1.54Å分辨率X射线晶体结构和与角质模拟低聚聚酯C 24 H 42 O 8配合形成的模型结构。这些努力随后指导了我们设计在底物结合位点附近残基较少的角质酶变体。与野生型酶相比,L90A和I213A变体对角质表现出增强的水解活性(分别为5倍和2.4倍),并且还显示出更高的棉花精练效率。



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号