当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
Levels and sources of PBDEs and PCBs in human nails from e-waste, urban, and rural areas in South China.
Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts ( IF 5.5 ) Pub Date : 2020-07-03 , DOI: 10.1039/d0em00221f Hua-Jun Meng 1 , Bin Tang , Jing Zheng , She-Xia Ma , Feng-Shan Cai , Xi Zhuang , Jun-Li Wang , Yun-Jiang Yu
Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts ( IF 5.5 ) Pub Date : 2020-07-03 , DOI: 10.1039/d0em00221f Hua-Jun Meng 1 , Bin Tang , Jing Zheng , She-Xia Ma , Feng-Shan Cai , Xi Zhuang , Jun-Li Wang , Yun-Jiang Yu
Affiliation

|
Human nails have been increasingly used as a biomarker for human exposure to persistent organic pollutants (POPs). In the present study, the fingernails of e-waste-dismantling workers from Longtang town, Qingyuan city, rural residents from Shijiao town, Qingyuan city, and urban residents from Guangzhou city, respectively, were collected from South China to monitor the human burdens of polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDEs) and polychlorinated biphenyl (PCBs). The median concentrations of 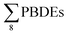 in the nails of the e-waste-dismantling workers, and urban and rural residents were 412, 129, and 82.1 ng g−1, respectively, and the median concentrations of
in the nails of the e-waste-dismantling workers, and urban and rural residents were 412, 129, and 82.1 ng g−1, respectively, and the median concentrations of 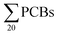 were 108, 8.4, and 22.1 ng g−1, respectively. The levels of PCBs and PBDEs in the nails of e-waste-dismantling workers were significantly higher as compared to those for urban and rural residents (p < 0.05), implying the continuous and greater exposure to these chemicals in the e-waste recycling areas. BDE 209 (92–98%) was the major congener of PBDEs and CB 52 (26–51%) was the main congener of PCB in nail samples. However, no significant gender difference was observed for PBDE and PCB levels in nails from all three investigated areas, and no significant correlation was found between their levels and the age of the participants. The enantiomer fractions (EFs) of CBs 95 and 132 indicated that the external sources (e.g. dust and/or air) were the primary sources for CBs 95 and 132 in human nails from the e-waste area, while the contribution from the internal sources (e.g. serum) could be in a small percentage. The results of this study indicate that human nails can be used as a proper indicator of human exposure to PCBs and PBDEs, and further studies are needed by a comprehensive investigation of the relationships between the PCB and PBDE levels in the nails and serum and/or other internal tissues.
were 108, 8.4, and 22.1 ng g−1, respectively. The levels of PCBs and PBDEs in the nails of e-waste-dismantling workers were significantly higher as compared to those for urban and rural residents (p < 0.05), implying the continuous and greater exposure to these chemicals in the e-waste recycling areas. BDE 209 (92–98%) was the major congener of PBDEs and CB 52 (26–51%) was the main congener of PCB in nail samples. However, no significant gender difference was observed for PBDE and PCB levels in nails from all three investigated areas, and no significant correlation was found between their levels and the age of the participants. The enantiomer fractions (EFs) of CBs 95 and 132 indicated that the external sources (e.g. dust and/or air) were the primary sources for CBs 95 and 132 in human nails from the e-waste area, while the contribution from the internal sources (e.g. serum) could be in a small percentage. The results of this study indicate that human nails can be used as a proper indicator of human exposure to PCBs and PBDEs, and further studies are needed by a comprehensive investigation of the relationships between the PCB and PBDE levels in the nails and serum and/or other internal tissues.
中文翻译:

华南,城市和农村地区电子垃圾中人指甲中多溴二苯醚和多氯联苯的含量和来源。
人指甲已越来越多地用作人类暴露于持久性有机污染物(POPs)的生物标记。在本研究中,分别从华南地区收集了清远市龙塘镇,清远市石角镇农村居民和广州市城市居民的电子垃圾处理工人的指甲,以监测其人类负担。多溴联苯醚(PBDEs)和多氯联苯(PCBs)。的平均含量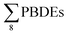 在电子垃圾拆解工人,城市和农村居民的指甲是412,129,和82.1纳克g ^ -1分别,和的平均含量
在电子垃圾拆解工人,城市和农村居民的指甲是412,129,和82.1纳克g ^ -1分别,和的平均含量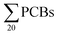 分别为108,8.4和22.1纳克摹- 1个, 分别。与城市和农村居民相比,电子垃圾处理工人指甲中的多氯联苯和多溴二苯醚的含量显着更高(p <0.05),这意味着电子垃圾回收区中这些化学物质的暴露量不断增加。 。BDE 209(92–98%)是多溴二苯醚的主要同源物,而CB 52(26–51%)是指甲样品中PCB的主要同源物。然而,在所有三个调查区域中,指甲中的PBDE和PCB含量均未观察到明显的性别差异,并且其含量与受试者年龄之间也未发现显着相关性。CB 95和132的对映异构体分数(EFs)表示外部来源(例如灰尘和/或空气)是来自电子废物区域的人类指甲中CB 95和132的主要来源,而内部来源(例如血清)的贡献可能很小。这项研究的结果表明,人类指甲可以用作人体接触多氯联苯和多溴二苯醚的适当指标,并且需要全面研究指甲中多氯联苯和多溴二苯醚的含量与血清和/或血清之间的关系,以进行进一步的研究。其他内部组织。
分别为108,8.4和22.1纳克摹- 1个, 分别。与城市和农村居民相比,电子垃圾处理工人指甲中的多氯联苯和多溴二苯醚的含量显着更高(p <0.05),这意味着电子垃圾回收区中这些化学物质的暴露量不断增加。 。BDE 209(92–98%)是多溴二苯醚的主要同源物,而CB 52(26–51%)是指甲样品中PCB的主要同源物。然而,在所有三个调查区域中,指甲中的PBDE和PCB含量均未观察到明显的性别差异,并且其含量与受试者年龄之间也未发现显着相关性。CB 95和132的对映异构体分数(EFs)表示外部来源(例如灰尘和/或空气)是来自电子废物区域的人类指甲中CB 95和132的主要来源,而内部来源(例如血清)的贡献可能很小。这项研究的结果表明,人类指甲可以用作人体接触多氯联苯和多溴二苯醚的适当指标,并且需要全面研究指甲中多氯联苯和多溴二苯醚的含量与血清和/或血清之间的关系,以进行进一步的研究。其他内部组织。
更新日期:2020-08-19
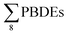 in the nails of the e-waste-dismantling workers, and urban and rural residents were 412, 129, and 82.1 ng g−1, respectively, and the median concentrations of
in the nails of the e-waste-dismantling workers, and urban and rural residents were 412, 129, and 82.1 ng g−1, respectively, and the median concentrations of 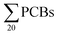 were 108, 8.4, and 22.1 ng g−1, respectively. The levels of PCBs and PBDEs in the nails of e-waste-dismantling workers were significantly higher as compared to those for urban and rural residents (p < 0.05), implying the continuous and greater exposure to these chemicals in the e-waste recycling areas. BDE 209 (92–98%) was the major congener of PBDEs and CB 52 (26–51%) was the main congener of PCB in nail samples. However, no significant gender difference was observed for PBDE and PCB levels in nails from all three investigated areas, and no significant correlation was found between their levels and the age of the participants. The enantiomer fractions (EFs) of CBs 95 and 132 indicated that the external sources (e.g. dust and/or air) were the primary sources for CBs 95 and 132 in human nails from the e-waste area, while the contribution from the internal sources (e.g. serum) could be in a small percentage. The results of this study indicate that human nails can be used as a proper indicator of human exposure to PCBs and PBDEs, and further studies are needed by a comprehensive investigation of the relationships between the PCB and PBDE levels in the nails and serum and/or other internal tissues.
were 108, 8.4, and 22.1 ng g−1, respectively. The levels of PCBs and PBDEs in the nails of e-waste-dismantling workers were significantly higher as compared to those for urban and rural residents (p < 0.05), implying the continuous and greater exposure to these chemicals in the e-waste recycling areas. BDE 209 (92–98%) was the major congener of PBDEs and CB 52 (26–51%) was the main congener of PCB in nail samples. However, no significant gender difference was observed for PBDE and PCB levels in nails from all three investigated areas, and no significant correlation was found between their levels and the age of the participants. The enantiomer fractions (EFs) of CBs 95 and 132 indicated that the external sources (e.g. dust and/or air) were the primary sources for CBs 95 and 132 in human nails from the e-waste area, while the contribution from the internal sources (e.g. serum) could be in a small percentage. The results of this study indicate that human nails can be used as a proper indicator of human exposure to PCBs and PBDEs, and further studies are needed by a comprehensive investigation of the relationships between the PCB and PBDE levels in the nails and serum and/or other internal tissues.
中文翻译:

华南,城市和农村地区电子垃圾中人指甲中多溴二苯醚和多氯联苯的含量和来源。
人指甲已越来越多地用作人类暴露于持久性有机污染物(POPs)的生物标记。在本研究中,分别从华南地区收集了清远市龙塘镇,清远市石角镇农村居民和广州市城市居民的电子垃圾处理工人的指甲,以监测其人类负担。多溴联苯醚(PBDEs)和多氯联苯(PCBs)。的平均含量
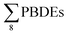 在电子垃圾拆解工人,城市和农村居民的指甲是412,129,和82.1纳克g ^ -1分别,和的平均含量
在电子垃圾拆解工人,城市和农村居民的指甲是412,129,和82.1纳克g ^ -1分别,和的平均含量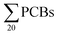 分别为108,8.4和22.1纳克摹- 1个, 分别。与城市和农村居民相比,电子垃圾处理工人指甲中的多氯联苯和多溴二苯醚的含量显着更高(p <0.05),这意味着电子垃圾回收区中这些化学物质的暴露量不断增加。 。BDE 209(92–98%)是多溴二苯醚的主要同源物,而CB 52(26–51%)是指甲样品中PCB的主要同源物。然而,在所有三个调查区域中,指甲中的PBDE和PCB含量均未观察到明显的性别差异,并且其含量与受试者年龄之间也未发现显着相关性。CB 95和132的对映异构体分数(EFs)表示外部来源(例如灰尘和/或空气)是来自电子废物区域的人类指甲中CB 95和132的主要来源,而内部来源(例如血清)的贡献可能很小。这项研究的结果表明,人类指甲可以用作人体接触多氯联苯和多溴二苯醚的适当指标,并且需要全面研究指甲中多氯联苯和多溴二苯醚的含量与血清和/或血清之间的关系,以进行进一步的研究。其他内部组织。
分别为108,8.4和22.1纳克摹- 1个, 分别。与城市和农村居民相比,电子垃圾处理工人指甲中的多氯联苯和多溴二苯醚的含量显着更高(p <0.05),这意味着电子垃圾回收区中这些化学物质的暴露量不断增加。 。BDE 209(92–98%)是多溴二苯醚的主要同源物,而CB 52(26–51%)是指甲样品中PCB的主要同源物。然而,在所有三个调查区域中,指甲中的PBDE和PCB含量均未观察到明显的性别差异,并且其含量与受试者年龄之间也未发现显着相关性。CB 95和132的对映异构体分数(EFs)表示外部来源(例如灰尘和/或空气)是来自电子废物区域的人类指甲中CB 95和132的主要来源,而内部来源(例如血清)的贡献可能很小。这项研究的结果表明,人类指甲可以用作人体接触多氯联苯和多溴二苯醚的适当指标,并且需要全面研究指甲中多氯联苯和多溴二苯醚的含量与血清和/或血清之间的关系,以进行进一步的研究。其他内部组织。



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号