当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol.
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
Changes of Serum IgG Dimer Levels after Treatment with IVIg in Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology ( IF 6.2 ) Pub Date : 2019-09-12 , DOI: 10.1007/s11481-019-09871-0 Martin K R Svačina 1 , Philip Röth 1 , Ilja Bobylev 1 , Alina Sprenger 1 , Gang Zhang 2 , Kazim A Sheikh 2 , Helmar C Lehmann 1
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology ( IF 6.2 ) Pub Date : 2019-09-12 , DOI: 10.1007/s11481-019-09871-0 Martin K R Svačina 1 , Philip Röth 1 , Ilja Bobylev 1 , Alina Sprenger 1 , Gang Zhang 2 , Kazim A Sheikh 2 , Helmar C Lehmann 1
Affiliation
Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg) are standard treatment for Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). Their exact mechanisms of action are versatile and not fully understood. One possible mechanism is neutralization of circulating autoantibodies via binding to anti- idiotypic antibodies forming idiotype-anti-idiotype dimeric IgG immune complexes. To examine the role of immune complex formation as mechanism of action for IVIg in GBS, 34 C57Bl/6 mice were either treated with anti-ganglioside antibodies and IVIg or IVIg and PBS alone, whereas eight additional mice were treated either with anti-ganglioside autoantibodies and IVIg or anti-ganglioside autoantibodies alone. Subsequently IgG dimer formation was assessed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and enzyme- linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). In addition, IgG dimer formation was measured in sera of eight GBS patients who were treated with IVIg. In mice, a significant increase of dimeric IgG after administration of anti-ganglioside antibodies and IVIg could be observed. Re-monomerized IgG dimers showed immunoreactivity against gangliosides and serum immunoreactivity was significantly reduced after IVIg infusion. Likewise also in GBS patients, IgG dimer formation could be detected after IVIg treatment. Our data indicate that dimeric IgG immune complexes contain anti-idiotypic antibodies and provide proof of concept that IVIg treatment in GBS results in measurable amounts of IgG dimers. Larger patient cohorts are needed to evaluate serum IgG dimer increase as a possible marker for treatment response in GBS.
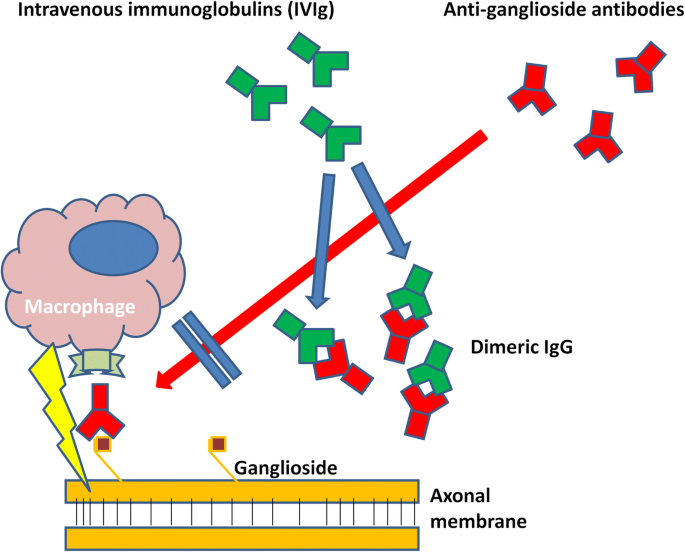 Mechanism of action: Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg) and anti-ganglioside antibodies form dimeric IgG immune complexes, preventing axonal damage in Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
Mechanism of action: Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg) and anti-ganglioside antibodies form dimeric IgG immune complexes, preventing axonal damage in Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
中文翻译:

格林-巴利综合征IVIg治疗后血清IgG二聚体水平的变化。
静脉注射免疫球蛋白(IVIg)是格林-巴利综合征(GBS)的标准治疗方法。它们的确切作用机制是多用途的,尚未完全了解。一种可能的机制是通过与形成独特型-抗独特型二聚体IgG免疫复合物的抗独特型抗体结合而中和循环的自身抗体。为了检查免疫复合物形成作为GBS中IVIg作用机理的作用,对34只C57Bl / 6小鼠分别用抗神经节苷脂抗体和IVIg或IVIg和PBS治疗,而另外八只小鼠则用抗神经节苷脂自身抗体治疗以及IVIg或抗神经节苷脂自身抗体。随后,通过高效液相色谱(HPLC)和酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)评估IgG二聚体的形成。此外,在八名接受IVIg治疗的GBS患者的血清中测量了IgG二聚体形成。在小鼠中,可以观察到在施用抗神经节苷脂抗体和IVIg后二聚体IgG显着增加。重新单体化的IgG二聚体显示出对神经节苷脂的免疫反应性,输注IVIg后血清免疫反应性显着降低。同样在GBS患者中,IVIg治疗后也可以检测到IgG二聚体形成。我们的数据表明,二聚体IgG免疫复合物包含抗独特型抗体,并提供了概念证明,即GBS中的IVIg处理会导致可测量量的IgG二聚体。需要更大的患者队列来评估血清IgG二聚体增加,作为GBS中治疗反应的可能标志。施用抗神经节苷脂抗体和IVIg后,二聚体IgG显着增加。重新单体化的IgG二聚体显示出对神经节苷脂的免疫反应性,输注IVIg后血清免疫反应性显着降低。同样在GBS患者中,IVIg治疗后也可以检测到IgG二聚体形成。我们的数据表明,二聚体IgG免疫复合物包含抗独特型抗体,并提供了概念证明,即GBS中的IVIg处理会导致可测量量的IgG二聚体。需要更大的患者队列来评估血清IgG二聚体增加,作为GBS中治疗反应的可能标志。施用抗神经节苷脂抗体和IVIg后,二聚体IgG显着增加。重新单体化的IgG二聚体显示出对神经节苷脂的免疫反应性,输注IVIg后血清免疫反应性显着降低。同样在GBS患者中,IVIg治疗后也可以检测到IgG二聚体形成。我们的数据表明,二聚体IgG免疫复合物包含抗独特型抗体,并提供了概念证明,即GBS中的IVIg处理会导致可测量量的IgG二聚体。需要更大的患者队列来评估血清IgG二聚体增加,作为GBS中治疗反应的可能标志。重新单体化的IgG二聚体显示出对神经节苷脂的免疫反应性,输注IVIg后血清免疫反应性显着降低。同样在GBS患者中,IVIg治疗后也可以检测到IgG二聚体形成。我们的数据表明,二聚体IgG免疫复合物包含抗独特型抗体,并提供了概念证明,即GBS中的IVIg处理会导致可测量量的IgG二聚体。需要更大的患者队列来评估血清IgG二聚体增加,作为GBS中治疗反应的可能标志。重新单体化的IgG二聚体显示出对神经节苷脂的免疫反应性,输注IVIg后血清免疫反应性显着降低。同样在GBS患者中,IVIg治疗后也可以检测到IgG二聚体形成。我们的数据表明,二聚体IgG免疫复合物包含抗独特型抗体,并提供了概念证明,即GBS中的IVIg处理会导致可测量量的IgG二聚体。需要更大的患者队列来评估血清IgG二聚体增加,作为GBS中治疗反应的可能标志。 作用机制:静脉免疫球蛋白(IVIg)和抗神经节苷脂抗体形成二聚体IgG免疫复合物,从而防止了格林-巴利综合征的轴突损伤。
作用机制:静脉免疫球蛋白(IVIg)和抗神经节苷脂抗体形成二聚体IgG免疫复合物,从而防止了格林-巴利综合征的轴突损伤。
更新日期:2019-09-12
 Mechanism of action: Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg) and anti-ganglioside antibodies form dimeric IgG immune complexes, preventing axonal damage in Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
Mechanism of action: Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg) and anti-ganglioside antibodies form dimeric IgG immune complexes, preventing axonal damage in Guillain-Barré Syndrome.中文翻译:

格林-巴利综合征IVIg治疗后血清IgG二聚体水平的变化。
静脉注射免疫球蛋白(IVIg)是格林-巴利综合征(GBS)的标准治疗方法。它们的确切作用机制是多用途的,尚未完全了解。一种可能的机制是通过与形成独特型-抗独特型二聚体IgG免疫复合物的抗独特型抗体结合而中和循环的自身抗体。为了检查免疫复合物形成作为GBS中IVIg作用机理的作用,对34只C57Bl / 6小鼠分别用抗神经节苷脂抗体和IVIg或IVIg和PBS治疗,而另外八只小鼠则用抗神经节苷脂自身抗体治疗以及IVIg或抗神经节苷脂自身抗体。随后,通过高效液相色谱(HPLC)和酶联免疫吸附测定(ELISA)评估IgG二聚体的形成。此外,在八名接受IVIg治疗的GBS患者的血清中测量了IgG二聚体形成。在小鼠中,可以观察到在施用抗神经节苷脂抗体和IVIg后二聚体IgG显着增加。重新单体化的IgG二聚体显示出对神经节苷脂的免疫反应性,输注IVIg后血清免疫反应性显着降低。同样在GBS患者中,IVIg治疗后也可以检测到IgG二聚体形成。我们的数据表明,二聚体IgG免疫复合物包含抗独特型抗体,并提供了概念证明,即GBS中的IVIg处理会导致可测量量的IgG二聚体。需要更大的患者队列来评估血清IgG二聚体增加,作为GBS中治疗反应的可能标志。施用抗神经节苷脂抗体和IVIg后,二聚体IgG显着增加。重新单体化的IgG二聚体显示出对神经节苷脂的免疫反应性,输注IVIg后血清免疫反应性显着降低。同样在GBS患者中,IVIg治疗后也可以检测到IgG二聚体形成。我们的数据表明,二聚体IgG免疫复合物包含抗独特型抗体,并提供了概念证明,即GBS中的IVIg处理会导致可测量量的IgG二聚体。需要更大的患者队列来评估血清IgG二聚体增加,作为GBS中治疗反应的可能标志。施用抗神经节苷脂抗体和IVIg后,二聚体IgG显着增加。重新单体化的IgG二聚体显示出对神经节苷脂的免疫反应性,输注IVIg后血清免疫反应性显着降低。同样在GBS患者中,IVIg治疗后也可以检测到IgG二聚体形成。我们的数据表明,二聚体IgG免疫复合物包含抗独特型抗体,并提供了概念证明,即GBS中的IVIg处理会导致可测量量的IgG二聚体。需要更大的患者队列来评估血清IgG二聚体增加,作为GBS中治疗反应的可能标志。重新单体化的IgG二聚体显示出对神经节苷脂的免疫反应性,输注IVIg后血清免疫反应性显着降低。同样在GBS患者中,IVIg治疗后也可以检测到IgG二聚体形成。我们的数据表明,二聚体IgG免疫复合物包含抗独特型抗体,并提供了概念证明,即GBS中的IVIg处理会导致可测量量的IgG二聚体。需要更大的患者队列来评估血清IgG二聚体增加,作为GBS中治疗反应的可能标志。重新单体化的IgG二聚体显示出对神经节苷脂的免疫反应性,输注IVIg后血清免疫反应性显着降低。同样在GBS患者中,IVIg治疗后也可以检测到IgG二聚体形成。我们的数据表明,二聚体IgG免疫复合物包含抗独特型抗体,并提供了概念证明,即GBS中的IVIg处理会导致可测量量的IgG二聚体。需要更大的患者队列来评估血清IgG二聚体增加,作为GBS中治疗反应的可能标志。
 作用机制:静脉免疫球蛋白(IVIg)和抗神经节苷脂抗体形成二聚体IgG免疫复合物,从而防止了格林-巴利综合征的轴突损伤。
作用机制:静脉免疫球蛋白(IVIg)和抗神经节苷脂抗体形成二聚体IgG免疫复合物,从而防止了格林-巴利综合征的轴突损伤。

























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号