Abstract
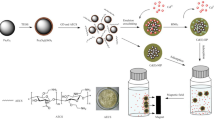
The authors report on the preparation of sol-gel coated magnetized carbon nanotubes whose surface were imprinted with Cd2+ ions and the application of these materials on selective preconcentration of Cd2+ ions in different water samples. Fe3O4 particles and tetraethyl orthosilicate were used as a magnetic ingredient and as a surface modifier for the carbon nanotubes, respectively. The Cd2+-imprinted polymer was prepared by grafting copolymerization of Cd2+ ions as template, methacryloylsulfamethizole and 2-vinylpyridine as polymerizable ligands, methacrylic acid as functional monomer, and ethyleneglycoldimethacrylate as crosslinker. The resulting magnetic nanoparticles were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectrometry, the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller method, and by scanning electron microscopy. Isothermal absorption, absorption kinetics and selectivity were studied in detail. The experimental conditions were optimized. Figures of merit include (a) a maximum adsorption capacity of 81 mg·g−1; (b) relative selectivity coefficients of 2.41, 2.36, 1.41, 1.66, and 1.70 for Cd2+/Ni2+, Cd2+/Co2+, Cd2+/Zn2+, Cd2+/Cu2+, and Cd2+/Pb2+, respectively; (c) a detection limit of 0.29 ng·mL−1, (d) an enrichment factor of 55.5; (e) an intra-day precisions of 1.13%; and (f) an inter-day precision of 1.39%. The method was successfully applied to the determination of cadmium in spiked samples including feed water of an ammonia production unit, tap water, industrial waste water from a petrochemical plant, river water from the Garrahi River, bay water from Khor Musa, and marsh water from the Shadegan wetland.

Trace amounts of Cd2+ ions in some environmental and industrial water samples were separated and preconcentrated by a new surface ion-imprinted polymer, chemically grafted on the surface of the magnetized carbon nanotubes, before determination using flame atomic absorption spectrometer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gawin M, Konefal J, Trzewik B, Walas S, Tobiasz A, Mrowiec H, Witek E (2010) Preparation of a new Cd (II)-imprinted polymer and its application to determination of cadmium (II) via flow-injection-flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 80:1305
Shaikh ZA, Northup JB, Vestergaard P (1999) Dependence of cadmium-metallothionein nephrotoxicity on glutathione. J Toxic Environ Health A 57:211
Crosby NT (1977) Determination of metals in foods, a review. Analyst 102:225
Branger C, Meouche W, Margaillan A (2013) Recent advances on ion-imprinted polymers. React Funct Polym 73:859
Aziz-Zanjani MO, Mehdinia A (2014) A review on procedures for the preparation of coatings for solid phase microextraction. Microchim Acta 181:1169
Masqué N, Marcé RM, Borrull F, Cormack PA, Sherrington DC (2000) Synthesis and evaluation of a molecularly imprinted polymer for selective on-line solid-phase extraction of 4-nitrophenol from environmental water. Anal Chem 72:4122
Önnby L, Pakade V, Mattiasson B, Kirsebom H (2012) Polymer composite adsorbents using particles of molecularly imprinted polymers or aluminium oxide nanoparticles for treatment of arsenic contaminated waters. Water Res 46:4111
Sims MB (2014) RAFT polymerization of sulfonamide-containing methacrylamides. The University of Southern Mississippi, Hattiesburg
Gao L, Chen L, Li X (2015) Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on carbon nanotubes for extraction of carbamates. Microchim Acta 182:781
Shamsipur M, Fasihi J, Ashtari K (2007) Grafting of ion-imprinted polymers on the surface of silica gel particles through covalently surface-bound initiators: a selective sorbent for uranyl ion. Anal Chem 79:7116
Singh DK, Mishra S (2010) Synthesis and characterization of hg (II)-ion-imprinted polymer: kinetic and isotherm studies. Desalination 257:177
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) Kinetic models for the sorption of dye from aqueous solution by wood. Process Saf Environ Prot 76:183
Xie F, Lin X, Wu X, Xie Z (2008) Solid phase extraction of lead (II), copper (II), cadmium (II) and nickel (II) using gallic acid-modified silica gel prior to determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 74:836
Hall KR, Eagleton LC, Acrivos A, Vermeulen T (1966) Pore-and solid-diffusion kinetics in fixed-bed adsorption under constant-pattern conditions. Ind Eng Chem Fundam 5:212
Greenberg AE, Connors JJ, Jenkins D, Franson MAH (1981) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater: selected analytical methods approved and cited by the United States Environmental Protection Agency. 15th American Public Health Association, Washington D.C.
Bae SY, Southard GL, Murray GM (1999) Molecularly imprinted ion exchange resin for purification, preconcentration and determination of UO2 2+ by spectrophotometry and plasma spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 397:173
Molochnikov LS, Kovalyova EG, Zagorodni AA, Muhammed M, Sultanov YM, Efendiev AA (2003) Coordination of cu (II) and Ni (II) in polymers imprinted so as to optimize amine chelate formation. Polymer 44:4805
Segatelli MG, Santos VS, Presotto ABT, Yoshida IVP, Tarley CRT (2010) Cadmium ion-selective sorbent preconcentration method using ion imprinted poly (ethylene glycol dimethacrylate-co-vinylimidazole). React Funct Polym 70:325
Wang J, Liu F (2014) Synthesis and application of ion-imprinted interpenetrating polymer network gel for selective solid phase extraction of Cd2+. Chem Eng J 242:117
Zhai Y, Liu Y, Chang X, Chen S, Huang X (2007) Selective solid-phase extraction of trace cadmium (II) with an ionic imprinted polymer prepared from a dual-ligand monomer. Anal Chim Acta 593:123
Fang GZ, Tan J, Yan XP (2005) An ion-imprinted functionalized silica gel sorbent prepared by a surface imprinting technique combined with a sol−gel process for selective solid-phase extraction of cadmium (II). Anal Chem 77:1734
Zhang N, Hu B (2012) Cadmium (II) imprinted 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane coated stir bar for selective extraction of trace cadmium from environmental water samples followed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry detection. Anal Chim Acta 723:54
Aboufazeli F, Zhad HRLZ, Sadeghi O, Karimi M, Najafi E (2014) Novel cd (II) ion imprinted polymer coated on multiwall carbon nanotubes as a highly selective sorbent for cadmium determination in food samples. J AOAC Int 97:173
Behbahani M, Barati M, Bojdi MK, Pourali AR, Bagheri A, Tapeh NAG (2013) A nanosized cadmium (II)-imprinted polymer for use in selective trace determination of cadmium in complex matrices. Microchim Acta 180:1117
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank ShahidChamran University of Ahvaz Research Council for financial support of this work (Grant 1395).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM1
(DOCX 239 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zargar, B., Khazaeifar, A. Synthesis of an ion-imprinted sorbent by surface imprinting of magnetized carbon nanotubes for determination of trace amounts of cadmium ions. Microchim Acta 184, 4521–4529 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2489-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2489-4