Tensor network decompositions for absolutely maximally entangled states
1MTA-ELTE ``Momentum'' Integrable Quantum Dynamics Research Group, Department of Theoretical Physics, ELTE Eötvös Loránd University, Hungary
2School of Mathematics, Monash University, Australia
| Published: | 2024-05-08, volume 8, page 1339 |
| Eprint: | arXiv:2308.07042v3 |
| Doi: | https://doi.org/10.22331/q-2024-05-08-1339 |
| Citation: | Quantum 8, 1339 (2024). |
Find this paper interesting or want to discuss? Scite or leave a comment on SciRate.
Abstract
Absolutely maximally entangled (AME) states of $k$ qudits (also known as perfect tensors) are quantum states that have maximal entanglement for all possible bipartitions of the sites/parties. We consider the problem of whether such states can be decomposed into a tensor network with a small number of tensors, such that all physical and all auxiliary spaces have the same dimension $D$. We find that certain AME states with $k=6$ can be decomposed into a network with only three 4-leg tensors; we provide concrete solutions for local dimension $D=5$ and higher. Our result implies that certain AME states with six parties can be created with only three two-site unitaries from a product state of three Bell pairs, or equivalently, with six two-site unitaries acting on a product state on six qudits. We also consider the problem for $k=8$, where we find similar tensor network decompositions with six 4-leg tensors.
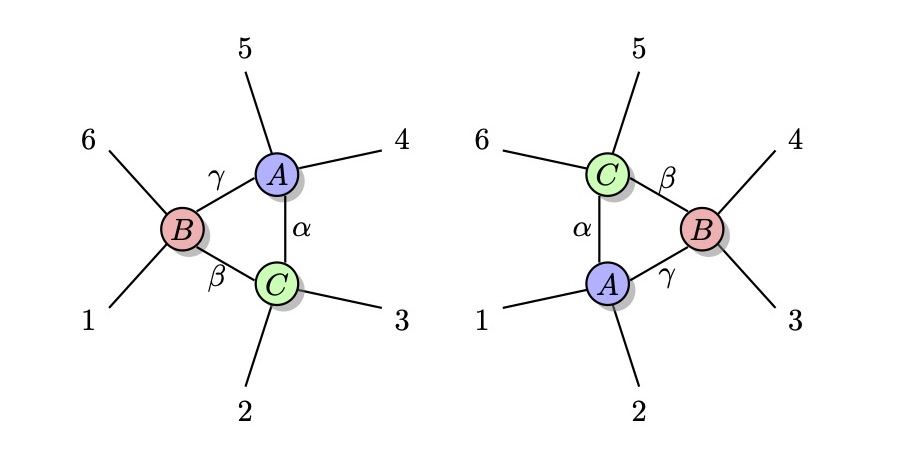
Featured image: Tensor network decompositions for a quantum state on six sites.
Popular summary
► BibTeX data
► References
[1] R. Orús, ``Tensor networks for complex quantum systems,'' Nat. Rev. Phys. 1 (2019) no. 9, 538–550, arXiv:1812.04011 [cond-mat.str-el].
https://doi.org/10.1038/s42254-019-0086-7
arXiv:1812.04011
[2] D. Perez-Garcia, F. Verstraete, M. M. Wolf, and J. I. Cirac, ``Matrix Product State Representations,'' Quantum Info. Comput. 7 (2007) no. 5, 401–430, quant-ph/0608197.
https://doi.org/10.26421/QIC7.5-6-1
arXiv:quant-ph/0608197
[3] J. I. Cirac, D. Pérez-García, N. Schuch, and F. Verstraete, ``Matrix product states and projected entangled pair states: Concepts, symmetries, theorems,'' Rev. Mod. Phys. 93 (2021) 045003, arXiv:2011.12127 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.93.045003
arXiv:2011.12127
[4] P. Facchi, G. Florio, G. Parisi, and S. Pascazio, ``Maximally multipartite entangled states,'' Phys. Rev. A 77 (2008) no. 6, 060304, arXiv:0710.2868 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.77.060304
arXiv:0710.2868
[5] W. Helwig, W. Cui, J. I. Latorre, A. Riera, and H.-K. Lo, ``Absolute maximal entanglement and quantum secret sharing,'' Phys. Rev. A 86 (2012) no. 5, 052335, arXiv:1204.2289 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.86.052335
arXiv:1204.2289
[6] W. Helwig and W. Cui, ``Absolutely Maximally Entangled States: Existence and Applications,'' arXiv e-prints (2013) , arXiv:1306.2536 [quant-ph].
arXiv:1306.2536
[7] D. Goyeneche and K. Życzkowski, ``Genuinely multipartite entangled states and orthogonal arrays,'' Phys. Rev. A 90 (2014) no. 2, 022316, arXiv:1404.3586 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.90.022316
arXiv:1404.3586
[8] M. Gaeta, A. Klimov, and J. Lawrence, ``Maximally entangled states of four nonbinary particles,'' Phys. Rev. A 91 (2015) no. 1, 012332, arXiv:1411.6178 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.91.012332
arXiv:1411.6178
[9] Z. Raissi, C. Gogolin, A. Riera, and A. Acín, ``Optimal quantum error correcting codes from absolutely maximally entangled states,'' J. Phys. A 51 (2018) no. 7, 075301, arXiv:1701.03359 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8121/aaa151
arXiv:1701.03359
[10] D. Goyeneche, D. Alsina, J. I. Latorre, A. Riera, and K. Życzkowski, ``Absolutely maximally entangled states, combinatorial designs, and multiunitary matrices,'' Phys. Rev. A 92 (2015) no. 3, 032316, arXiv:1506.08857 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.92.032316
arXiv:1506.08857
[11] D. Goyeneche, Z. Raissi, S. Di Martino, and K. Życzkowski, ``Entanglement and quantum combinatorial designs,'' Phys. Rev. A 97 (2018) no. 6, 062326, arXiv:1708.05946 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.97.062326
arXiv:1708.05946
[12] A. S. Hedayat, N. J. Sloane, and J. Stufken, Orthogonal Arrays: Theory and Applications. Springer, 1999.
[13] P. Hosur, X.-L. Qi, D. A. Roberts, and B. Yoshida, ``Chaos in quantum channels,'' J. High Energy Phys. 2016 (2016) 4, arXiv:1511.04021 [hep-th].
https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP02(2016)004
arXiv:1511.04021
[14] F. Huber and N. Wyderka, ``Table of AME states.'' Online available, 2021. https://www.tp.nt.uni-siegen.de/+fhuber/ame.html.
https://www.tp.nt.uni-siegen.de/+fhuber/ame.html
[15] F. Huber, C. Eltschka, J. Siewert, and O. Gühne, ``Bounds on absolutely maximally entangled states from shadow inequalities, and the quantum MacWilliams identity,'' J. Phys. A 51 (2018) no. 17, 175301, arXiv:1708.06298 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8121/aaade5
arXiv:1708.06298
[16] S. A. Rather, A. Burchardt, W. Bruzda, G. Rajchel-Mieldzioć, A. Lakshminarayan, and K. Życzkowski, ``Thirty-six Entangled Officers of Euler: Quantum Solution to a Classically Impossible Problem,'' Phys. Rev. Lett. 128 (2022) no. 8, 080507, arXiv:2104.05122 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.080507
arXiv:2104.05122
[17] K. Życzkowski, W. Bruzda, G. Rajchel-Mieldzioć, A. Burchardt, S. A. Rather, and A. Lakshminarayan, ``9 $\times$ 4 = 6 $\times$ 6: Understanding the quantum solution to the Euler's problem of 36 officers,'' J. Phys.: Conf. Series 2448 (2023) no. 1, 012003, arXiv:2204.06800 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2448/1/012003
arXiv:2204.06800
[18] S. A. Rather, N. Ramadas, V. Kodiyalam, and A. Lakshminarayan, ``Absolutely maximally entangled state equivalence and the construction of infinite quantum solutions to the problem of 36 officers of Euler,'' Phys. Rev. A 108 (2023) no. 3, 032412, arXiv:2212.06737 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.108.032412
arXiv:2212.06737
[19] L. Chen and D. L. Zhou, ``Graph states of prime-power dimension from generalized CNOT quantum circuit,'' Sci. Rep. 6 (2016) 27135, arXiv:1507.05386 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27135
arXiv:1507.05386
[20] A. Cervera-Lierta, J. I. Latorre, and D. Goyeneche, ``Quantum circuits for maximally entangled states,'' Phys. Rev. A 100 (2019) no. 2, 022342, arXiv:1904.07955 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.100.022342
arXiv:1904.07955
[21] D. N. Page, ``Average entropy of a subsystem,'' Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 (1993) no. 9, 1291–1294, arXiv:gr-qc/9305007 [gr-qc].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.71.1291
arXiv:gr-qc/9305007
[22] J. Haferkamp, P. Faist, N. B. T. Kothakonda, J. Eisert, and N. Yunger Halpern, ``Linear growth of quantum circuit complexity,'' Nat. Phys. 18 (2022) no. 5, 528–532, arXiv:2106.05305 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-022-01539-6
arXiv:2106.05305
[23] T. Farrelly, R. J. Harris, N. A. McMahon, and T. M. Stace, ``Tensor-Network Codes,'' Phys. Rev. Lett. 127 (2021) no. 4, 040507, arXiv:2009.10329 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.127.040507
arXiv:2009.10329
[24] C. Cao and B. Lackey, ``Quantum Lego: Building Quantum Error Correction Codes from Tensor Networks,'' PRX Quantum 3 (2022) no. 2, 020332, arXiv:2109.08158 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PRXQuantum.3.020332
arXiv:2109.08158
[25] T. Farrelly, D. K. Tuckett, and T. M. Stace, ``Local tensor-network codes,'' New J. Phys. 24 (2022) no. 4, 043015, arXiv:2109.11996 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/ac5e87
arXiv:2109.11996
[26] F. Pastawski, B. Yoshida, D. Harlow, and J. Preskill, ``Holographic quantum error-correcting codes: toy models for the bulk/boundary correspondence,'' J. High Energy Phys. 2015 (2015) 149, arXiv:1503.06237 [hep-th].
https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP06(2015)149
arXiv:1503.06237
[27] T. Kibe, P. Mandayam, and A. Mukhopadhyay, ``Holographic spacetime, black holes and quantum error correcting codes: A review,'' Eu. Phys. J. C 82 (2022) no. 5, 463, arXiv:2110.14669 [hep-th].
https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-022-10382-1
arXiv:2110.14669
[28] A. Jahn and J. Eisert, ``Holographic tensor network models and quantum error correction: a topical review,'' Quantum Sci. Tech. 6 (2021) no. 3, 033002, arXiv:2102.02619 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1088/2058-9565/ac0293
arXiv:2102.02619
[29] J. Berger and T. J. Osborne, ``Perfect tangles,'' arXiv e-prints (2018) , arXiv:1804.03199 [quant-ph].
arXiv:1804.03199
[30] M. Doroudiani and V. Karimipour, ``Planar maximally entangled states,'' Phys. Rev. A 102 (2020) no. 1, 012427, arXiv:2004.00906 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.102.012427
arXiv:2004.00906
[31] R. J. Harris, N. A. McMahon, G. K. Brennen, and T. M. Stace, ``Calderbank-Shor-Steane holographic quantum error-correcting codes,'' Phys. Rev. A 98 (2018) 052301, arXiv:1806.06472 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.98.052301
arXiv:1806.06472
[32] Y.-L. Wang, ``Planar k-uniform states: a generalization of planar maximally entangled states,'' Quant. Inf. Proc. 20 (2021) no. 8, 271, arXiv:2106.12209 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03204-y
arXiv:2106.12209
[33] B. Bertini, P. Kos, and T. Prosen, ``Exact Correlation Functions for Dual-Unitary Lattice Models in 1+1 Dimensions,'' Phys. Rev. Lett. 123 (2019) no. 21, , arXiv:1904.02140 [cond-mat.stat-mech].
https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.123.210601
arXiv:1904.02140
[34] V. F. R. Jones, ``Planar algebras, I,'' New Zeal. J. Math. 52 (2021) 1–107, arXiv:math/9909027 [math.QA].
https://doi.org/10.53733/172
arXiv:math/9909027
[35] U. Krishnan and V. S. Sunder, ``On Biunitary Permutation Matrices and Some Subfactors of Index 9,'' Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 348 (1996) no. 12, 4691–4736.
https://doi.org/10.1090/S0002-9947-96-01669-8
[36] G. Evenbly, ``Hyperinvariant Tensor Networks and Holography,'' Phys. Rev. Lett. 119 (2017) no. 14, 141602, arXiv:1704.04229 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.141602
arXiv:1704.04229
[37] M. Steinberg and J. Prior, ``Conformal Properties of Hyperinvariant Tensor Networks,'' Sci. Rep. 12 (2022) 532, arXiv:2012.09591 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2012.09591
arXiv:2012.09591
[38] D. J. Reutter and J. Vicary, ``Biunitary constructions in quantum information,'' Higher Structures 3 (2019) no. 1, 109–154, arXiv:1609.07775 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.21136/HS.2019.04
arXiv:1609.07775
[39] P. W. Claeys, A. Lamacraft, and J. Vicary, ``From dual-unitary to biunitary: a 2-categorical model for exactly-solvable many-body quantum dynamics,'' arXiv:2302.07280 [quant-ph].
arXiv:2302.07280
[40] C. Jonay, V. Khemani, and M. Ippoliti, ``Triunitary quantum circuits,'' Phys. Rev. Res. 3 (2021) no. 4, 043046, arXiv:2106.07686 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevResearch.3.043046
arXiv:2106.07686
[41] R. Milbradt, L. Scheller, C. Aßmus, and C. B. Mendl, ``Ternary unitary quantum lattice models and circuits in $2 + 1$ dimensions,'' Phys. Rev. Lett. 130 (2023) 090601, arXiv:2206.01499 [cond-mat.stat-mech].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.090601
arXiv:2206.01499
[42] Y. Kasim and T. Prosen, ``Dual unitary circuits in random geometries,'' J. Phys. A 56 (2022) no. 2, 025003, arXiv:2206.09665 [cond-mat.stat-mech].
https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8121/acb1e0
arXiv:2206.09665
[43] G. M. Sommers, D. A. Huse, and M. J. Gullans, ``Crystalline Quantum Circuits,'' PRX Quantum 4 (2023) 030313, arXiv:2210.10808 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PRXQuantum.4.030313
arXiv:2210.10808
[44] M. Mestyán, B. Pozsgay, and I. M. Wanless, ``Multi-directional unitarity and maximal entanglement in spatially symmetric quantum states,'' SciPost Phys. 16 (2024) no. 1, 010, arXiv:2210.13017 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.21468/SciPostPhys.16.1.010
arXiv:2210.13017
[45] J. I. Latorre and G. Sierra, ``Platonic Entanglement,'' Quantum Inf. Comput. 21 (13 & 14) (2021) 1081–1090, arXiv:2107.04329 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.26421/qic21.13-14-1
arXiv:2107.04329
[46] T. Gombor and B. Pozsgay, ``Superintegrable cellular automata and dual unitary gates from Yang-Baxter maps,'' SciPost Phys. 12 (2022) 102, arXiv:2112.01854 [cond-mat.stat-mech].
https://doi.org/10.21468/SciPostPhys.12.3.102
arXiv:2112.01854
[47] R. Roth and A. Lempel, ``On MDS codes via Cauchy matrices,'' IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 35 (1989) no. 6, 1314–1319.
https://doi.org/10.1109/18.45291
[48] G. Kéri, ``Types of superregular matrices and the number of $n$-arcs and complete $n$-arcs in PG$(r, q)$,'' J. Comb. Des. 14 (2006) no. 5, 363–390.
https://doi.org/10.1002/jcd.20091
[49] K. A. Bush, ``Orthogonal arrays of index unity,'' Ann. Math. Statistics 23 (1952) 426–434.
https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177729387
[50] G. Gour and N. R. Wallach, ``All maximally entangled four-qubit states,'' J. Math. Phys. 51 (2010) no. 11, 112201–112201, arXiv:1006.0036 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3511477
arXiv:1006.0036
[51] W. Helwig, ``Absolutely Maximally Entangled Qudit Graph States,'' arxiv e-prints (2013) , arXiv:1306.2879 [quant-ph].
arXiv:1306.2879
[52] M. van den Nest, J. Dehaene, and B. de Moor, ``Graphical description of the action of local Clifford transformations on graph states,'' Phys. Rev. A 69 (2004) no. 2, 022316, arXiv:quant-ph/0308151 [quant-ph].
https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.69.022316
arXiv:quant-ph/0308151
[53] M. Bahramgiri and S. Beigi, ``Graph States Under the Action of Local Clifford Group in Non-Binary Case,'' arXiv e-prints (2006) , arXiv:quant-ph/0610267 [quant-ph].
arXiv:quant-ph/0610267
Cited by
[1] Márton Mestyán, Balázs Pozsgay, and Ian M. Wanless, "Multi-directional unitarity and maximal entanglement in spatially symmetric quantum states", SciPost Physics 16 1, 010 (2024).
[2] Suhail Ahmad Rather, "Construction of perfect tensors using biunimodular vectors", arXiv:2309.01504, (2023).
The above citations are from SAO/NASA ADS (last updated successfully 2024-05-23 10:17:08). The list may be incomplete as not all publishers provide suitable and complete citation data.
On Crossref's cited-by service no data on citing works was found (last attempt 2024-05-23 10:17:06).
This Paper is published in Quantum under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license. Copyright remains with the original copyright holders such as the authors or their institutions.