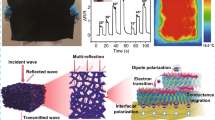
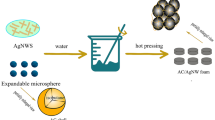
Abstract
With the accelerated development of modern detection and communication technology, the multifunctional wearable materials with excellent electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, infrared stealth, and human monitoring for improving military combat capability have received extensive attention. In this work, the lightweight melamine foam (MF)@silver nanowires (AgNWs)-iron nanowires (FeNWs) (AgFe-MF) was fabricated by a vacuum-assisted dip-coating method. Due to the porous structure and synergistic electrical and magnetic losses, this lightweight (0.115 g/cm3) composite foam with an ultra-low filler content (0.62 vol.%) exhibited an ideal EMI shielding efficiency of 38.4 dB. On the other hand, the AgFe-MF realized a powerful multifunctional integration. The surface saturation temperature of the AgFe-MF reached 94.2 °C under a low applied voltage of 1.8 V and remained extremely fast heating and cooling response and terrific working stability, resulting in excellent infrared stealth and camouflage effects. Furthermore, taking virtues of the elastic porous conductive architecture, the AgFe-MF was utilized as a piezoresistive sensor exhibiting board compressive interval of 0–1.62 kPa (50% strain) with a good sensitivity of 0.57 kPa−1. This work will provide new ideas and insights for developing multifunctional wearable devices in the fields of EMI shielding, thermal management, and piezoresistive sensing.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, M. M.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Q. Q.; You, X.; Yang, J. S.; Dong, S. M. Aosorption-based electromagnetic interference shielding composites with sandwich structure by one-step electrodeposition method. Carbon 2023, 202, 414–424.
Cheng, H. R.; Xing, L. L.; Zuo, Y.; Pan, Y. M.; Huang, M. N.; Alhadhrami, A.; Ibrahim, M. M.; El-Bahy, Z. M.; Liu, C. T.; Shen, C. Y. et al. Constructing nickel chain/MXene networks in melamine foam towards phase change materials for thermal energy management and absorption-dominated electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 755–765.
Mariappan, P. M.; Raghavan, D. R.; Aleem, S. H. E. A.; Zobaa, A. F. Effects of electromagnetic interference on the functional usage of medical equipment by 2G/3G/4G cellular phones: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 727–738.
Ma, L.; Hamidinejad, M.; Wei, L. F.; Zhao, B.; Park, C. B. Absorption-dominant EMI shielding polymer composite foams: Microstructure and geometry optimization. Mater. Today Phys. 2023, 30, 100940.
Jia, L.; Ding, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Tian, X. Y. A controllable gradient structure of hydrophobic composite fabric constructed by silver nanowires and polyvinylidene fluoride microspheres for electromagnetic interference shielding with low reflection. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 156, 106884.
Yao, Y. Y.; Jin, S. H.; Wang, D. X.; Wang, J. F.; Li, D. Z.; Lv, X. J.; Shu, Q. H. Flexible magnetoelectric coupling nanocomposite films with multilayer network structure for dual-band EMI shielding. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 222, 109387.
Yu, Y. H.; Yi, P.; Xu, W. B.; Sun, X.; Deng, G.; Liu, X. F.; Shui, J. L.; Yu, R. H. Environmentally tough and stretchable MXene organohydrogel with exceptionally enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding performances. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 77.
Yu, X. C.; Liang, X. W.; Zhao, T.; Zhu, P. L.; Sun, R.; Wong, C. P. Thermally welded honeycomb-like silver nanowires aerogel backfilled with polydimethylsiloxane for electromagnetic interference shielding. Mater. Lett. 2021, 285, 129065.
Zhou, Y. Y.; Sang, G. L.; Yu, M.; Xu, P.; Ding, Y. S. Electrical and magnetic network design for improving electromagnetic interference shielding performance of waterborne polyurethane fabrics. Mater. Lett. 2022, 314, 131862.
Wan, C. C.; Li, J. Graphene oxide/cellulose aerogels nanocomposite: Preparation, pyrolysis, and application for electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 172–179.
Zheng, Q.; Wang, J. Q.; Yu, M. J.; Cao, W. Q.; Zhai, H. Z.; Cao, M. S. Heterodimensional structure porous nanofibers embedded confining magnetic nanocrystals for electromagnetic functional material and device. Carbon 2023, 210, 118049.
Zhang, X.; Guo, Y. L.; Feng, Y. J.; Hou, M. H.; Wang, J. Facile synthesis of ultra-lightweight Ni/NiO/NixPy foams with hollow sandwich micro-tubes for absorption-dominated electromagnetic interference shielding. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 651, 129764.
Li, S. S.; Mo, W. J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. Constructing 3D tent-like frameworks in melamine hybrid foam for superior microwave absorption and thermal insulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140133.
Rong, H. W.; Song, H. H.; Gao, T.; Li, Y. X.; Zhao, R. Z.; Zhang, X. F. Ultralight melamine foam derived metal nanoparticles encapsulated CNTs/porous carbon composite for electromagnetic absorption. Synth. Met. 2023, 294, 117306.
Zuo, T. C.; Xie, C. L.; Wang, W.; Yu, D. Ti3C2Tx MXene-ferroferric oxide/carbon nanotubes/waterborne polyurethane-based asymmetric composite aerogels for absorption-dominated electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 4716–4725.
Jiang, S.; Qian, K.; Yu, K. J.; Zhou, H. F.; Weng, Y. X.; Zhang, Z. W. Study on ultralight and flexible Fe3O4/melamine derived carbon foam composites for high-efficiency microwave absorption. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 779, 138873.
Cheng, H. R.; Pan, Y. M.; Wang, X.; Liu, C. T.; Shen, C. Y.; Schubert, D. W.; Guo, Z. H.; Liu, X. H. Ni flower/MXene-melamine foam derived 3D magnetic/conductive networks for ultra-efficient microwave absorption and infrared stealth. Nano- Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 63.
Xiao, Y. Y.; He, Y. J.; Wang, R. Q.; Lei, Y. Z.; Yang, J. H.; Qi, X. D.; Wang, Y. Mussel-inspired strategy to construct 3D silver nanoparticle network in flexible phase change composites with excellent thermal energy management and electromagnetic interference shielding capabilities. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2022, 239, 109962.
Liu, J.; Zhang, H. B.; Xie, X.; Yang, R.; Liu, Z. S.; Liu, Y. F.; Yu, Z. Z. Multifunctional, superelastic, and lightweight MXene/polyimide aerogels. Small 2018, 14, 1802479.
Wang, Y. C.; Wang, Y. Z.; Shu, J. C.; Cao, W. Q.; Li, C. S.; Cao, M. S. Graphene implanted shape memory polymers with dielectric gene dominated highly efficient microwave drive. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2303560.
Zhang, M.; Cao, M. S.; Wang, Q. Q.; Wang, X. X.; Cao, W. Q.; Yang, H. J.; Yuan, J. A multifunctional stealthy material for wireless sensing and active camouflage driven by configurable polarization. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 132, 42–49.
Cheng, Y. J.; Sun, X. X.; Yang, S.; Wang, D.; Liang, L.; Wang, S. S.; Ning, Y. H.; Yin, W. L.; Li, Y. B. Multifunctional elastic rGO hybrid aerogels for microwave absorption, infrared stealth and heat insulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139376.
Gong, S.; Sheng, X. X.; Li, X. L.; Sheng, M. J.; Wu, H.; Lu, X.; Qu, J. P. A multifunctional flexible composite film with excellent multi-source driven thermal management, electromagnetic interference shielding, and fire safety performance, inspired by a “brick-mortar” sandwich structure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200570.
Zhang, D. B.; Yin, R.; Zheng, Y. J.; Li, Q. M.; Liu, H.; Liu, C. T.; Shen, C. Y. Multifunctional MXene/CNTs based flexible electronic textile with excellent strain sensing, electromagnetic interference shielding and Joule heating performances. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 438, 135587.
Chen, Y. M.; Luo, H.; Guo, H. T.; Liu, K. M.; Mei, C. T.; Li, Y.; Duan, G. G.; He, S. J.; Han, J. Q.; Zheng, J. J. et al. Anisotropic cellulose nanofibril composite sponges for electromagnetic interference shielding with low reflection loss. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 276, 118799.
Lee, H.; Dellatore, S. M.; Miller, W. M.; Messersmith, P. B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430.
Ma, Z. L.; Xiang, X. L.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Y. L.; Gu, J. W. Multifunctional wearable silver nanowire decorated leather nanocomposites for Joule heating, electromagnetic interference shielding and piezoresistive sensing. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202200705.
Yang, P. A.; Ruan, H. B.; Sun, Y.; Li, R.; Lu, Y.; Xiang, C. Y. Excellent microwave absorption performances of high length-diameter ratio iron nanowires with low filling ratio. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 395708.
Li, Y. Q.; Chen, Y. M.; Huang, X. B.; Jiang, S. H.; Wang, G. Anisotropy-functionalized cellulose-based phase change materials with reinforced solar-thermal energy conversion and storage capacity. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 129086.
Yang, P. A.; Huang, Y. X.; Li, R.; Huang, X.; Ruan, H. B.; Shou, M. J.; Li, W. J.; Zhang, Y. X.; Li, N.; Dong, L. C. Optimization of Fe@Ag core-shell nanowires with improved impedance matching and microwave absorption properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132878.
Peng, Q.; Ma, M.; Chu, Q. D.; Lin, H.; Tao, W. T.; Shao, W. Q.; Chen, S.; Shi, Y. Q.; He, H. W.; Wang, X. Absorption-dominated electromagnetic interference shielding composite foam based on porous and bi-conductive network structures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 10857–10866.
Li, Q. Y.; Guo, W. M.; Kong, X. T.; Xu, J. L.; Xu, C. S.; Chen, Y. E.; Chen, J.; Jia, X. Y.; Ding, Y. MnFe2O4/rGO/diatomite composites with excellent wideband electromagnetic microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 941, 168851.
Hang, T. Y.; Zheng, J. J.; Zheng, Y. F.; Jiang, S. H.; Zhou, L. J.; Sun, Z. X.; Li, X. P.; Tong, G. X.; Chen, Y. M. Wheat-like Ni-coated core–shell silver nanowires for effective electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2023, 649, 394–402.
Wang, X. X.; Shu, J. C.; Cao, W. Q.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, J.; Cao, M. S. Eco-mimetic nanoarchitecture for green EMI shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 1068–1077.
Che, R. C.; Peng, L. M.; Duan, X. F.; Chen, Q.; Liang, X. L. Microwave absorption enhancement and complex permittivity and permeability of Fe encapsulated within carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 401–405.
Liu, Q. H.; Cao, Q.; Bi, H.; Liang, C. Y.; Yuan, K. P.; She, W.; Yang, Y. J.; Che, R. C. CoNi@SiO2@TiO2 and CoNi@air@TiO2 microspheres with strong wideband microwave absorption. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 486–490.
Zhu, S. Q.; Shu, J. C.; Cao, M. S. Novel MOF-derived 3D hierarchical needlelike array architecture with excellent EMI shielding, thermal insulation and supercapacitor performance. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 7322–7331.
Wang, X. X.; Zheng, Q.; Zheng, Y. J.; Cao, M. S. Green EMI shielding: Dielectric/magnetic “genes” and design philosophy. Carbon 2023, 206, 124–141.
Che, R. C.; Zhi, C. Y.; Liang, C. Y.; Zhou, X. G. Fabrication and microwave absorption of carbon nanotubes/CoFe2O4 spinel nanocomposite. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 033105.
Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Tan, S. J.; Peymanfar, R.; Aslibeiki, B.; Ji, G. B. Ultrabroad microwave absorption ability and infrared stealth property of nano-micro CuS@rGO lightweight aerogels. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 171.
Huang, Q. Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Tan, S. J.; Tang, S. L.; Ji, G. B. A dual-band transceiver with excellent heat insulation property for microwave absorption and low infrared emissivity compatibility. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137279.
Ma, Z. L.; Kang, S. L.; Ma, J. Z.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Y. L.; Liu, C.; Wei, A. J.; Xiang, X. L.; Wei, L. F.; Gu, J. W. Ultraflexible and mechanically strong double-layered aramid nanofiber-Ti3C2Tx MXene/silver nanowire nanocomposite papers for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 8368–8382.
Huang, C. Y.; Yang, G.; Huang, P.; Hu, J. M.; Tang, Z. H.; Li, Y. Q.; Fu, S. Y. Flexible pressure sensor with an excellent linear response in a broad detection range for human motion monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 3476–3485.
Qian, K. P.; Zhou, J. Y.; Miao, M.; Wu, H. M.; Thaiboonrod, S.; Fang, J. H.; Feng, X. Highly ordered thermoplastic polyurethane/aramid nanofiber conductive foams modulated by kevlar polyanion for piezoresistive sensing and electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 88.
Zheng, J. J.; Hang, T. Y.; Li, Z. H.; He, W. W.; Jiang, S. H.; Li, X. P.; Chen, Y. M.; Wu, Z. Y. High-performance and multifunctional conductive aerogel films for outstanding electromagnetic interference shielding, Joule heating and energy harvesting. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144548.
Hang, T. Y.; Zhou, L. J.; Li, Z. H.; Zheng, Y. F.; Yao, Y. Q.; Cao, Y. X.; Xu, C. H.; Jiang, S. H.; Chen, Y. M.; Zheng, J. J. Constructing gradient reflection and scattering porous framework in composite aerogels for enhanced microwave absorption. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 329, 121777.
Hang, T. Y.; Chen, Y. M.; Yin, F. Q.; Shen, J. H.; Li, X. P.; Li, Z. C.; Zheng, J. J. Highly stretchable polyvinyl alcohol composite conductive hydrogel sensors reinforced by cellulose nanofibrils and liquid metal for information transmission. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128855.
Chen, Y. M.; Zhang, L.; Mei, C. T.; Li, Y.; Duan, G. G.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Ma, C. X.; Jiang, S. H. Wood-inspired anisotropic cellulose nanofibril composite sponges for multifunctional applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35513–35522.
Hang, T. Y.; Xu, C. H.; Shen, J. H.; Zheng, J. J.; Zhou, L. J.; Li, M. J.; Li, X. P.; Jiang, S. H.; Yang, P. G.; Zhou, W. et al. Ultra-flexible silver/iron nanowire decorated melamine composite foams for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption and thermal management. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2024, 654, 945–954.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LQ22E030016), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52275137 and 51705467), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2022M722831), the Postdoctoral Research Selected Funding Project of Zhejiang Province (No. ZJ2022063), and the Self-Topic Fund of Zhejiang Normal University (No. 2020ZS04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2024_6565_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
High-performance wearable bimetallic nanowire-assisted composite foams for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding, infrared stealth, and piezoresistive sensing
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hang, T., Zhou, L., Xu, C. et al. High-performance wearable bimetallic nanowire-assisted composite foams for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding, infrared stealth, and piezoresistive sensing. Nano Res. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6565-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6565-9