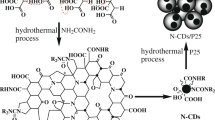
Abstract
Regulating the doping of carbon dots (CDs) and the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is essential to selectively control their application in photocatalytic organic reactions. This study successfully synthesized five newly developed nitrogen-doped carbon dots (CDs 1–5) with varying nitrogen content, which have the ability to generate ROS when exposed to light radiation, specifically superoxide anion radicals (\({{\rm{O}}_2}^{ - }\)) and singlet oxygen (1O2). The utilization of the aforementioned nitrogen-doped CDs as photocatalysts enables the realization of their potential in facilitating efficient photocatalytic organic conversion. Simultaneously, it was observed that the photocatalytic efficiency exhibited a gradual decrease when the nitrogen content in the CDs increased. In order to provide more evidence for this claim, we employed a set of five CDs in the context of photocatalytic dehalogenation of α-bromoacetophenone, photocatalytic oxidative coupling reaction of amines to imines, photooxidation reaction of sulfides to sulfoxides, and cross-dehydrogenation coupling (CDC) reaction, in which it was further observed that there was a steady decrease in the yields of photocatalytic organic reactions as the nitrogen content in CDs increased. Notably, CDs 1 exhibited the best photocatalytic efficiency, thereby reinforcing the hypothesis that a higher nitrogen content corresponds to a decreased catalytic efficiency. This study not only investigates the impact of the nitrogen content on the catalytic performance of CDs, but also offers valuable insights for the future utilization of CDs for photocatalytic organic reactions in water.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kang, Z. H.; Lee, S. T. Carbon dots: Advances in nanocarbon applications. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 19214–19224.
Arcudi, F.; Dordevic, L.; Prato, M. Design, synthesis, and functionalization strategies of tailored carbon nanodots. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2070–2079.
Baker, S. N.; Baker, G. A. Luminescent carbon nanodots: Emergent nanolights. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6726–6744.
Chen, Z. L.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. H. Diversity and tailorability of photoelectrochemical properties of carbon dots. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 3110–3124.
Wang, H. L.; Ai, L.; Song, H. Q.; Song, Z. Q.; Yong, X.; Qu, S. N.; Lu, S. Y. Innovations in the solid-state fluorescence of carbon dots: Strategies, optical manipulations, and applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2303756.
Ru, Y.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Lu, S. Y. Aggregation in carbon dots: Special Issue: Emerging Investigators. Aggregate 2022, 3, e296.
Lim, S. Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Q. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381.
Dordevic, L.; Arcudi, F.; Cacioppo, M.; Prato, M. A multifunctional chemical toolbox to engineer carbon dots for biomedical and energy applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 112–130.
Gao, J.; Zhu, M. M.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. H. Advances, challenges and promises of carbon dots. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2017, 4, 1963–1986.
Li, F.; Li, Y. Y.; Yang, X.; Han, X. X.; Jiao, Y.; Wei, T. T.; Yang, D. Y.; Xu, H. P.; Nie, G. J. Highly fluorescent chiral N-S-doped carbon dots from cysteine: Affecting cellular energy metabolism. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2377–2382.
Guo, L.; Ge, J. C.; Liu, W. M.; Niu, G. L.; Jia, Q. Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, P. F. Tunable multicolor carbon dots prepared from well-defined polythiophene derivatives and their emission mechanism. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 729–734.
Xu, X. Y.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y. L.; Ploehn, H. J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W. A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737.
Ai, L.; Shi, R.; Yang, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, T. R.; Lu, S. Y. Efficient combination of g-C3N4 and CDs for enhanced photocatalytic performance: A review of synthesis, strategies, and applications. Small 2021, 17, 2007523.
Shi, R.; Li, Z.; Yu, H. J.; Shang, L.; Zhou, C.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Wu, L. Z.; Zhang, T. R. Effect of nitrogen doping level on the performance of N-doped carbon quantum Dot/TiO2 composites for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 4650–4656.
Liu, D.; Chen, S. T.; Li, R. J.; Peng, T. Y. Review of Z-scheme heterojunctions for photocatalytic energy conversion. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2020, 37, 2010017.
Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Gupta, B. K.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L. H.; Song, L.; Alemany, L. B.; Zhan, X. B.; Gao, G. H. et al. Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 844–849.
Jiang, K.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wu, A. G.; Cai, C. Z.; Lin, H. W. Red, green, and blue luminescence by carbon dots: Full-color emission tuning and multicolor cellular imaging. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5360–5363.
Wang, Q.; Pang, E.; Tan, Q. X.; Zhao, S. J.; Yi, J. N.; Zeng, J.; Lan, M. H. Regulating photochemical properties of carbon dots for theranostic applications. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobi. 2023, 15, e1862.
Ding, H.; Yu, S. B.; Wei, J. S.; Xiong, H. M. Full-color light-emitting carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 484–491.
Du, J. J.; Xu, N.; Fan, J. L.; Sun, W.; Peng, X. J. Carbon dots for in vivo bioimaging and theranostics. Small 2019, 15, 1805087.
Zhao, H. X.; Liu, L. Q.; Liu, Z. D.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. J.; Huang, C. Z. Highly selective detection of phosphate in very complicated matrixes with an off-on fluorescent probe of europium-adjusted carbon dots. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2604–2606.
Wei, W. L.; Xu, C.; Ren, J. S.; Xu, B. L.; Qu, X. G. Sensing metal ions with ion selectivity of a crown ether and fluorescence resonance energy transfer between carbon dots and graphene. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1284–1286.
Walther, B. K.; Dinu, C. Z.; Guldi, D. M.; Sergeyev, V. G.; Creager, S. E.; Cooke, J. P.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. Nanobiosensing with graphene and carbon quantum dots: Recent advances. Mater. Today 2020, 39, 23–46.
Dhenadhayalan, N.; Lin, K. C.; Saleh, T. A. Recent advances in functionalized carbon dots toward the design of efficient materials for sensing and catalysis applications. Small 2022, 16, 1905767.
Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, K.; Wu, A. G.; Lin, H. W. Toward high-efficient red emissive carbon dots: Facile preparation, unique properties, and applications as multifunctional theranostic agents. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 8659–8668.
Pan, L. L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, K.; Lin, H. W. Near-infrared emissive carbon dots for two-photon fluorescence bioimaging. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17350–17356.
Zhang, X. Y.; Zeng, Q. S.; Xiong, Y.; Ji, T. J.; Wang, C.; Shen, X. Y.; Lu, M.; Wang, H. R.; Wen, S. P.; Zhang, Y. et al. Energy level modification with carbon dot interlayers enables efficient perovskite solar cells and quantum dot based light-emitting diodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910530.
Wang, Q. L.; Huang, X. X.; Long, Y. J.; Wang, X. L.; Zhang, H. J.; Zhu, R.; Liang, L. P.; Teng, P.; Zheng, H. Z. Hollow luminescent carbon dots for drug delivery. Carbon 2013, 59, 192–199.
Ding, H.; Du, F. Y.; Liu, P. C.; Chen, Z. J.; Shen, J. C. DNA-carbon dots function as fluorescent vehicles for drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6889–6897.
Yu, H. J.; Shi, R.; Zhao, Y. F.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Wu, L. Z.; Tung, C. H.; Zhang, T. R. Smart utilization of carbon dots in semiconductor photocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9454–9477.
Wang, R.; Lu, K. Q.; Tang, Z. R.; Xu, Y. J. Recent progress in carbon quantum dots: Synthesis, properties and applications in photocatalysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 3717–3734.
Han, M.; Zhu, S. J.; Lu, S. Y.; Song, Y. B.; Feng, T. L.; Tao, S. Y.; Liu, J. J.; Yang, B. Recent progress on the photocatalysis of carbon dots: Classification, mechanism and applications. Nano Today 2018, 19, 201–218.
Rosso, C.; Filippini, G.; Prato, M. Carbon dots as nano-organocatalysts for synthetic applications. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 8090–8105.
Romero, N. A.; Nicewicz, D. A. Organic photoredox catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10075–10166.
Hou, W. D.; Guo, H. Z.; Wu, M. H.; Wang, L. Amide covalent bonding engineering in heterojunction for efficient solar-driven CO2 reduction. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 20560–20569.
Shen, X. Y.; Wang, Z. M.; Guo, H. Z.; Lei, Z. D.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L. Solvent engineering of oxygen-enriched carbon dots for efficient electrochemical hydrogen peroxide production. Small 2023, 19, 2303156.
Hu, B. J.; Huang, K.; Tang, B. J.; Lei, Z. D.; Wang, Z. M.; Guo, H. Z.; Lian, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L. Graphene quantum dot-mediated atom-layer semiconductor electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 217.
Yoon, T. P.; Ischay, M. A.; Du, J. A. Visible light photocatalysis as a greener approach to photochemical synthesis. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 527–532.
Hutton, G. A. M.; Martindale, B. C. M.; Reisner, E. Carbon dots as photosensitisers for solar-driven catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6111–6123.
Li, H. T.; Liu, R. H.; Lian, S. Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Kang, Z. H. Near-infrared light controlled photocatalytic activity of carbon quantum dots for highly selective oxidation reaction. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 3289–3297.
Lei, T.; Wei, S. M.; Feng, K.; Chen, B.; Tung, C. H.; Wu, L. Z. Borylation of diazonium salts by highly emissive and crystalline carbon dots in water. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 1715–1719.
Li, X. M.; Qiao, S. P.; Zhao, L. L.; Liu, S. D.; Li, F.; Yang, F. H.; Luo, Q.; Hou, C. X.; Xu, J. Y.; Liu, J. Q. Template-free construction of highly ordered monolayered fluorescent protein nanosheets: A bioinspired artificial light-harvesting system. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1861–1869.
He, T. T.; Wei, H. P.; Zhou, Y. B.; Jiang, L. Y.; Baell, J. B.; Yu, Y.; Huang, F. Visible light-induced borylation and arylation of small organic molecules using carbon dots. Org. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 2918–2926.
Li, F.; Yang, D. Y.; Xu, H. P. Non-metal-heteroatom-doped carbon dots: Synthesis and properties. Chem.—Eur. J. 2019, 25, 1165–1176.
Gentile, G.; Mamone, M.; Rosso, C.; Amato, F.; Lanfrit, C.; Filippini, G.; Prato, M. Tailoring the chemical structure of nitrogen-doped carbon dots for nano-aminocatalysis in aqueous media. ChemSusChem 2023, 16, e202202399.
Dong, Y. Q.; Pang, H. C.; Yang, H. B.; Guo, C. X.; Shao, J. W.; Chi, Y. W.; Li, C. M.; Yu, T. Carbon-based dots co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur for high quantum yield and excitation-independent emission. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7800–7804.
Liu, Q.; Li, Y. N.; Zhang, H. H.; Chen, B.; Tung, C. H.; Wu, L. Z. Reactivity and mechanistic insight into visible-light-induced aerobic cross-dehydrogenative coupling reaction by organophotocatalysts. Chem.—Eur. J. 2012, 18, 620–627.
Wang, X. Z.; Meng, Q. Y.; Zhong, J. J.; Gao, X. W.; Lei, T.; Zhao, L. M.; Li, Z. J.; Chen, B.; Tung, C. H.; Wu, L. Z. The singlet excited state of BODIPY promoted aerobic cross-dehydrogenative-coupling reactions under visible light. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 11256–11259.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52205210) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Nos. ZR2020MB018, ZR2022QE033, and ZR2021QB049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, KK., Ma, CQ., Dong, RZ. et al. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots as photocatalysts for organic synthesis: Effect of nitrogen content on catalytic activity. Nano Res. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6451-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-024-6451-6