Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2018-10-17 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1414-y Dina Lakayan , Rob Haselberg , Rabah Gahoual , Govert W. Somsen , Jeroen Kool
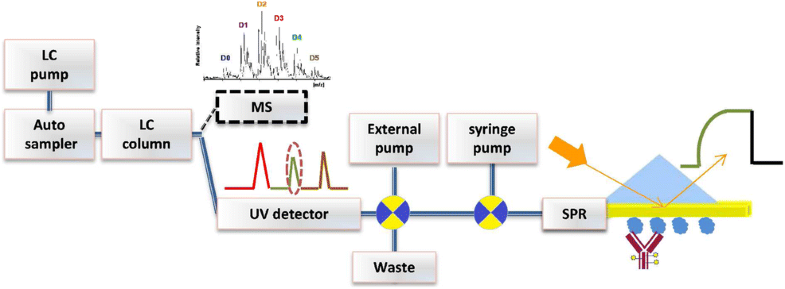
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are highly potent biopharmaceuticals designed for targeted cancer therapies. mAbs and ADCs can undergo modifications during production and storage which may affect binding to target receptors, potentially altering drug efficacy. In this work, liquid chromatography was coupled online to surface plasmon resonance (LC-SPR) to allow label-free affinity evaluation of mAb and ADC sample constituents (size and charge variants), under near-native conditions. Trastuzumab and its ADC trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) were used as a test sample and were analyzed by aqueous size-exclusion chromatography (SEC)-SPR before and after exposure to aggregate-inducing conditions. SEC-SPR allowed separation of the formed aggregates and measurement of their affinity towards the ligand-binding domain of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) receptor immobilized on the surface of the SPR sensor chip. The monomer and aggregates of the mAb and ADC were shown to have similar antigen affinity. Conjugation of drugs to trastuzumab appeared to accelerate the aggregate formation. In addition, cation-exchange chromatography (CEX) was coupled to SPR enabling monitoring the maximum ligand-analyte binding capacity (Rmax) of individual charge variants present in mAbs. Deamidated species and lysine variants in trastuzumab sample were separated but did not show different binding affinities to the immobilized HER2-binding domain. In order to allow protein variant assignment, parallel MS detection was added to the LC-SPR setup using a column effluent split. The feasibility of the LC-MS/SPR system was demonstrated by analysis of trastuzumab and T-DM1 providing information on antibody glycoforms and/or determination of the drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR), while simultaneously monitoring binding of eluting species to HER2.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

液相色谱-表面等离振子共振生物传感偶联的单克隆抗体和抗体-药物偶联物制剂的亲和力分析
单克隆抗体(mAb)和抗体-药物偶联物(ADC)是专为靶向癌症治疗设计的高效生物药物。mAb和ADC在生产和储存过程中可能会发生修饰,这可能会影响与靶标受体的结合,从而潜在地改变药物功效。在这项工作中,液相色谱在线耦合至表面等离振子共振(LC-SPR),从而可以在接近天然条件下对mAb和ADC样品成分(大小和电荷变量)进行无标记的亲和力评估。曲妥珠单抗及其ADC曲妥珠单抗Emtansine(T-DM1)用作测试样品,并在暴露于聚集体诱导条件之前和之后通过水相尺寸排阻色谱法(SEC)-SPR进行分析。SEC-SPR允许分离形成的聚集体,并测量它们对固定在SPR传感器芯片表面的人表皮生长因子受体2(HER2)受体的配体结合结构域的亲和力。已显示mAb和ADC的单体和聚集体具有相似的抗原亲和力。药物与曲妥珠单抗的结合似乎加速了聚集体的形成。此外,阳离子交换色谱(CEX)与SPR偶联,可监测最大的配体与分析物的结合能力(R max)(以mAbs表示)的各个电荷变体。分离了曲妥珠单抗样品中的脱酰胺基物种和赖氨酸变体,但对固定化的HER2结合域未显示出不同的结合亲和力。为了允许蛋白质变体分配,使用色谱柱流出物拆分将平行质谱检测添加到LC-SPR设置中。LC-MS / SPR系统的可行性通过曲妥珠单抗和T-DM1的分析得到证明,可提供有关抗体糖型的信息和/或确定药物-抗体比率(DAR),同时监控洗脱物质与HER2的结合。

ᅟ


























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号