Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2018-08-31 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1338-6 Bianbian Huo , Mingli Chen , Junjie Chen , Yuanyuan Li , Wanjun Zhang , Jianhua Wang , Weijie Qin , Xiaohong Qian
Urine is an attractive and non-invasive alternative source to tissue, blood or other biofluids for biomarker screening in clinical research. In normal human adult urine, 48% of the total urinary protein is in the sediment, 49% is soluble and the remaining 3% is contained in urinary extracellular vesicles (EVs). The soluble proteins and EV proteins in urine have attracted particular attention in recent years as cancer diagnostics. Furthermore, considering the important role of N-glycoproteins in practically all physiological processes, including regulating receptor-ligand binding, cell-cell interactions, inflammatory response and tumour progression, N-glycoproteome in human urine is an invaluable target for monitoring the physiological status and pathological changes of the kidney and urinary tract. Given the different origins of the soluble proteins and EV proteins in the urine, different N-glycoproteome patterns exist. Therefore, isolating the soluble N-glycoproteins and EV N-glycoproteins for separate analysis will provide a more specific and comprehensive view and provide a deeper understanding of human urinary N-glycoproteome. In this work, we developed a sequential separation method that isolates urinary soluble proteins and EV proteins via stepwise ultrafiltration based on their obvious size difference. A facile and reproducible protein isolation was achieved using this strategy. Subsequent N-glycoproteome enrichment and identification revealed distinct patterns in the two sub-proteomes of urine with more than 60% differential N-glycopeptides. A more comprehensive picture of the urinary N-glycoproteome with close to 1800 identified N-glycopeptides was obtained by this new analysis strategy, therefore making it advantageous for urinary biomarker screening.
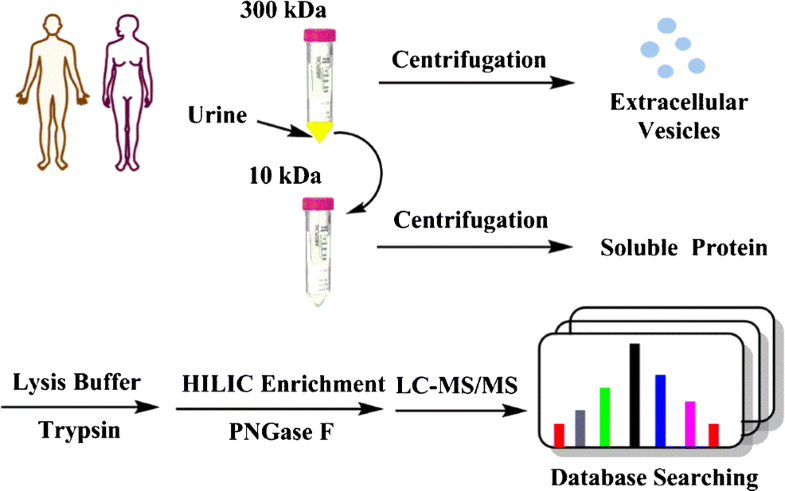
A sequential separation method that isolates urinary soluble proteins and EV proteins via stepwise ultrafiltration was developed in this work. Subsequent N-glycopeptides enrichment and mass spectrometry analysis reveals distinct N-glycoproteome patterns in the two sub-proteomes of urine and a deep mapping of close to 1800 N-glycopeptides.
中文翻译:

顺序分离策略用于人尿N-糖蛋白组的简便分离和综合分析
尿液是用于临床研究中生物标志物筛选的组织,血液或其他生物流体的一种有吸引力且无创的替代来源。在正常的成人尿液中,总尿蛋白中的48%位于沉积物中,49%可溶,其余3%包含在尿细胞外囊泡(EVs)中。近年来,尿液中的可溶性蛋白和EV蛋白作为癌症诊断技术引起了人们的特别关注。此外,考虑到N-糖蛋白在几乎所有生理过程中的重要作用,包括调节受体-配体结合,细胞-细胞相互作用,炎性反应和肿瘤进展,人尿中N-糖蛋白组是监测生理状态和生命的重要指标。肾脏和尿路的病理变化。考虑到尿液中可溶性蛋白和EV蛋白的来源不同,存在不同的N-糖基蛋白质组模式。因此,分离可溶性N-糖蛋白和EV N-糖蛋白以进行单独分析将提供更具体和全面的观点,并提供对人尿N-糖蛋白组学的更深入了解。在这项工作中,我们开发了一种顺序分离方法,该方法基于明显的大小差异,通过逐步超滤来分离尿中可溶性蛋白和EV蛋白。使用此策略可以轻松,可重现地分离蛋白质。随后的N-糖蛋白组富集和鉴定揭示了尿液的两个亚蛋白组中有60%的差异N-糖肽存在不同的模式。

在这项工作中开发了一种通过逐步超滤分离尿液可溶性蛋白和EV蛋白的顺序分离方法。随后的N-糖肽富集和质谱分析揭示了尿液的两个子蛋白质组中不同的N-糖蛋白组学模式,以及接近1800个N-糖肽的深层作图。


























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号