Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2018-08-29 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1326-x Agnes Magri , Matheus F. Soler , André M. Lopes , Eduardo M. Cilli , Patrick S. Barber , Adalberto Pessoa , Jorge F. B. Pereira
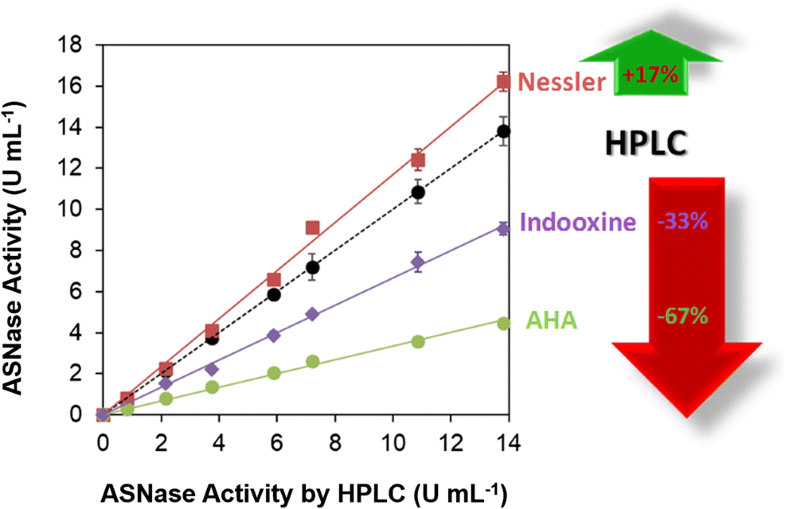
L-asparaginase or ASNase (L-asparagine aminohydrolase, E.C.3.5.1.1) is an enzyme clinically accepted as an antitumor agent to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and lymphosarcoma through the depletion of L-asparagine (L-Asn) resulting in cytotoxicity to leukemic cells. ASNase is also important in the food industry, preventing acrylamide formation in processed foods. Several quantification techniques have been developed and used for the measurement of the ASNase activity, but standard pharmaceutical quality control methods were hardly reported, and in general, no official quality control guidelines were defined. To overcome this lack of information and to demonstrate the advantages and limitations, this work properly compares the traditional colorimetric methods (Nessler; L-aspartic acid β-hydroxamate (AHA); and indooxine) and the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method. A comparison of the methods using pure ASNase shows that the colorimetric methods both overestimate (Nessler) and underestimate (AHA and indooxine) the ASNase activity when compared to the values obtained with HPLC, considered the most precise method as this method monitors both substrate consumption and product formation, allowing for overall mass-balance. Correlation and critical analysis of each method relative to the HPLC method were carried out, resulting in a demonstration that it is crucial to select a proper method for the quantification of ASNase activity, allowing bioequivalence studies and individualized monitoring of different ASNase preparations.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

L-天冬酰胺酶活性定量方法的关键分析-比色法与高效液相色谱法
L-天冬酰胺酶或ASNase(L-天冬酰胺氨基水解酶,EC3.5.1.1)是一种临床公认的抗肿瘤药物,可通过消耗L-天冬酰胺(L-Asn)来治疗急性淋巴细胞白血病(ALL)和淋巴肉瘤。对白血病细胞有细胞毒性。ASNase在食品工业中也很重要,可防止加工食品中丙烯酰胺的形成。已经开发了几种定量技术并将其用于ASNase活性的测量,但是几乎没有报道标准的药物质量控制方法,并且总体上,没有定义正式的质量控制指南。为了克服信息的不足并证明其优势和局限性,这项工作正确地比较了传统比色法(Nessler; L-天冬氨酸β-异羟肟酸酯(AHA);和吲哚辛胺)和高效液相色谱(HPLC)方法。与使用纯ASNase的方法进行的比较显示,与通过HPLC获得的值相比,比色法高估了(Nessler)和低估了(AHA和吲哚辛胺)ASNase的活性,被认为是最精确的方法,因为该方法同时监控底物消耗和产品形成,实现整体质量平衡。进行了每种方法相对于HPLC方法的相关性和关键分析,结果表明,选择合适的方法定量ASNase活性,进行生物等效性研究和不同ASNase制剂的个性化监测至关重要。与使用纯ASNase的方法进行的比较显示,与通过HPLC获得的值相比,比色法高估了(Nessler)和低估了(AHA和吲哚辛胺)ASNase的活性,被认为是最精确的方法,因为该方法既监测底物消耗,又监测产品形成,实现整体质量平衡。相对于HPLC方法,进行了每种方法的相关性和关键分析,结果表明,选择合适的方法定量ASNase活性,进行生物等效性研究和不同ASNase制剂的个性化监测至关重要。与使用纯ASNase的方法进行的比较显示,与通过HPLC获得的值相比,比色法高估了(Nessler)和低估了(AHA和吲哚辛胺)ASNase的活性,被认为是最精确的方法,因为该方法既监测底物消耗,又监测产品形成,实现整体质量平衡。相对于HPLC方法,进行了每种方法的相关性和关键分析,结果表明,选择合适的方法定量ASNase活性,进行生物等效性研究和不同ASNase制剂的个性化监测至关重要。被认为是最精确的方法,因为该方法同时监控基材消耗和产品形成,从而实现整体质量平衡。相对于HPLC方法,进行了每种方法的相关性和关键分析,结果表明,选择合适的方法定量ASNase活性,进行生物等效性研究和不同ASNase制剂的个性化监测至关重要。被认为是最精确的方法,因为该方法同时监控基材消耗和产品形成,从而实现整体质量平衡。相对于HPLC方法,进行了每种方法的相关性和关键分析,结果表明,选择合适的方法定量ASNase活性,进行生物等效性研究和不同ASNase制剂的个性化监测至关重要。

ᅟ



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号