Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2018-10-10 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1392-0 Feng Shao , Renato Zenobi
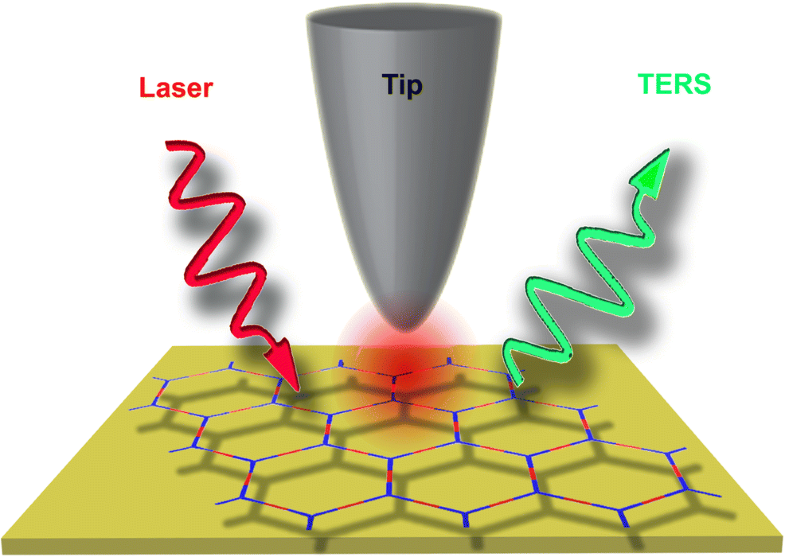
Two-dimensional (2D) materials have been one of the most extensively studied classes of modern materials, due to their astonishing chemical, optical, electronic, and mechanical properties, which are different from their bulk counterparts. The edges, grain boundaries, local strain, chemical bonding, molecular orientation, and the presence of nanodefects in these 2D monolayers (MLs) will strongly affect their properties. Currently, it is still challenging to investigate such atomically thin 2D monolayers with nanoscale spatial resolution, especially in a label-free and non-destructive way. Tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS), which combines the merits of both scanning probe microscopy (SPM) and Raman spectroscopy, has become a powerful analytical technique for studying 2D monolayers, because it allows very high-resolution and high-sensitivity local spectroscopic investigation and imaging and also provides rich chemical information. This review provides a summary of methods to study 2D monolayers and an overview of TERS, followed by an introduction to the current state-of-the-art and theoretical understanding the spatial resolution in TERS experiments. Surface selection rules are also discussed. We then focus on the capabilities and potential of TERS for nanoscale chemical imaging of 2D materials, such as graphene, transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs), and 2D polymers. We predict that TERS will become widely accepted and used as a versatile imaging tool for chemical investigation of 2D materials at the nanoscale.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

尖端增强拉曼光谱:原理,实践和在2D材料纳米光谱成像中的应用
二维(2D)材料由于其惊人的化学,光学,电子和机械性能而与大体积的同类产品不同,因此已成为现代材料研究最广泛的类别之一。这些2D单层(ML)中的边缘,晶界,局部应变,化学键,分子取向以及纳米缺陷的存在将极大地影响其性能。目前,研究具有纳米级空间分辨率的原子薄的2D单分子层仍然具有挑战性,尤其是以无标记且无损的方式。尖端增强拉曼光谱(TERS)结合了扫描探针显微镜(SPM)和拉曼光谱的优点,已成为研究2D单分子膜的强大分析技术,因为它可以进行非常高分辨率和高灵敏度的局部光谱研究和成像,并且还可以提供丰富的化学信息。这篇综述提供了研究2D单分子层的方法的概述以及TERS的概述,然后介绍了当前的最新技术以及对TERS实验中空间分辨率的理论理解。还讨论了表面选择规则。然后,我们将重点关注TERS在2D材料(例如石墨烯,过渡金属二卤化物(TMDC)和2D聚合物)的纳米级化学成像中的功能和潜力。我们预测,TERS将被广泛接受并用作在纳米级对2D材料进行化学研究的通用成像工具。这篇综述提供了研究2D单分子层的方法的概述以及TERS的概述,然后介绍了当前的最新技术以及对TERS实验中空间分辨率的理论理解。还讨论了表面选择规则。然后,我们将重点关注TERS在2D材料(例如石墨烯,过渡金属二卤化物(TMDC)和2D聚合物)的纳米级化学成像中的功能和潜力。我们预测,TERS将被广泛接受并用作在纳米级对2D材料进行化学研究的通用成像工具。这篇综述提供了研究2D单分子层的方法的概述以及TERS的概述,然后介绍了当前的最新技术以及对TERS实验中空间分辨率的理论理解。还讨论了表面选择规则。然后,我们将重点关注TERS在2D材料(例如石墨烯,过渡金属二卤化物(TMDC)和2D聚合物)的纳米级化学成像中的功能和潜力。我们预测,TERS将被广泛接受并用作在纳米级对2D材料进行化学研究的通用成像工具。然后,我们将重点关注TERS在2D材料(例如石墨烯,过渡金属二卤化物(TMDC)和2D聚合物)的纳米级化学成像中的功能和潜力。我们预测,TERS将被广泛接受并用作在纳米级对2D材料进行化学研究的通用成像工具。然后,我们将重点关注TERS在2D材料(例如石墨烯,过渡金属二卤化物(TMDC)和2D聚合物)的纳米级化学成像中的功能和潜力。我们预测,TERS将被广泛接受并用作在纳米级对2D材料进行化学研究的通用成像工具。

ᅟ


























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号