Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2018-10-03 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1375-1 Dong-Ping Zhang , Ling-E Wang , Xiao-Ying Liu , Zhi-Hua Luo , Lei Zheng , Yun He , Bo Zhang
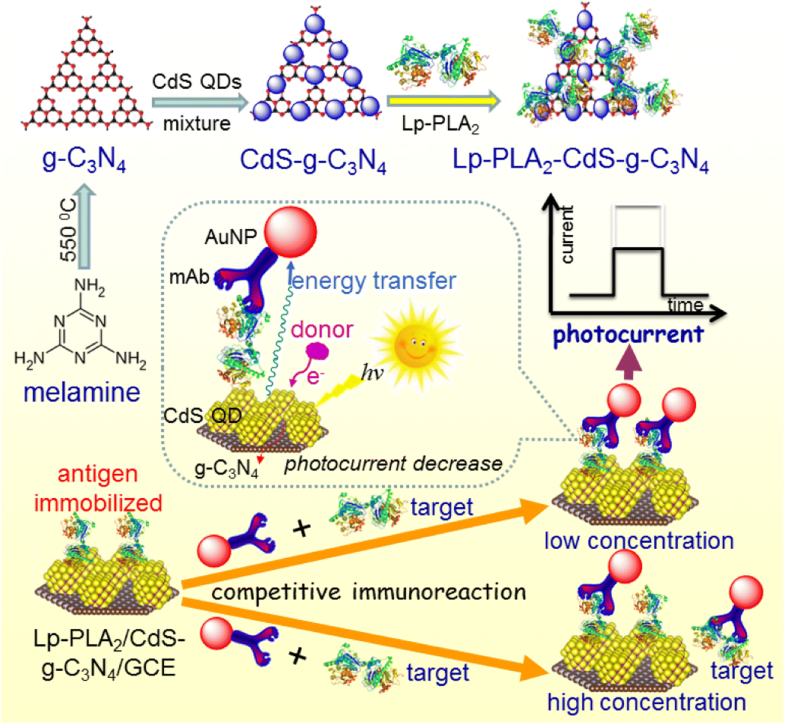
A facile and feasible photoelectrochemical (PEC) immunoassay based on plasmon-enhanced energy transfer between gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and CdS quantum dots (QDs)/g-C3N4 nanosheets was developed for the ultrasensitive detection of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2). To construct such a sensing platform, the immunosensor was prepared by immobilizing Lp-PLA2 on a CdS QDs/g-C3N4-modified electrode. A competitive-type immunoreaction was utilized for Lp-PLA2 detection, with AuNP-labeled anti-Lp-PLA2 antibody used as the competitor. Introducing AuNPs with the specific antibody for the antigen target Lp-PLA2 led to heavy quenching of the photocurrent of CdS QDs/g-C3N4 due to the plasmon-enhanced energy transfer between AuNPs and CdS QDs. The quenching efficiency decreased with increasing target Lp-PLA2 concentration. Under optimal conditions, the PEC immunosensor presented a good photocurrent response to the target Lp-PLA2 in the dynamic linear range of 0.01–300 ng mL−1, with a low detection limit of 5.3 pg mL−1. Other biomarkers and natural enzymes did not interfere with response of this system. The reproducibility and accuracy of this method for the analysis of human serum specimens were evaluated, and the results given by the method developed here were found to closely correspond to the results obtained with commercial Lp-PLA2 ELISA kits. Importantly, this protocol offers promise for the development of exciton–plasmon interaction-based PEC detection systems.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A的光电化学免疫分析
基于金纳米颗粒(AuNPs)和CdS量子点(QDs)/ gC 3 N 4纳米片之间的等离激元增强的能量转移,开发了一种简便可行的光电化学(PEC)免疫测定方法,用于脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A 2(Lp)的超灵敏检测。-PLA 2)。为了构建这样的感测平台,通过将Lp-PLA 2固定在CdS QDs / gC 3 N 4修饰的电极上来制备免疫传感器。竞争性免疫反应与AuNP标记的抗Lp-PLA 2一起用于Lp-PLA 2的检测抗体用作竞争者。由于AuNP和CdS QD之间的等离子体增强能量转移,将具有针对抗原靶标Lp-PLA 2的特异性抗体的AuNP引入导致CdS QDs / gC 3 N 4的光电流的严重淬灭。淬灭效率随目标Lp-PLA 2浓度的增加而降低。在最佳条件下,PEC免疫传感器在0.01–300 ng mL -1的动态线性范围内对目标Lp-PLA 2表现出良好的光电流响应,检测限低至5.3 pg mL -1。其他生物标志物和天然酶不干扰该系统的反应。评估了该方法用于分析人血清标本的可重复性和准确性,发现此处开发的方法给出的结果与商业Lp-PLA 2 ELISA试剂盒获得的结果非常吻合。重要的是,该协议为基于激子-等离子体激元相互作用的PEC检测系统的开发提供了希望。

ᅟ


























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号