Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.2 ) Pub Date : 2018-09-20 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-2062-3 Dilshadbek T. Usmanov 1, 2 , Satoshi Ninomiya 3 , Kenzo Hiraoka 1 , Hiroshi Wada 4 , Hiroshi Nakano 4 , Masaya Matsumura 5 , Sachiyo Sanada-Morimura 5 , Hiroshi Nonami 6
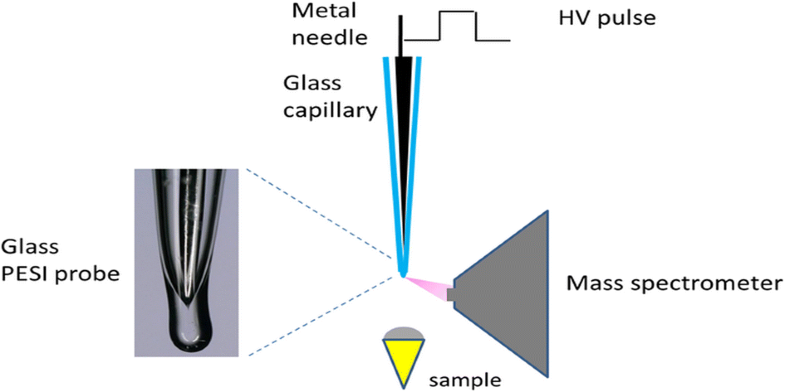
In electrospray, excess charges are supplied to a sample solution by the occurrence of electrochemical reactions. Recently, different versions of electrospray, e.g., dielectric barrier electrospray ionization, inductive desorption electrospray ionization, and electrostatic-ionization driven by dielectric polarization, have been reported in which the sample solution was not in direct contact with the metal electrode but separated by dielectric materials. The objective of the current work is to elucidate the mechanism of dielectric barrier electrospray. A sealed borosilicate glass capillary inserted with a fine acupuncture needle was used as a probe. A sample solution (~ 400 nL) was captured on the glass capillary tip and a positive high voltage (HV) pulse (+ 4.5 kV) was applied to the internal metal electrode. Mass spectra were measured as a function of the HV pulse width from μs to 10 s. Ions started to be detected with the pulse width of ~ 5 ms. The ion intensities increased slowly with time and reached a plateau in a few seconds. The charge distribution of cytochrome c [M + nH]n+ shifted to higher n values from a few ms to seconds. In addition to cone-jet mode normal electrospray that lasted until all the liquid sample was depleted from the glass tip, the polarization-induced electrospray ionization was observed at the early stage of the HV application.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

尖端密封的细玻璃毛细管插入针刺电极产生的电喷雾
在电喷雾中,过量的电荷通过发生电化学反应而提供给样品溶液。近来,已经报道了不同版本的电喷雾,例如介电势垒电喷雾电离,感应解吸电喷雾电离和由电介质极化驱动的静电电离,其中样品溶液未与金属电极直接接触,但被电介质分开。当前工作的目的是阐明电介质阻挡层电喷雾的机理。使用插入有细针刺针的密封的硼硅酸盐玻璃毛细管作为探针。在玻璃毛细管尖端上捕获样品溶液(〜400 nL),并将正高压(HV)脉冲(+ 4.5 kV)施加到内部金属电极上。测得的质谱是HV脉冲宽度(μs至10 s)的函数。开始以〜5 ms的脉冲宽度检测离子。离子强度随时间缓慢增加,并在几秒钟内达到平稳状态。细胞色素c的电荷分布[M + nH]n +从更高的n值从几毫秒变为几秒。除了持续到所有液体样品从玻璃尖端耗尽之前的锥形喷射模式正常电喷雾外,在HV应用的早期阶段还观察到了极化诱导的电喷雾电离。

ᅟ


























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号