Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2018-07-31 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1288-z Pratikkumar Rathod , Manjeet Kaur , Hsin-Pin Ho , Marissa E. Louis , Basant Dhital , Philip Durlik , Gregory S. Boutis , Kevin J. Mark , Jong I. Lee , Emmanuel J. Chang
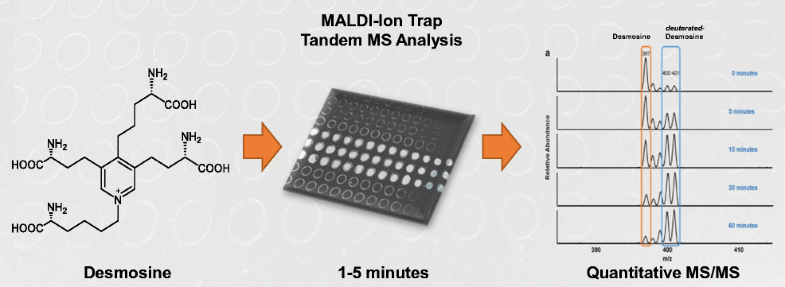
Desmosine (Des) and isodesmosine (Isodes), cross-linking amino acids in the biomolecule elastin, may be used as biomarkers for various pathological conditions associated with elastin degradation. The current study presents a novel approach to quantify Des and Isodes using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI)-tandem mass spectrometry (MS2) in a linear ion trap coupled to a vacuum MALDI source. MALDI-MS2 analyses of Des and Isodes are performed using stable-isotope-labeled desmosine d4 (labeled-Des) as an internal standard in different biological fluids, such as urine and serum. The method demonstrated linearity over two orders of magnitude with a detection limit of 0.02 ng/μL in both urine and serum without enrichment prior to mass spectrometry, and relative standard deviation of < 5%. The method is used to evaluate the time-dependent degradation of Des upon UV irradiation (254 nm) and found to be consistent with quantification by 1H NMR. This is the first characterized MALDI-MS2 method for quantification of Des and Isodes and illustrates the potential of MALDI-ion trap MS2 for effective quantification of biomolecules. The reported method represents improvement over current liquid chromatography-based methods with respect to analysis time and solvent consumption, while maintaining similar analytical characteristics.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

使用MALDI离子阱串联质谱法对地西米碱和异地西米碱进行定量
生物分子弹性蛋白中的交联氨基酸Desmosine(Des)和Isodesmosine(Isodes)可用作与弹性蛋白降解相关的各种病理学状况的生物标志物。当前的研究提出了一种在耦合至真空MALDI源的线性离子阱中使用基质辅助激光解吸电离(MALDI)串联质谱(MS 2)定量Des和Isode的新颖方法。使用稳定同位素标记的desmosine d 4对Des和Isodes进行MALDI-MS 2分析(标记为Des)作为不同生物体液(例如尿液和血清)中的内标。该方法在两个数量级上表现出线性,在尿液和血清中的检出限均为0.02 ng /μL,质谱分析前未富集,相对标准偏差<5%。该方法用于评估紫外线辐射(254 nm)时Des的时间依赖性降解,发现与1 H NMR定量结果一致。这是定量分析Des和Isode的第一种特征化MALDI-MS 2方法,它说明了MALDI离子阱MS 2的潜力用于有效定量生物分子。报告的方法在保持相似的分析特性的同时,相对于当前的基于液相色谱的方法,在分析时间和溶剂消耗方面均表现出改进。

ᅟ



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号