Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2018-08-20 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1316-z Zheng Xiang , Ruixuan Wan , Bingjie Zou , Xiemin Qi , Qing Huang , Shalen Kumar , Janet L. Pitman , Guohua Zhou , Qinxin Song
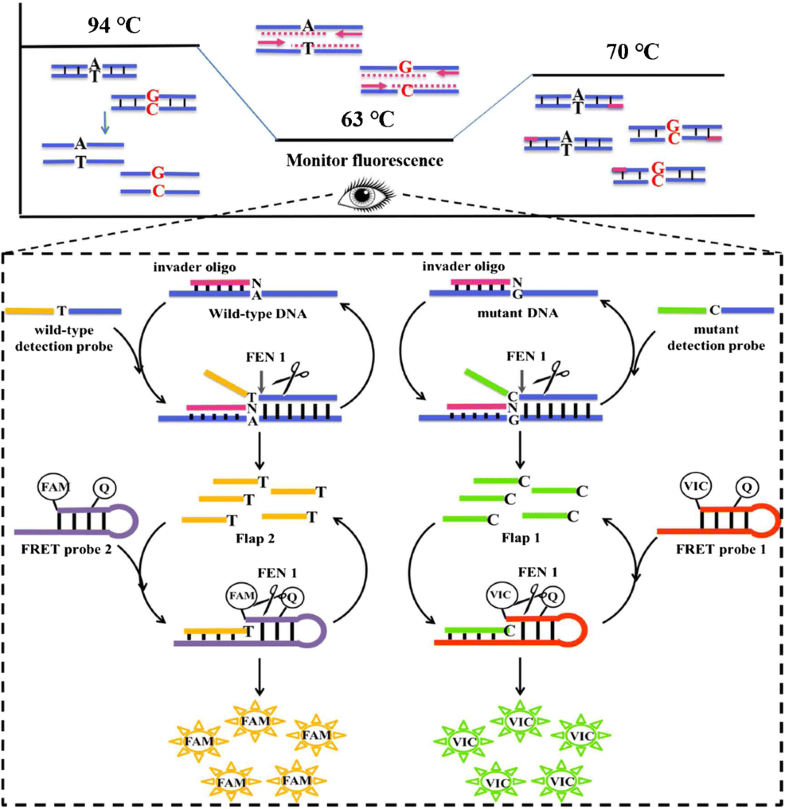
Detection of EGFR mutations in circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is beneficial to monitor the therapeutic effect, tumor progression, and drug resistance in real time. However, it requires that the mutation detection method has the ability to quantify the mutation abundance accurately. Although the next-generation sequencing (NGS) and digital PCR showed high sensitivity for quantifying mutations in cfDNA, the use of expensive equipment and the high-cost hampered their applications in the clinic. Herein, we propose a highly sensitive and specific real-time PCR by employing serial invasive reaction as a sequence identifier for quantifying EGFR mutation abundance in cfDNA (termed as qPCR-Invader). The mutation abundance can be quantified by using the difference of Ct values between mutant and wild-type targets without the need of making a standard curve. The method can quantify a mutation level as lower as 0.1% (10 copies/tube). Thirty-six tissue samples from non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients were detected by our method and 14/36 tissues gave EGFR L858R mutation-positive results, whereas ARMS-PCR just identified 12 of L858R mutant samples. The two inconsistent samples were confirmed as L858R mutant by pyrophosphorolysis-activated polymerization method, indicating that qPCR-Invader is more sensitive than ARMS-PCR for mutation detection. The L858R mutation abundances of 19 cfDNA samples detected by qPCR-Invader were close to that from NGS, indicating our method can precisely quantify mutation abundance in cfDNA. The qPCR-Invader just needs a common real-time PCR device to accomplish quantification of EGFR mutations, and the fluorescence probes are universal for any target detection. Therefore, it could be used in most laboratories to analyze mutations in cfDNA.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

通过使用串行侵入性反应作为序列标识符来定量cfDNA中EGFR突变丰度的高灵敏性和特异性实时PCR
循环无细胞DNA(cfDNA)中EGFR突变的检测有利于实时监测治疗效果,肿瘤进展和耐药性。但是,它要求突变检测方法具有准确定量突变丰度的能力。尽管下一代测序(NGS)和数字PCR对cfDNA中的突变定量显示出很高的灵敏度,但是昂贵的设备的使用和高昂的成本阻碍了它们在临床中的应用。在本文中,我们提出了一种高度敏感和实时的实时PCR技术,该技术采用串行侵入性反应作为序列标识符来量化cfDNA中的EGFR突变丰度(称为qPCR-Invader)。可以通过使用突变体和野生型靶之间的Ct值之差来定量突变丰度,而无需绘制标准曲线。该方法可将突变水平量化为低至0.1%(每管10拷贝)。通过我们的方法检测了36份来自非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)患者的组织样本,而14/36个组织的EGFR L858R突变阳性结果,而ARMS-PCR仅鉴定了12份L858R突变样本。通过焦磷酸解激活聚合法将两个不一致的样品确认为L858R突变体,表明qPCR-Invader在突变检测方面比ARMS-PCR更为灵敏。qPCR-Invader检测的19个cfDNA样品的L858R突变丰度与NGS接近,表明我们的方法可以精确定量cfDNA的突变丰度。qPCR-Invader只需一个通用的实时PCR装置即可完成EGFR突变的定量分析,而荧光探针对于任何靶标检测都是通用的。因此,它可以在大多数实验室中用于分析cfDNA中的突变。

ᅟ



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号