Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2018-05-17 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1131-6 Tina M. Binz , Franziska Gaehler , Clarissa D. Voegel , Mathias Hofmann , Markus R. Baumgartner , Thomas Kraemer
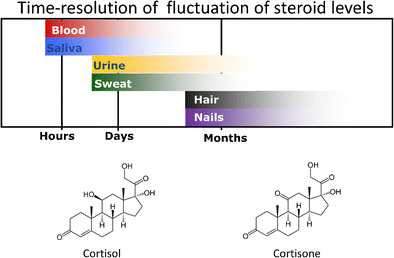
Hair samples are increasingly used for measuring the long-term stress mediator cortisol. However, hair is not always available and nails (finger or toe), as a keratinized matrix, may be an alternative to hair. In order to measure cortisol and cortisone in the nail matrix, an LC-MS/MS method has been developed and validated using 13C3-labeled surrogate analytes. Both analytes were measured in ESI negative mode as formic acid adducts. Different sample preparation techniques were assessed, and single-step extraction in methanol was established for determination of cortisone and cortisol in the nail matrix. The method was successfully validated with limits of detection (LOD) and limits of quantification (LOQ) of 0.5 and 1.0 pg/mg for cortisol and cortisone, respectively. The calibration curve was linear up to a concentration of 500 pg/mg. Recovery was good for both analytes and showed values over 50%. Matrix effects with ion suppression occurred for both substances but could be corrected by the use of internal standard. Accuracy and precision were in the accepted range of ± 20% for both substances. The method was successfully applied to determine cortisol and cortisone concentrations in authentic nail samples. Cortisol and cortisone concentrations varied significantly among different fingernails, being highest in the little fingernails and lowest in the thumbnails. It could be shown that even in only 1 mg nail sample cortisol and cortisone can be reliably quantified. No correlation between hair and nail cortisol and cortisone concentrations could be found. Furthermore, cortisol and cortisone concentrations were significantly higher in hair.
Graphical abstract
中文翻译:

LC-MS / MS对指甲中内源性皮质醇和可的松的系统研究及其与头发的相关性
头发样品越来越多地用于测量长期压力介质皮质醇。但是,头发并不总是可以使用,指甲(手指或脚趾)作为角质化基质,可以替代头发。为了测量指甲基质中的皮质醇和可的松,已开发出一种LC-MS / MS方法并使用13 C 3进行了验证。标记的替代分析物。两种分析物均以ESI阴性模式作为甲酸加合物进行测量。评估了不同的样品制备技术,并建立了甲醇中的一步萃取法,用于测定指甲基质中的可的松和皮质醇。皮质醇和可的松的检出限(LOD)和定量限(LOQ)分别为0.5和1.0 pg / mg,成功地验证了该方法。校准曲线是线性的,直到浓度为500 pg / mg。两种分析物的回收率均良好,显示值超过50%。两种物质均发生了具有离子抑制作用的基体效应,但可以通过使用内标进行校正。两种物质的准确性和精密度均在±20%的可接受范围内。该方法已成功应用于确定真实指甲样品中皮质醇和可的松的浓度。不同指甲之间的皮质醇和可的松浓度差异显着,在小指甲中最高,在缩略图中最低。可以证明,即使仅在1 mg指甲样品中,皮质醇和可的松也可以可靠地定量。头发和指甲的皮质醇和可的松浓度之间没有相关性。此外,头发中的皮质醇和可的松浓度明显更高。头发和指甲的皮质醇和可的松浓度之间没有相关性。此外,头发中的皮质醇和可的松浓度明显更高。头发和指甲的皮质醇和可的松浓度之间没有相关性。此外,头发中的皮质醇和可的松浓度明显更高。

图形概要



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号