Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.2 ) Pub Date : 2018-07-09 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-2012-0 Bojana Opačić 1 , Nathan M. Hoffman 1 , Zachary P. Gotlib 1 , Brian H. Clowers 1 , Peter T. A. Reilly 1
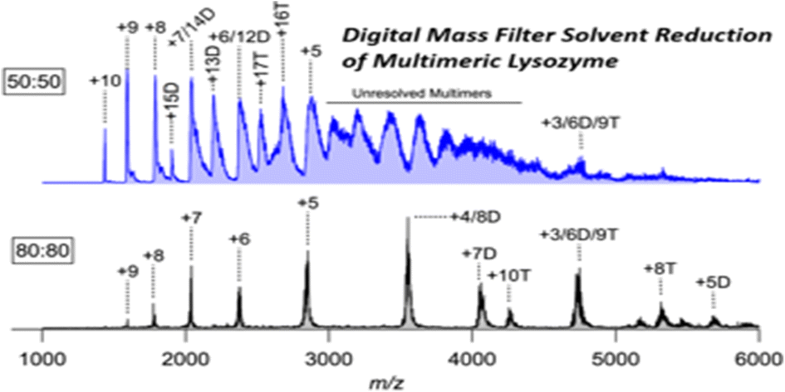
With advances in the precision of digital electronics, waveform generation technology has progressed to a state that enables the creation of m/z filters that are purely digitally driven. These advances present new methods of performing mass analyses that provide information from a chemical system that are inherently difficult to achieve by other means. One notable characteristic of digitally driven mass filters is the capacity to transmit ions at m/z ratios that vastly exceed the capabilities of traditional resonant systems. However, the capacity to probe ion m/z ratios that span multiple orders of magnitudes across multiple orders of magnitude presents a new set of issues requiring a solution. In the present work, when probing multiply charged protein species beyond m/z 2000 using a gentle atmospheric pressure interface, the presence of solvent adducts and poorly resolved multimers can severely degrade spectral fidelity. Increasing energy imparted into a target ion population is one approach minimizing these clusters; however, the use of digital waveform technology provides an alternative that maximizes ion transport efficiency and simultaneously minimizes solvent clustering. In addition to the frequency of the applied waveform, digital manipulation also provides control over the duty cycle of the target waveform. This work examines the conditions and approach leading to optimal digital waveform operation to minimize solvent clustering.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

在蛋白质的质量过滤器分析过程中使用数字波形缓解溶剂簇聚
随着数字电子技术精度的提高,波形生成技术已经发展到可以创建纯数字驱动的m / z滤波器的状态。这些进步提供了执行质量分析的新方法,这些方法提供了化学系统提供的信息,而这些信息固有地很难通过其他方式实现。数字驱动质量过滤器的一个显着特征是以m / z比传输离子的能力,大大超过了传统共振系统的能力。但是,探测离子的能力m / z跨越多个数量级的比率呈现出一系列需要解决的新问题。在目前的工作中,当探测超过m / z的多重带电蛋白质时2000年使用温和的大气压界面,溶剂加合物和不良拆分的多聚体的存在会严重降低光谱保真度。增加赋予目标离子群的能量是使这些簇最小化的一种方法。但是,数字波形技术的使用提供了一种替代方案,可以最大程度地提高离子传输效率,并同时最大程度地减少溶剂聚集。除了所施加波形的频率外,数字操作还可以控制目标波形的占空比。这项工作研究了导致最佳数字波形操作以最小化溶剂聚集的条件和方法。

ᅟ


























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号