Nano Research ( IF 9.9 ) Pub Date : 2018-06-05 , DOI: 10.1007/s12274-018-2097-6 Paola Castrucci , Filippo Fabbri , Tiziano Delise , Manuela Scarselli , Matteo Salvato , Sara Pascale , Roberto Francini , Isabelle Berbezier , Christoph Lechner , Fatme Jardali , Holger Vach , Maurizio De Crescenzi
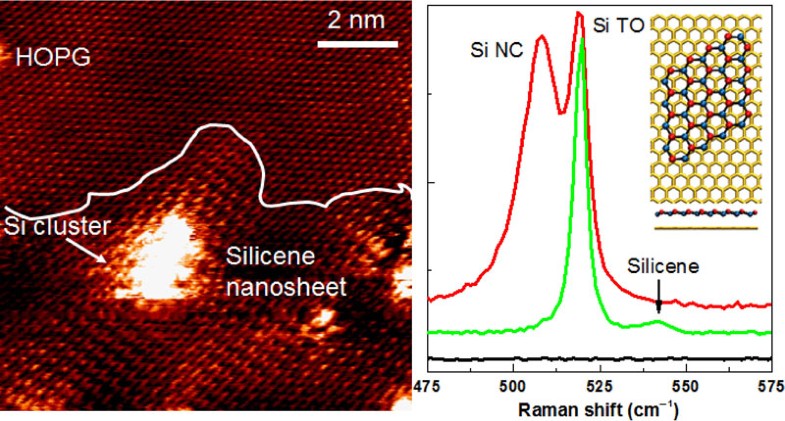
The fascinating properties of two dimensional (2D) crystals have gained increasing interest for many applications. The synthesis of a 2D silicon structure, namely silicene, is attracting great interest for possible development of next generation electronic devices. The main difficulty in working with silicene remains its strong tendency to oxidation when exposed to air as a consequence of its relatively highly buckled structure. In this work, we univocally identify the Raman mode of air-stable low-buckled silicene nanosheets synthesized on highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) located at 542.5 cm−1. The main focus of this work is Raman spectroscopy and mapping analyses in combination with ab initio calculations. Scanning tunneling microscopy images reveal the presence of a patchwork of Si three-dimensional (3D) clusters and contiguous Si areas presenting a honeycomb atomic arrangement, rotated by 30° with respect to the HOPG substrate underneath, with a lattice parameter of 0.41 ± 0.02 nm and a buckling of the Si atoms of 0.05 nm. Raman analysis supports the co-existence of 3D silicon clusters and 2D silicene. The Raman shift of low-buckled silicene on an inert substrate has not been reported so far and it is completely different from the one calculated for free-standing silicene and the ones measured for silicene grown on Ag(111) surfaces. Our experimental results are perfectly reproduced by our ab initio calculations of deposited silicene nanosheets. This leads us to conclude that the precise value of the observed Raman shift crucially depends on the strain between the silicene and the HOPG substrate.
中文翻译:

惰性石墨表面上的空气稳定性硅纳米片的拉曼研究
二维(2D)晶体的引人入胜的特性已在许多应用中引起了越来越多的关注。二维硅结构即硅的合成对下一代电子设备的可能发展引起了极大的兴趣。使用硅树脂的主要困难仍然是其暴露于空气中时由于其相对较高的弯曲结构而具有很强的氧化趋势。在这项工作中,我们明确地确定了在542.5 cm-1的高度取向的热解石墨(HOPG)上合成的空气稳定的低屈曲硅纳米片的拉曼模式。这项工作的主要焦点是在组合拉曼光谱和分析映射与从头计算。扫描隧道显微镜图像显示存在Si三维(3D)簇和连续的Si区域的拼凑,这些区域呈蜂窝状原子排列,相对于下方的HOPG衬底旋转了30°,晶格参数为0.41±0.02 nm并且Si原子的屈曲为0.05nm。拉曼分析支持3D硅团簇和2D硅石的共存。迄今为止,尚未报道惰性基材上低屈曲硅的拉曼位移,它与针对独立式硅所计算的拉曼位移和针对在Ag(111)表面上生长的硅所测得的拉曼位移完全不同。我们的实验从头开始就完美地再现了我们的实验结果沉积的硅纳米片的计算。这使我们得出结论,所观察到的拉曼位移的精确值关键取决于硅烯和HOPG衬底之间的应变。



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号