Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.2 ) Pub Date : 2018-05-31 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-1993-z Cheryl Frankfater 1 , Xuntian Jiang 2 , Fong-Fu Hsu 1
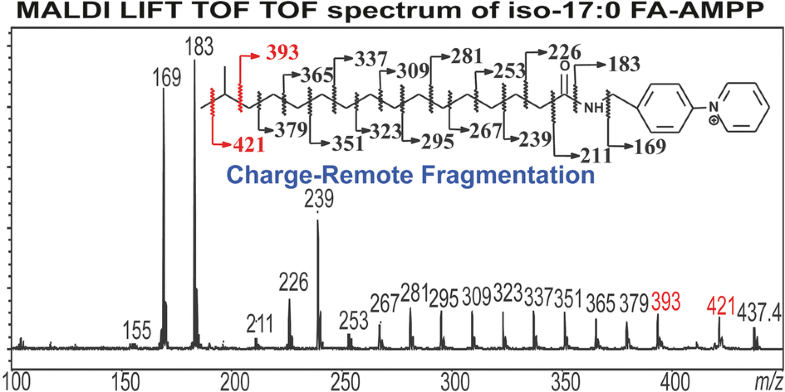
Charge remote fragmentation (CRF) elimination of CnH2n+2 residues along the aliphatic tail of long chain fatty acid is hall mark of keV high-energy CID fragmentation process. It is an important fragmentation pathway leading to structural characterization of biomolecules by CID tandem mass spectrometry. In this report, we describe MALDI LIFT TOF-TOF mass spectrometric approach to study a wide variety of fatty acids (FAs), which were derivatized to N-(4-aminomethylphenyl) pyridinium (AMPP) derivative, and desorbed as M+ ions by laser with or without matrix. The high-energy MALDI LIFT TOF-TOF mass spectra of FA-AMPP contain fragment ions mainly deriving from CRF cleavages of CnH2n+2 residues, as expected. These ions together with ions from specific cleavages of the bond(s) involving the functional group within the molecule provide more complete structural identification than those produced by low-energy CID/HCD using a linear ion-trap instrument. However, this LIFT TOF-TOF mass spectrometric approach inherits low sensitivity, a typical feature of high-energy CID tandem mass spectrometry. Because of the lack of unit mass precursor ion selection with sufficient sensitivity of the current LIFT TOF-TOF technology, product ion spectra from same chain length fatty acids with difference in one or two double bonds in a mixture are not distinguishable.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

MALDI LIFT-TOF / TOF质谱法表征长链脂肪酸为N-(4-氨基甲基苯基)吡啶鎓衍生物
沿长链脂肪酸脂族末端的C n H 2n + 2残基的电荷远程断裂(CRF)消除是keV高能CID断裂过程的标志。它是一条重要的片段化途径,可通过CID串联质谱法对生物分子进行结构表征。在本报告中,我们描述了MALDI LIFT TOF-TOF质谱方法,以研究多种脂肪酸(FAs),这些脂肪酸被衍生为N-(4-氨基甲基苯基)吡啶鎓(AMPP)衍生物,并被M +离子解吸带或不带矩阵的激光。FA-AMPP的高能MALDI LIFT TOF-TOF质谱包含的碎片离子主要来自C n H 2n + 2的CRF裂解残留物,如预期的那样。与使用线性离子阱仪器通过低能CID / HCD产生的离子相比,这些离子与来自涉及分子内官能团的键的特定裂解的离子一起提供了更完整的结构鉴定。但是,这种LIFT TOF-TOF质谱方法继承了低灵敏度,这是高能CID串联质谱的典型特征。由于目前的LIFT TOF-TOF技术缺乏足够的灵敏度来选择单位质量的前体离子,因此无法区分来自相同链长脂肪酸的混合物中具有一个或两个双键差异的产物离子光谱。

ᅟ


























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号