Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.2 ) Pub Date : 2018-05-22 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-1969-z Jiana Duan 1 , I Jonathan Amster 1
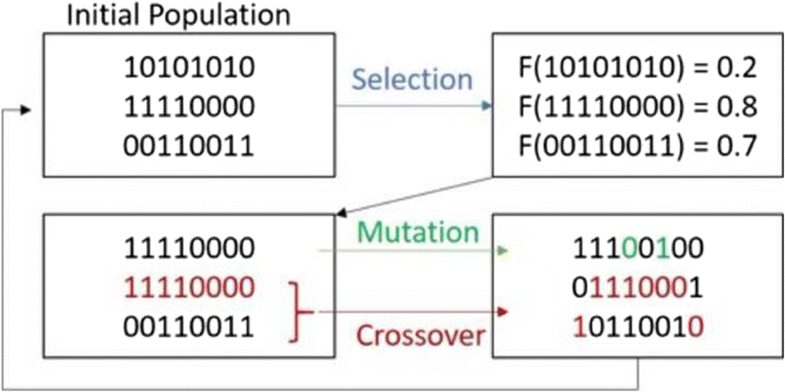
The biological interactions between glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) and other biomolecules are heavily influenced by structural features of the glycan. The structure of GAGs can be assigned using tandem mass spectrometry (MS2), but analysis of these data, to date, requires manually interpretation, a slow process that presents a bottleneck to the broader deployment of this approach to solving biologically relevant problems. Automated interpretation remains a challenge, as GAG biosynthesis is not template-driven, and therefore, one cannot predict structures from genomic data, as is done with proteins. The lack of a structure database, a consequence of the non-template biosynthesis, requires a de novo approach to interpretation of the mass spectral data. We propose a model for rapid, high-throughput GAG analysis by using an approach in which candidate structures are scored for the likelihood that they would produce the features observed in the mass spectrum. To make this approach tractable, a genetic algorithm is used to greatly reduce the search-space of isomeric structures that are considered. The time required for analysis is significantly reduced compared to an approach in which every possible isomer is considered and scored. The model is coded in a software package using the MATLAB environment. This approach was tested on tandem mass spectrometry data for long-chain, moderately sulfated chondroitin sulfate oligomers that were derived from the proteoglycan bikunin. The bikunin data was previously interpreted manually. Our approach examines glycosidic fragments to localize SO3 modifications to specific residues and yields the same structures reported in literature, only much more quickly.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

一种解释糖胺聚糖串联质谱的自动化、高通量方法
糖胺聚糖 (GAG) 和其他生物分子之间的生物相互作用很大程度上受到聚糖结构特征的影响。GAG 的结构可以使用串联质谱 (MS 2 ) 进行分配,但迄今为止,对这些数据的分析需要手动解释,这是一个缓慢的过程,为更广泛地部署这种方法来解决生物学相关问题带来了瓶颈。自动解释仍然是一项挑战,因为 GAG 生物合成不是模板驱动的,因此无法像蛋白质那样从基因组数据预测结构。非模板生物合成导致结构数据库的缺乏,需要采用从头的方法来解释质谱数据。我们提出了一种快速、高通量 GAG 分析的模型,通过使用一种方法对候选结构进行评分,以评估它们产生质谱中观察到的特征的可能性。为了使这种方法易于处理,使用遗传算法来大大减少所考虑的异构体结构的搜索空间。与考虑并评分每种可能的异构体的方法相比,分析所需的时间显着减少。该模型使用 MATLAB 环境编码在软件包中。该方法在串联质谱数据上进行了测试,用于检测源自蛋白聚糖 bikunin 的长链、适度硫酸化的硫酸软骨素低聚物。Bikunin 数据之前是手动解释的。我们的方法检查糖苷片段,将 SO 3修饰定位到特定残基,并产生与文献中报道的相同结构,只是速度更快。

ᅟ


























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号