Journal of the American Society for Mass Spectrometry ( IF 3.2 ) Pub Date : 2018-05-11 , DOI: 10.1007/s13361-018-1972-4 Thierry N. J. Fouquet 1 , Robert B. Cody 2 , Yuka Ozeki 3 , Shinya Kitagawa 3 , Hajime Ohtani 3 , Hiroaki Sato 1
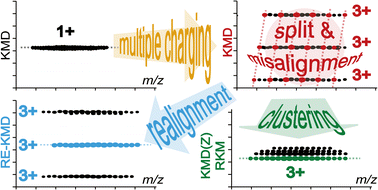
The Kendrick mass defect (KMD) analysis of multiply charged polymeric distributions has recently revealed a surprising isotopic split in their KMD plots—namely a 1/z difference between KMDs of isotopes of an oligomer at charge state z. Relying on the KMD analysis of actual and simulated distributions of poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO), the isotopic split is mathematically accounted for and found to go with an isotopic misalignment in certain cases. It is demonstrated that the divisibility (resp. indivisibility) of the nominal mass of the repeating unit (R) by z is the condition for homolog ions to line up horizontally (resp. misaligned obliquely) in a KMD plot. Computing KMDs using a fractional base unit R/z eventually corrects the misalignments for the associated charge state while using the least common multiple of all the charge states as the divisor realigns all the points at once. The isotopic split itself can be removed by using either a new charge-dependent KMD plot compatible with any fractional base unit or the remainders of KM (RKM) recently developed for low-resolution data all found to be linked in a unified theory. These original applications of the fractional base units and the RKM plots are of importance theoretically to satisfy the basics of a mass defect analysis and practically for a correct data handling of single stage and tandem mass spectra of multiply charged homo- and copolymers.
ᅟ
中文翻译:

关于带正电荷的聚合物离子的Kendrick质量缺陷图:分裂,错位以及如何校正它们
最近对多电荷聚合物分布进行的Kendrick质量缺陷(KMD)分析显示,其KMD图中存在令人惊讶的同位素分裂-即低聚物在电荷状态z下的同位素KMD之间存在1 / z的差异。依靠KMD对聚环氧乙烷(PEO)实际和模拟分布的分析,可以对同位素分裂进行数学解释,并发现在某些情况下存在同位素错位。结果表明,重复单元(R)的标称质量的可除性(resin。indivisibility)除以z是在KMD图中同源离子水平排列(相对于斜向错位)的条件。使用分数基本单位R / z计算KMD最终校正所有相关电荷状态的失准,同时使用所有电荷状态的最小公倍数,因为除数可一次重新对准所有点。同位素分裂本身可以通过使用与任何分数基础单位兼容的新的电荷依赖性KMD图或最近为低分辨率数据开发的KM(RKM)其余部分(都在统一理论中关联)来消除。分数基础单位和RKM图的这些原始应用在理论上对满足质量缺陷分析的基础以及在实际中正确处理多重荷电均聚物和共聚物的单级和串联质谱数据具有重要意义。

ᅟ



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号