Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2018-04-14 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-1032-8 N. M. Elzahar , N. Magdy , Amira M. El-Kosasy , Michael G. Bartlett
Synthetic antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotides (PS) have undergone rapid development as novel therapeutic agents. The increasing significance of this class of drugs requires significant investment in the development of quality control methods. The determination of the many degradation pathways of such complex molecules presents a significant challenge. However, an understanding of the potential impurities that may arise is necessary to continue to advance these powerful new therapeutics. In this study, four different antisense oligonucleotides representing several generations of oligonucleotide therapeutic agents were evaluated under various stress conditions (pH, thermal, and oxidative stress) using ion-pairing reversed-phase liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (IP-RPLC-MS/MS) to provide in-depth characterization and identification of the degradation products. The oligonucleotide samples were stressed under different pH values at 45 and 90 °C. The main degradation products were observed to be losses of nucleotide moieties from the 3′- and 5′-terminus, depurination, formation of terminal phosphorothioates, and production of ribose, ribophosphorothioates (Rp), and phosphoribophosphorothioates (pRp). Moreover, the effects of different concentrations of hydrogen peroxide were studied resulting in primarily extensive desulfurization and subsequent oxidation of the phosphorothioate linkage to produce the corresponding phosphodiester. The reaction kinetics for the degradation of the oligonucleotides under the different stress conditions were studied and were found to follow pseudo-first-order kinetics. Differences in rates exist even for oligonucleotides of similar length but consisting of different sequences.
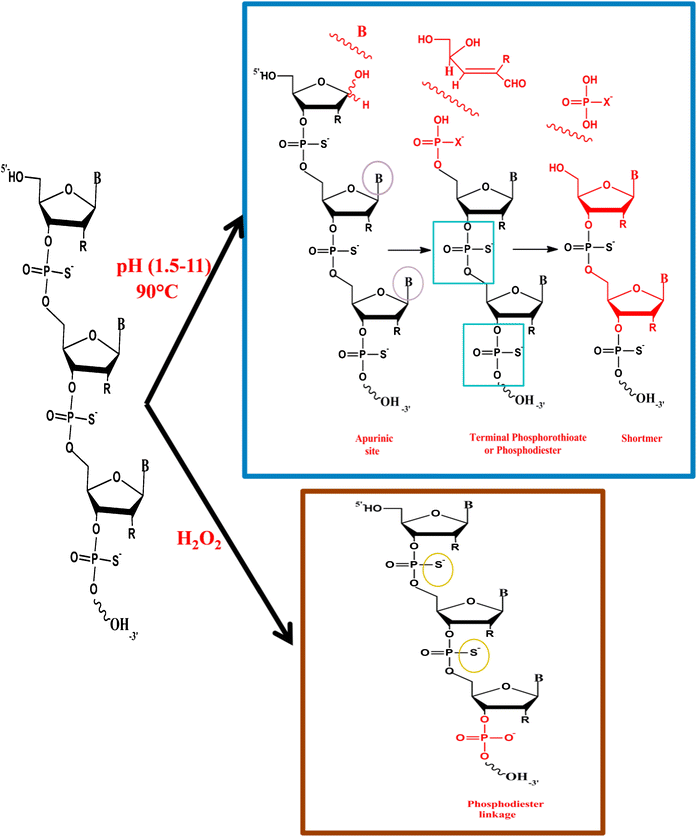
Identification of degradation products across several generations of oligonucleotide therapeutics using LC-MS
中文翻译:

使用液相色谱质谱法对治疗性寡核苷酸的降解产物进行表征
合成的反义硫代磷酸酯寡核苷酸(PS)已作为新的治疗剂迅速发展。这类药物日益重要的意义要求在质量控制方法开发方面进行大量投资。确定这种复杂分子的许多降解途径提出了重大挑战。但是,必须了解可能出现的潜在杂质,才能继续推进这些功能强大的新疗法。在这项研究中,代表了几代寡核苷酸治疗剂的四种不同的反义寡核苷酸在各种胁迫条件(pH,温度,离子对反相液相色谱串联质谱(IP-RPLC-MS / MS)进行深入表征和鉴定降解产物。在45和90°C的不同pH值下对寡核苷酸样品施加压力。观察到主要降解产物是3'和5'末端的核苷酸部分的损失,脱嘌呤,末端硫代磷酸酯的形成以及核糖,硫代磷酸硫代磷酸酯(Rp)和硫代磷酸氢硫代磷酸酯(pRp)的产生。而且 以及核糖,硫代磷酸核糖酯和硫代磷酸核糖酯的生产。而且 以及核糖,硫代磷酸核糖酯和硫代磷酸核糖酯的生产。而且,研究了不同浓度的过氧化氢的作用,该作用主要导致广泛的脱硫和随后的硫代磷酸酯键的氧化,以产生相应的磷酸二酯。研究了在不同应力条件下降解寡核苷酸的反应动力学,发现其遵循伪一级动力学。即使对于长度相似但由不同序列组成的寡核苷酸,速率也存在差异。

使用LC-MS鉴定几代寡核苷酸治疗剂的降解产物


























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号