Nano Research ( IF 9.9 ) Pub Date : 2018-04-03 , DOI: 10.1007/s12274-018-2044-6 Huipeng Li , Zhanwei Zhou , Feiran Zhang , Yuxin Guo , Xue Yang , Hulin Jiang , Fei Tan , David Oupicky , Minjie Sun
In this study, a networked swellable dextrin nanogel (DNG) was developed to achieve stimulated responsive small interfering RNA (siRNA) release for melanoma tumor therapy. siRNA was loaded into multidimensional dextrin nanogels by charge condensation with positive arginine residues modified in the dextrin backbone. Moreover, the networked nanogel was destroyed and loosened based on its bioreducible responsive property to control accelerated siRNA release in a bioreducible intracellular environment, while it remained stable under normal physiological conditions. We demonstrated that DNGs had swellable and disassembly properties under reduced buffer condition by transmission electron microscopy evaluation. The DNGs achieved an endosomal escape followed by selective release of the cargo into the cytosol by glutathione-triggered disassembly according to confocal microscopy observation. Thus, this smart nanogel achieved outstanding luciferase gene silencing efficiency and decreased Bcl2 protein expression in vitro and in vivo based on western blot analysis. Moreover, this nanogel exhibited superior anti-tumor activity for B16F10 xenograft tumors in C57BL/6 mice. These results demonstrate that the networked DNGs are effective for gene condensation and controlled intracellular release for tumor therapy. Overall, these findings suggest that this multidimensional swellable stimuli-responsive dextrin nanogel is an innovative strategy with great promise for gene and drug delivery.
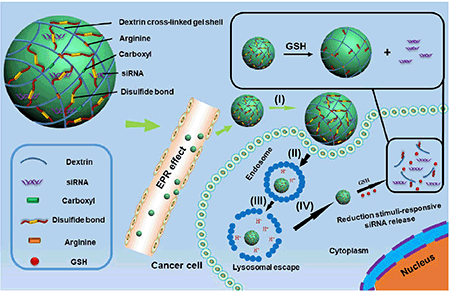
中文翻译:

负载Bcl2 siRNA的网络化可溶糊精纳米凝胶用于黑色素瘤治疗
在这项研究中,开发了一种网络化的可溶糊精纳米凝胶(DNG),以实现刺激性反应性小干扰RNA(siRNA)的释放,用于黑色素瘤肿瘤治疗。通过在糊精骨架中修饰的正精氨酸残基进行电荷缩合,将siRNA加载到多维糊精纳米凝胶中。此外,网络化的纳米凝胶由于其生物可还原的响应特性而被破坏和疏松,以控制在生物可还原的细胞内环境中加速的siRNA释放,而在正常生理条件下仍保持稳定。通过透射电子显微镜评估,我们证明了DNG在减少的缓冲条件下具有可膨胀和可拆卸的特性。根据共聚焦显微镜观察,DNGs实现了内体逃逸,然后通过谷胱甘肽触发的拆卸将货物选择性释放到胞质溶胶中。因此,这种智能纳米凝胶实现了出色的荧光素酶基因沉默效率并降低了Bcl2蛋白表达基于蛋白质印迹分析的体外和体内。此外,这种纳米凝胶对C57BL / 6小鼠的B16F10异种移植肿瘤表现出优异的抗肿瘤活性。这些结果证明,联网的DNG对于基因浓缩有效,并且在肿瘤治疗中控制细胞内释放。总体而言,这些发现表明,这种多维可溶胀的刺激响应性糊精纳米凝胶是一种创新的策略,对基因和药物的输送具有广阔的前景。




























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号