Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2018-01-20 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-0859-3 Kun Deng , Yong Zhang , Xuedong Tong
A new homogeneous electrochemical sensing system was developed for sensitive detection of microRNA-21 (miRNA-21) based on target-induced glucose release from propylamine-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticle (MSN) with glucometer readout. Glucose molecules (as the signal tracers) were initially gated into the pores through the interaction of the negatively charged anchor DNA with the aminated MSN. Upon addition of target miRNA, the analyte competitively hybridized with anchor DNA to form the RNA-DNA duplex, thus resulting in detachment of anchor DNA from the MSN accompanying the pore opening. The loaded glucose molecules released out from the pores because of concentration gradients, which could be detected by using a portable personal glucometer (PGM). Experimental results indicated that the PGM signal increased with the increasing miRNA level, and exhibited a good linear dependence on the miRNA-21 concentration from 50 pM to 5.0 nM with a detection limit of 19 pM under optimum conditions. Additionally, multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles also showed good stability and favorable selectivity, and satisfactory accuracy for the miRNA detection in cell lysates with quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Such good analytical performance endows it as a promising scheme for the efficient and convenient detection of miRNA in clinical diagnosis and therapy.
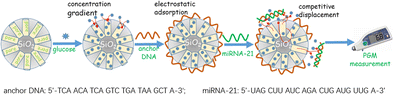
An electrochemical sensing system is designed for detection of microRNA-21 based on target-induced glucose release from propylamine-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticle with glucometer readout.
中文翻译:

基于葡萄糖胺读数的丙胺官能化介孔二氧化硅对microRNA-21的灵敏电化学检测
开发了一种新的均相电化学传感系统,用于基于丙胺官能化的介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒(MSN)的靶诱导葡萄糖释放,并通过血糖仪读数灵敏检测microRNA-21(miRNA-21)。葡萄糖分子(作为信号示踪剂)最初是通过带负电荷的锚定DNA与胺化MSN的相互作用进入到孔中的。加入靶标miRNA后,分析物与锚定DNA竞争性杂交,形成RNA-DNA双链体,从而导致锚定DNA与MSN分离,并伴随开孔。负载的葡萄糖分子由于浓度梯度而从孔中释放出来,可以使用便携式个人血糖仪(PGM)进行检测。实验结果表明,PGM信号随miRNA水平的增加而增加,并且在最佳条件下对miRNA-21的浓度从50 pM到5.0 nM表现出良好的线性依赖性,检测限为19 pM。此外,多功能介孔二氧化硅纳米粒子还显示出良好的稳定性和良好的选择性,并通过定量实时聚合酶链反应(qRT-PCR)在细胞裂解物中检测miRNA的令人满意的准确性。如此出色的分析性能使其成为在临床诊断和治疗中有效,便捷地检测miRNA的有前途的方案。多功能介孔二氧化硅纳米粒子还显示出良好的稳定性和良好的选择性,并通过定量实时聚合酶链反应(qRT-PCR)在细胞裂解物中检测miRNA的准确性令人满意。如此出色的分析性能使其成为在临床诊断和治疗中有效,便捷地检测miRNA的有前途的方案。多功能介孔二氧化硅纳米粒子还显示出良好的稳定性和良好的选择性,并通过定量实时聚合酶链反应(qRT-PCR)在细胞裂解物中检测miRNA的准确性令人满意。如此出色的分析性能使其成为在临床诊断和治疗中有效,便捷地检测miRNA的有前途的方案。

设计了一种电化学传感系统,用于基于具有葡萄糖计读数的丙胺官能化介孔二氧化硅纳米粒子从靶标诱导的葡萄糖释放来检测microRNA-21。


























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号