Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2018-01-31 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-0858-4 Jaroslava Švarc-Gajić , Sabrina Clavijo , Ruth Suárez , Aleksandra Cvetanović , Víctor Cerdà
Cherry stems have been used in traditional medicine mostly for the treatment of urinary tract infections. Extraction with subcritical water, according to its selectivity, efficiency and other aspects, differs substantially from conventional extraction techniques. The complexity of plant subcritical water extracts is due to the ability of subcritical water to extract different chemical classes of different physico-chemical properties and polarities in a single run. In this paper, dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) with simultaneous derivatisation was optimised for the analysis of complex subcritical water extracts of cherry stems to allow simple and rapid preparation prior to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). After defining optimal extracting and dispersive solvents, the optimised method was used for the identification of compounds belonging to different chemical classes in a single analytical run. The developed sample preparation protocol enabled simultaneous extraction and derivatisation, as well as convenient coupling with GC-MS analysis, reducing the analysis time and number of steps. The applied analytical protocol allowed simple and rapid chemical screening of subcritical water extracts and was used for the comparison of subcritical water extracts of sweet and sour cherry stems.
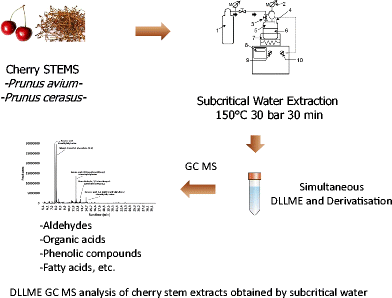
DLLME GC MS analysis of cherry stem extracts obtained by subcritical water
中文翻译:

酸甜樱桃茎亚临界水提取物的同时分散液-液微萃取衍生化和气相色谱质谱分析
樱桃茎已被用于传统医学中,主要用于治疗尿路感染。根据亚临界水的选择性,效率和其他方面,亚临界水的萃取与常规萃取技术有很大不同。植物亚临界水提取物的复杂性是由于亚临界水能够在单次运行中提取具有不同理化性质和极性的不同化学类别的能力。在本文中,优化了同时衍生化的分散液-液微萃取(DLLME),用于分析樱桃茎的复杂亚临界水提取物,从而可以在气相色谱-质谱(GC-MS)之前进行简单快速的制备。确定最佳的萃取和分散溶剂后,该优化方法可在一次分析中用于鉴定属于不同化学类别的化合物。先进的样品制备方案可实现同时提取和衍生化,以及与GC-MS分析的便捷结合,从而减少了分析时间和步骤数。应用的分析规程允许对亚临界水提取物进行简单,快速的化学筛选,并用于比较甜和酸樱桃茎的亚临界水提取物。

DLLME GC MS分析亚临界水制得的樱桃茎提取物



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号