Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2018-02-12 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-0921-1 Niklas Köke , Daniel Zahn , Thomas P. Knepper , Tobias Frömel
Analysis of polar organic chemicals in the aquatic environment is exacerbated by the lack of suitable and widely applicable enrichment methods. In this work, we assessed the suitability of a novel combination of well-known solid-phase extraction (SPE) materials in one cartridge as well as an evaporation method and for the enrichment of 26 polar model substances (predominantly log D < 0) covering a broad range of physico-chemical properties in three different aqueous matrices. The multi-layer solid-phase extraction (mlSPE) and evaporation method were investigated for the recovery and matrix effects of the model substances and analyzed with hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HILIC-MS/MS). In total, 65% of the model substances were amenable (> 10% recovery) to the mlSPE method with a mean recovery of 76% while 73% of the model substances were enriched with the evaporation method achieving a mean recovery of 78%. Target and non-target screening comparison of both methods with a frequently used reversed-phase SPE method utilizing “hydrophilic and lipophilic balanced” (HLB) material was performed. Target analysis showed that the mlSPE and evaporation method have pronounced advantages over the HLB method since the HLB material retained only 30% of the model substances. Non-target screening of a ground water sample with the investigated enrichment methods showed that the median retention time of all detected features on a HILIC system decreased in the order mlSPE (3641 features, median tR 9.7 min), evaporation (1391, 9.3 min), HLB (4414, 7.2 min), indicating a higher potential of the described methods to enrich polar analytes from water compared with HLB-SPE.
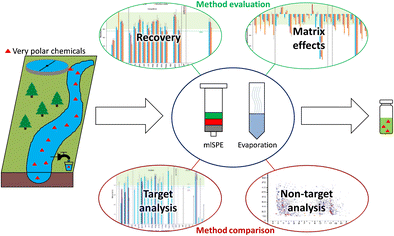
Schematic of the method evaluation (recovery and matrix effects) and method comparison (target and non-target analysis) of the two investigated enrichment methods for very polar chemicals in aqueousmatrices.
中文翻译:

多层固相萃取和蒸发-从水性基质中富集极性有机化学物质的方法
缺乏合适且广泛适用的富集方法加剧了水生环境中极性有机化学物质的分析。在这项工作中,我们评估了一种新型固相萃取(SPE)材料在一个滤芯中的新颖组合以及蒸发方法的适用性以及对26种极性模型物质(主要是log D <0)的富集性的适用性。在三种不同的水性基质中具有广泛的理化性质。研究了多层固相萃取(mlSPE)和蒸发法对模型物质的回收率和基质效应,并通过亲水作用液相色谱-串联质谱(HILIC-MS / MS)进行了分析。总共有65%的模型物质符合要求(> 到mlSPE方法中,回收率为10%,平均回收率为76%,而蒸发方法富集了73%的模型物质,平均回收率为78%。使用“亲水和亲脂平衡”(HLB)材料,将两种方法与经常使用的反相SPE方法进行目标和非目标筛选比较。目标分析表明,mlSPE和蒸发方法比HLB方法具有明显优势,因为HLB材料仅保留了30%的模型物质。使用研究的富集方法对地下水样品进行非目标筛查表明,HILIC系统上所有检测到的特征的中位保留时间以mlSPE的顺序减少(3641个特征,中值 使用“亲水和亲脂平衡”(HLB)材料,将两种方法与经常使用的反相SPE方法进行目标和非目标筛选比较。目标分析表明,mlSPE和蒸发方法比HLB方法具有明显优势,因为HLB材料仅保留了30%的模型物质。使用研究的富集方法对地下水样品进行非目标筛查表明,HILIC系统上所有检测到的特征的中位保留时间以mlSPE的顺序减少(3641个特征,中值 使用“亲水和亲脂平衡”(HLB)材料,将两种方法与经常使用的反相SPE方法进行目标和非目标筛选比较。目标分析表明,mlSPE和蒸发方法比HLB方法具有明显优势,因为HLB材料仅保留了30%的模型物质。使用研究的富集方法对地下水样品进行非目标筛查表明,HILIC系统上所有检测到的特征的中位保留时间以mlSPE的顺序减少(3641个特征,中值 目标分析表明,mlSPE和蒸发方法比HLB方法具有明显优势,因为HLB材料仅保留了30%的模型物质。使用研究的富集方法对地下水样品进行非目标筛查表明,HILIC系统上所有检测到的特征的中位保留时间以mlSPE的顺序减少(3641个特征,中值 目标分析表明,mlSPE和蒸发方法比HLB方法具有明显优势,因为HLB材料仅保留了30%的模型物质。使用研究的富集方法对地下水样品进行非目标筛查表明,HILIC系统上所有检测到的特征的中位保留时间以mlSPE的顺序减少(3641个特征,中值t R 9.7分钟),蒸发(1391,9.3分钟),HLB(4414,7.2分钟),表明与HLB-SPE相比,上述方法从水中富集极性分析物的潜力更高。

两种研究的水基质中极性极强的化学物质富集方法的方法评估(回收率和基质效应)和方法比较(目标分析和非目标分析)的示意图。



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号