Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2018-02-08 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-018-0869-1 Maria Monica Castellanos , Kevin Mattison , Susan Krueger , Joseph E. Curtis
Protein-protein interactions in monoclonal antibody solutions are important for the stability of a therapeutic drug and directly influence viscosity in concentrated protein solutions. This study describes the use of small-angle scattering to estimate protein-protein interactions at high concentrations of the IgG1 NISTmAb reference material and validate colloidal models for interacting molecules. In particular, we studied the colloidal stability of the NISTmAb at high protein concentrations and analyzed protein-protein interactions upon adding sodium chloride and its effect on viscosity. Isotropic colloidal models for interacting molecules were combined with an ensemble of atomistic structures from molecular simulation to account for the flexibility of the NISTmAb in solution. In histidine formulation buffer, net repulsive electrostatic interactions are important for the colloidal stability of the NISTmAb at high concentrations. Addition of sodium chloride increased the viscosity of the NISTmAb and decreased the colloidal stability due to charge screening of the repulsive interactions. The interactions at high concentrations (up to ~ 250 mg/mL) were consistent with those from light scattering at low concentrations (below ~ 20 mg/mL). However, in the presence of sodium chloride, the screening of charges was less pronounced with increasing protein concentration and the interactions approached those of the repulsive hard-sphere models. Additionally, we studied the NISTmAb under frozen conditions using in situ neutron scattering to analyze the crowded state as proteins are excluded from the water-rich phase. In the frozen samples, where protein concentration can reach hundreds of mg/mL in the protein-rich phase, sodium chloride did not affect the molecular spacing and crowding of the NISTmAb.
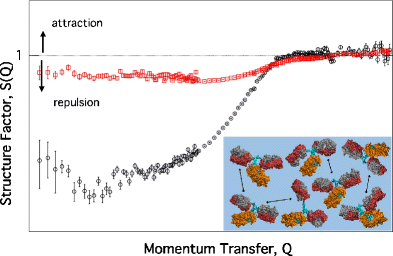
Net repulsive interactions in concentrated NISTmAb solutions assessed by small-angle neutronscattering.
中文翻译:

使用小角度散射和分子模拟表征NISTmAb参考材料
单克隆抗体溶液中的蛋白质相互作用对治疗药物的稳定性很重要,并直接影响浓缩蛋白质溶液中的粘度。这项研究描述了使用小角度散射来估算高浓度的IgG1 NISTmAb参考材料中的蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用,并验证相互作用分子的胶体模型。特别是,我们研究了NISTmAb在高蛋白质浓度下的胶体稳定性,并分析了添加氯化钠后蛋白质与蛋白质之间的相互作用及其对粘度的影响。用于分子相互作用的各向同性胶体模型与分子模拟中的原子结构集合相结合,以解决溶液中NISTmAb的灵活性。在组氨酸制剂缓冲液中,净排斥静电相互作用对于高浓度下NISTmAb的胶体稳定性很重要。由于排斥相互作用的电荷筛选,氯化钠的添加增加了NISTmAb的粘度并降低了胶体稳定性。高浓度(约〜250 mg / mL)下的相互作用与低浓度(约20 mg / mL以下)下光散射的相互作用一致。然而,在存在氯化钠的情况下,电荷的筛选随着蛋白质浓度的增加而变得不那么明显,并且相互作用接近于排斥性硬球模型的相互作用。另外,我们在冷冻条件下使用原位中子散射研究了NISTmAb,以分析蛋白质从富水相中排除时的拥挤状态。在冷冻样品中

通过小角中子散射评估的浓缩NISTmAb溶液中的净排斥相互作用。


























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号