Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry ( IF 4.3 ) Pub Date : 2018-01-08 , DOI: 10.1007/s00216-017-0840-6 Michael Beverly , Caitlin Hagen , Olga Slack
The 3′-polyadenosine (poly A) tail of in vitro transcribed (IVT) mRNA was studied using liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Poly A tails were cleaved from the mRNA using ribonuclease T1 followed by isolation with dT magnetic beads. Extracted tails were then analyzed by LC-MS which provided tail length information at single-nucleotide resolution. A 2100-nt mRNA with plasmid-encoded poly A tail lengths of either 27, 64, 100, or 117 nucleotides was used for these studies as enzymatically added poly A tails showed significant length heterogeneity. The number of As observed in the tails closely matched Sanger sequencing results of the DNA template, and even minor plasmid populations with sequence variations were detected. When the plasmid sequence contained a discreet number of poly As in the tail, analysis revealed a distribution that included tails longer than the encoded tail lengths. These observations were consistent with transcriptional slippage of T7 RNAP taking place within a poly A sequence. The type of RNAP did not alter the observed tail distribution, and comparison of T3, T7, and SP6 showed all three RNAPs produced equivalent tail length distributions. The addition of a sequence at the 3′ end of the poly A tail did, however, produce narrower tail length distributions which supports a previously described model of slippage where the 3′ end can be locked in place by having a G or C after the poly nucleotide region.
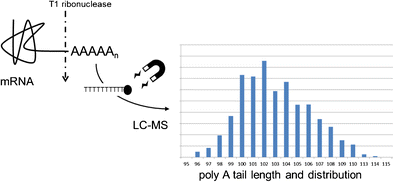
Determination of mRNA poly A tail length using magnetic beads and LC-MS.
中文翻译:

用LC-MS分析体外转录的mRNA的Poly A尾长
使用液相色谱-质谱联用技术(LC-MS)研究了体外转录(IVT)mRNA的3'-聚腺苷(poly A)尾巴。使用核糖核酸酶T1从mRNA上切割出poly A尾巴,然后用dT磁珠分离。然后通过LC-MS分析提取的尾巴,其以单核苷酸分辨率提供尾巴长度信息。这些研究使用的质粒编码的poly A尾巴长度为27、64、100或117个核苷酸的2100-nt mRNA被用于这些研究,因为酶法添加的poly A尾巴显示出明显的长度异质性。在尾巴中观察到的As数量与DNA模板的Sanger测序结果非常匹配,甚至检测到具有序列变异的次要质粒群体。当质粒序列的尾部含有少量的聚As时,分析揭示了一种分布,其中包含的尾巴比编码的尾巴长。这些观察结果与在poly A序列内发生的T7 RNAP的转录滑动一致。RNAP的类型没有改变观察到的尾巴分布,T3,T7和SP6的比较显示,所有三个RNAP产生了相等的尾巴长度分布。但是,在poly A尾巴的3'端添加序列确实会产生较窄的尾巴长度分布,这支持了先前描述的滑动模型,其中3'端可以通过在插入后的G或C锁定在适当的位置多核苷酸区域。RNAP的类型没有改变观察到的尾巴分布,T3,T7和SP6的比较显示,所有三个RNAP产生了相等的尾巴长度分布。但是,在poly A尾巴的3'端添加序列确实会产生较窄的尾巴长度分布,这支持了先前描述的滑动模型,其中3'端可以通过在插入后的G或C锁定在适当的位置多核苷酸区域。RNAP的类型没有改变观察到的尾巴分布,T3,T7和SP6的比较显示,所有三个RNAP产生了相等的尾巴长度分布。但是,在poly A尾巴的3'端添加序列确实会产生较窄的尾巴长度分布,这支持了先前描述的滑动模型,其中3'端可以通过在插入后的G或C锁定在适当的位置多核苷酸区域。

使用磁珠和LC-MS测定mRNA poly A的尾巴长度。


























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号