当前位置:
X-MOL 学术
›
Catal. Sci. Technol.
›
论文详情
Our official English website, www.x-mol.net, welcomes your feedback! (Note: you will need to create a separate account there.)
Plasma-assisted catalytic reforming of toluene to hydrogen rich syngas
Catalysis Science & Technology ( IF 5 ) Pub Date : 2017-08-21 00:00:00 , DOI: 10.1039/c7cy00970d Lina Liu 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Qiang Wang 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Jianwei Song 1, 2, 3, 4 , Shakeel Ahmad 3, 4, 6, 7 , Xiaoyi Yang 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Yifei Sun 2, 4, 5, 6, 8
Catalysis Science & Technology ( IF 5 ) Pub Date : 2017-08-21 00:00:00 , DOI: 10.1039/c7cy00970d Lina Liu 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Qiang Wang 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Jianwei Song 1, 2, 3, 4 , Shakeel Ahmad 3, 4, 6, 7 , Xiaoyi Yang 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 , Yifei Sun 2, 4, 5, 6, 8
Affiliation

|
The combination of non-thermal plasma (NTP) and transition metal catalysts is an alternative method for reducing tar derived from biomass gasification, converting it to a mix of mainly H2 and CO (syngas). In this study, Ni- and Fe-based steam reforming catalysts supported on CaO, SiO2, γ-Al2O3 and ZSM-5 were combined with a coaxial dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma reactor for converting toluene, selected as a simple tar model compound. The catalysts supported by ZSM-5 showed the best potential for increasing toluene conversion, promoting the formation of syngas, reducing the production of undesirable liquid by-products (such as benzene and ethylbenzene) and corroborating the resistance to catalyst deactivation caused by sintering and carbon deposition. Toluene cracking has been investigated in a plasma-alone (PA), a post-plasma catalysis (PPC) and an in-plasma catalysis (IPC) system. The IPC system exhibited the highest toluene conversion efficiency and selectivity for syngas formation, compared with the PA and PPC systems. A maximum toluene conversion of 86.5% was achieved in the IPC system over Ni/ZSM-5, together with a maximum gas selectivity (63.3% for H2, 18.2% for CO, and 4.6% for CH4), and a minimum selectivity to the undesirable liquid by-products (2.5% for benzene and 0.66% for ethylbenzene and a low carbon selectivity of 6.7%). In addition, the reaction mechanism was significantly different in the IPC system from those in the PA and PPC system, since the catalyst in the IPC system might influence the discharge properties and the reaction between excited and short lifetime reactive plasma species (OH˙, O˙, 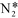 …) and toluene and its intermediates. Finally, a mechanism of toluene cracking has been proposed, after analysis of the gas and liquid products and characterization of the fresh and used catalysts.
…) and toluene and its intermediates. Finally, a mechanism of toluene cracking has been proposed, after analysis of the gas and liquid products and characterization of the fresh and used catalysts.
中文翻译:

等离子体辅助的甲苯催化重整为富氢合成气
非热等离子体(NTP)和过渡金属催化剂的组合是减少源自生物质气化的焦油,将其转化为主要为H 2和CO(合成气)的混合物的替代方法。在这项研究中,Ni基以及Fe基的蒸汽重整催化剂支撑在氧化钙,二氧化硅2,γ-Al系2 ö 3将ZSM-5和ZSM-5与同轴电介质阻挡放电(DBD)等离子体反应器结合使用,以转化为简单的焦油模型化合物的甲苯。ZSM-5负载的催化剂显示出最大的潜力,可提高甲苯的转化率,促进合成气的形成,减少不良的液体副产物(如苯和乙苯)的产生并增强由烧结和碳引起的催化剂失活的抵抗力沉积。甲苯裂解已在单独等离子体(PA),等离子体后催化(PPC)和等离子体内催化(IPC)系统中进行了研究。与PA和PPC系统相比,IPC系统显示出最高的甲苯转化效率和生成合成气的选择性。在IPC系统中,Ni / ZSM-5的最大甲苯转化率为86.5%,2,CO的18.2%和CH 4的4.6%)以及对不良液体副产物的最小选择性(苯为2.5%,乙苯为0.66%,低碳选择性为6.7%)。此外,由于IPC系统中的催化剂可能影响放电性能以及激发和短寿命反应性等离子体物质(OH˙,O)之间的反应,因此IPC系统中的反应机理与PA和PPC系统中的反应机理明显不同。 ˙,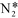 …)和甲苯及其中间体。最后,在分析了气态和液态产物并表征了新鲜和使用过的催化剂之后,提出了甲苯裂化的机理。
…)和甲苯及其中间体。最后,在分析了气态和液态产物并表征了新鲜和使用过的催化剂之后,提出了甲苯裂化的机理。
更新日期:2017-09-19
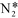 …) and toluene and its intermediates. Finally, a mechanism of toluene cracking has been proposed, after analysis of the gas and liquid products and characterization of the fresh and used catalysts.
…) and toluene and its intermediates. Finally, a mechanism of toluene cracking has been proposed, after analysis of the gas and liquid products and characterization of the fresh and used catalysts.
中文翻译:

等离子体辅助的甲苯催化重整为富氢合成气
非热等离子体(NTP)和过渡金属催化剂的组合是减少源自生物质气化的焦油,将其转化为主要为H 2和CO(合成气)的混合物的替代方法。在这项研究中,Ni基以及Fe基的蒸汽重整催化剂支撑在氧化钙,二氧化硅2,γ-Al系2 ö 3将ZSM-5和ZSM-5与同轴电介质阻挡放电(DBD)等离子体反应器结合使用,以转化为简单的焦油模型化合物的甲苯。ZSM-5负载的催化剂显示出最大的潜力,可提高甲苯的转化率,促进合成气的形成,减少不良的液体副产物(如苯和乙苯)的产生并增强由烧结和碳引起的催化剂失活的抵抗力沉积。甲苯裂解已在单独等离子体(PA),等离子体后催化(PPC)和等离子体内催化(IPC)系统中进行了研究。与PA和PPC系统相比,IPC系统显示出最高的甲苯转化效率和生成合成气的选择性。在IPC系统中,Ni / ZSM-5的最大甲苯转化率为86.5%,2,CO的18.2%和CH 4的4.6%)以及对不良液体副产物的最小选择性(苯为2.5%,乙苯为0.66%,低碳选择性为6.7%)。此外,由于IPC系统中的催化剂可能影响放电性能以及激发和短寿命反应性等离子体物质(OH˙,O)之间的反应,因此IPC系统中的反应机理与PA和PPC系统中的反应机理明显不同。 ˙,
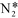 …)和甲苯及其中间体。最后,在分析了气态和液态产物并表征了新鲜和使用过的催化剂之后,提出了甲苯裂化的机理。
…)和甲苯及其中间体。最后,在分析了气态和液态产物并表征了新鲜和使用过的催化剂之后,提出了甲苯裂化的机理。



























 京公网安备 11010802027423号
京公网安备 11010802027423号